The advent of 3D printed rockets marks a revolutionary shift in aerospace technology, offering an innovative approach that promises to redefine space exploration. By leveraging additive manufacturing techniques, companies are able to produce rockets more efficiently and cost-effectively. This exploration into 3D printed rockets reveals their genius and potential impact on the future of space travel.
The Efficiency of 3D Printing in Rocket Manufacturing
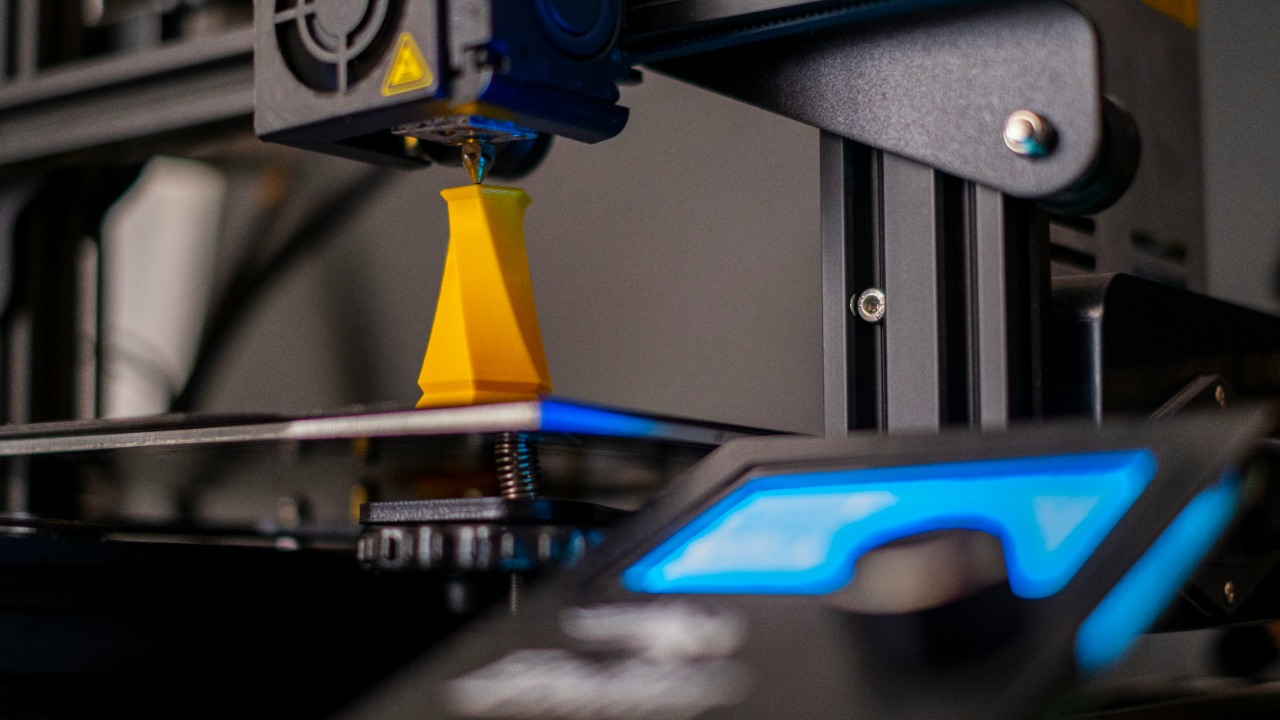

One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing in rocket manufacturing is its ability to reduce production time. Traditional rocket manufacturing involves complex processes and extensive timeframes, often stretching over several years. In contrast, 3D printing significantly shortens the production cycle, allowing for faster turnaround times. For instance, Rocket Lab’s 3D printed engine demonstrates the reduced lead time in producing critical components. This rapid production capability not only accelerates the development of rockets but also enables companies to iterate and innovate more quickly, adapting to new challenges and opportunities in the aerospace sector.
