China’s ambitious vision for establishing a colony on Mars is not just a testament to its space exploration capabilities but a pivotal step that could redefine humanity’s future. As China gears up to set its footprints on the Red Planet, the implications for science, technology, and global cooperation are immense and far-reaching.
The Vision Behind China’s Mars Colony
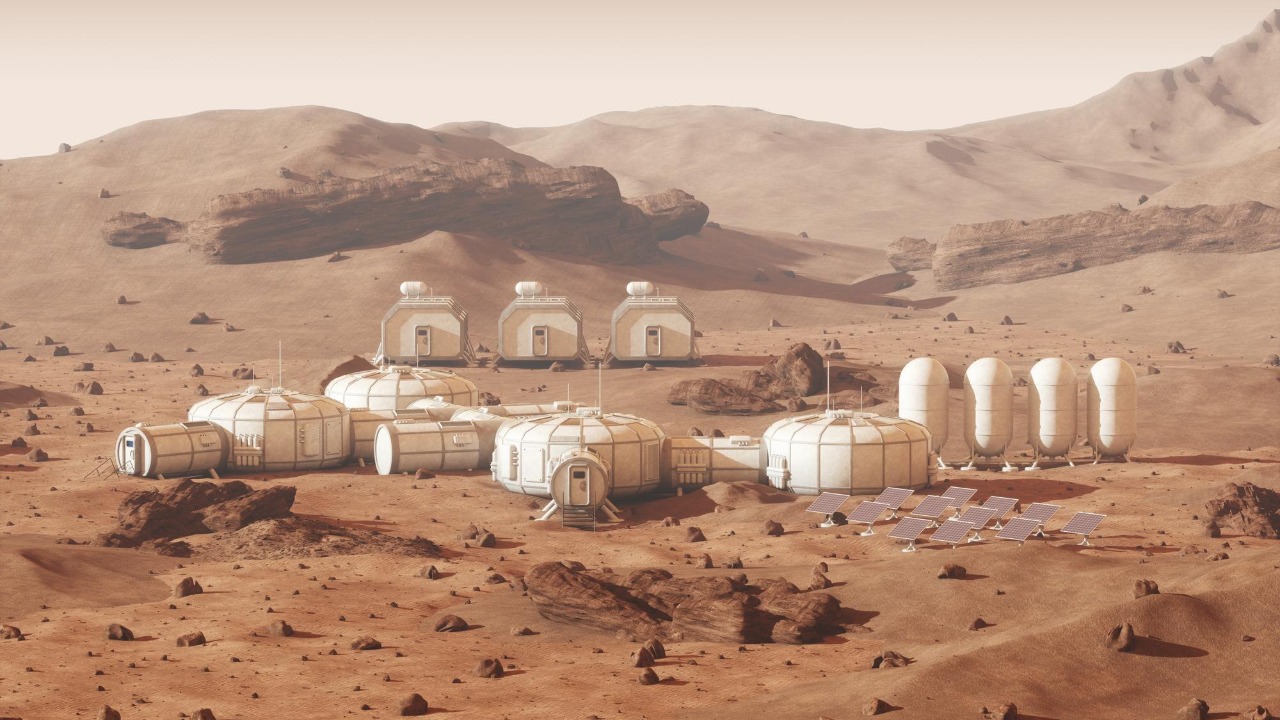

China’s journey into space exploration has been marked by significant milestones that underscore its strategic motivations for aiming at Mars. The nation’s ambitions were fueled by the successful launch of Tianwen-1, a mission that established China as a formidable player in the global space race. China’s space program, driven by a blend of national pride and a desire for scientific advancement, views the establishment of a Martian colony as a critical step towards asserting its dominance in space exploration.
The technological innovations China has achieved are noteworthy, including the development of advanced propulsion systems and autonomous landing technologies. These advancements are crucial for the successful establishment of a Martian colony. China’s plans include leveraging existing technologies, such as its Long March rockets, and developing new systems for sustainable human habitation on Mars. The success of these initiatives will not only demonstrate China’s prowess but also contribute significantly to global technological progress.
International collaboration and competition are inherent aspects of China’s Mars mission. While the mission has fostered partnerships with countries like Russia and the European Union, it also intensifies competition with established space powers such as the United States. This dynamic is shaping international relationships and could redefine the future of space exploration, where cooperation and rivalry go hand in hand.
Life in the Martian Colony
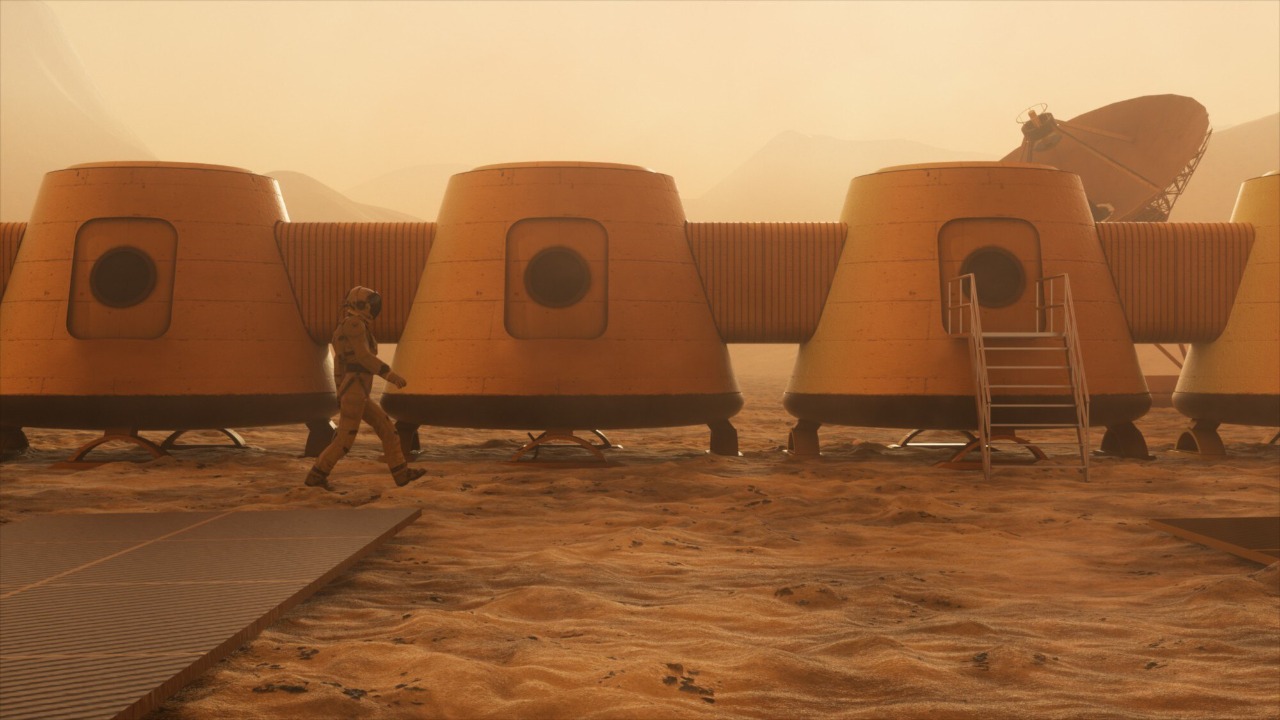

Living conditions in a Martian colony are a topic of intense research and speculation. Based on current simulations and research, habitats are expected to be highly efficient, self-sustaining, and designed to withstand the harsh Martian environment. Daily life will involve a structured routine focused on scientific research, resource management, and community building. The design of habitats will incorporate cutting-edge technologies to ensure safety, comfort, and efficiency for the colonists.
Sustainable resource management is at the forefront of China’s plans for a Mars colony. The management of water, air, food, and energy will rely on innovative technologies such as in-situ resource utilization and advanced recycling systems. China’s focus on sustainability aims to create a self-sufficient colony that minimizes reliance on Earth for supplies, addressing challenges related to resource scarcity and logistical constraints.
Psychological and social aspects play a crucial role in the success of a Martian colony. The psychological challenges of living in an isolated, extraterrestrial environment are significant, requiring robust support systems to maintain mental and emotional well-being. Social dynamics will be shaped by the small, close-knit community of colonists, necessitating effective communication and conflict resolution strategies to ensure harmony and cooperation.
Scientific and Technological Breakthroughs
A Mars colony offers unprecedented research opportunities and discoveries, from studying Martian geology to exploring potential signs of life. The colony will serve as a hub for scientific inquiry, providing valuable insights into the planet’s history and its potential for supporting life. These research avenues could lead to breakthroughs in astrobiology and our understanding of planetary evolution.
The technological innovations arising from the Mars mission have the potential to revolutionize various industries on Earth. Advances in robotics, materials science, and life-support systems developed for the colony could have applications in sectors such as healthcare, manufacturing, and environmental sustainability. These technological spinoffs could drive economic growth and improve quality of life on Earth.
The success of a Chinese Mars colony could have a profound impact on future space exploration missions and technologies. It would demonstrate the feasibility of long-term human habitation on another planet, paving the way for further exploration of the solar system. This achievement could inspire other nations to pursue ambitious space missions, fostering a new era of exploration and discovery.
Implications for Earth and Humanity

The economic implications of a Mars colony are vast, with potential commercial opportunities and global economic shifts on the horizon. The development of new industries related to space travel and resource extraction could create jobs and stimulate economic growth. The Mars colony could also serve as a catalyst for global investment in space exploration, altering the economic landscape.
Philosophical and ethical considerations arise from the human colonization of another planet. Questions about the moral implications of altering another planet’s environment, the equitable distribution of space resources, and the responsibilities of a multi-planetary species are central to the discourse surrounding Mars colonization. These issues require careful deliberation to ensure that space exploration aligns with ethical principles.
Contemplating the broader implications of Mars colonization for humanity’s future, the prospect of a multi-planetary existence becomes increasingly tangible. A successful Mars colony could serve as a blueprint for future settlements beyond Earth, offering solutions to challenges such as overpopulation and resource depletion. The long-term vision for humanity includes the possibility of thriving across multiple planets, expanding our horizons and ensuring the survival of our species.
Challenges and Criticisms

Establishing a sustainable colony on Mars presents significant technical and logistical hurdles. Challenges include developing reliable life-support systems, efficient transportation, and robust infrastructure to withstand Mars’ harsh conditions. Overcoming these obstacles requires innovation and perseverance, as well as substantial investment in research and development.
Political and social criticisms accompany China’s Mars ambitions, with concerns over resource allocation and global equity at the forefront. Critics argue that the resources dedicated to space exploration could be used to address pressing issues on Earth, such as poverty and climate change. Additionally, the geopolitical implications of China’s growing influence in space raise questions about power dynamics and international relations.
The environmental impact of colonizing Mars and the ethical considerations surrounding planetary protection are topics of considerable debate. Preserving Mars’ natural state and preventing contamination are essential to ensuring responsible exploration. The ethical questions related to altering another planet’s environment must be addressed to balance exploration with preservation.