Cost-effectiveness is another crucial benefit of 3D printed rockets. The use of additive manufacturing techniques allows for the reduction of material waste and labor costs, resulting in more budget-friendly manufacturing. By amalgamating components into singular structures, companies can decrease both assembly time and costs. This streamlined approach not only makes space exploration more affordable but also encourages smaller companies to enter the industry, fostering innovation and competition. As a result, the democratization of space technology becomes more feasible, opening up new possibilities for scientific discovery and commercial endeavors.
Technological Advancements in 3D Printed Rockets
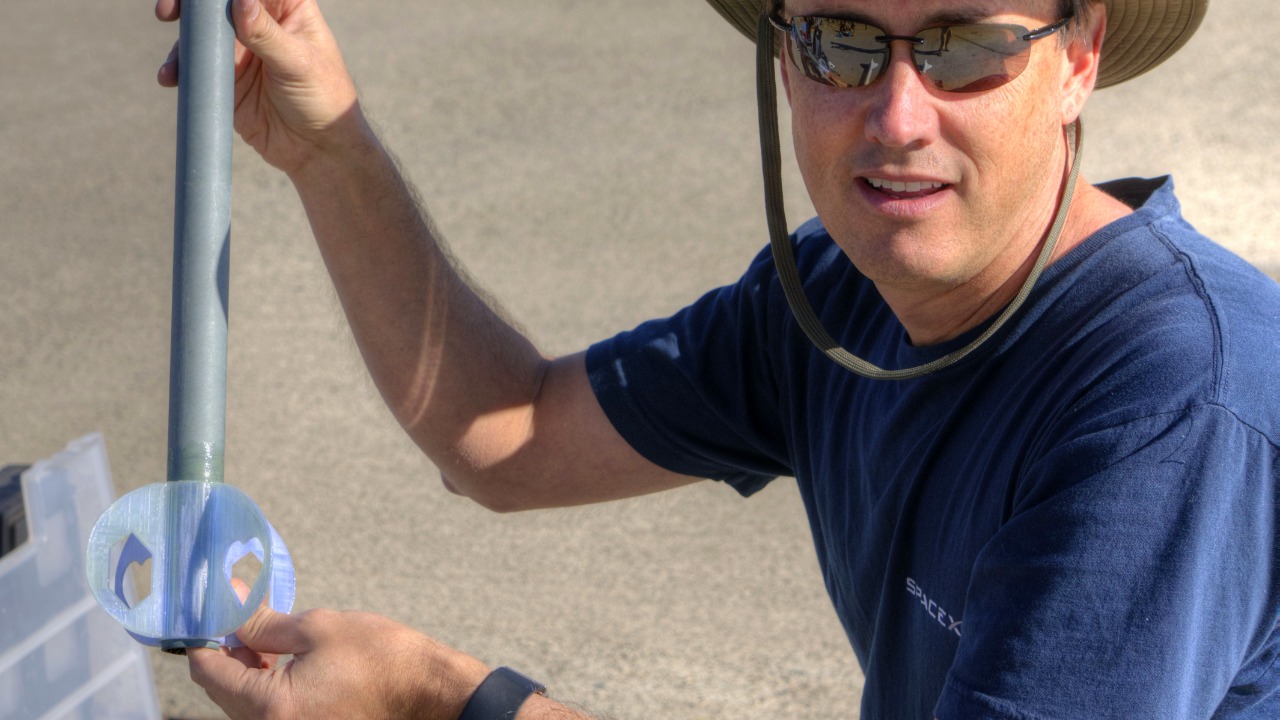

The technological advancements enabled by 3D printing are truly remarkable, especially in terms of complex design capabilities. 3D printing allows for the creation of intricate geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This capability facilitates the development of optimized designs, which can lead to improved rocket performance and efficiency. By enabling engineers to experiment with novel configurations and structures, 3D printing pushes the boundaries of what’s possible in aerospace design, paving the way for more efficient and capable rockets.
Material innovation is another area where 3D printing is making significant strides. The development of new materials specifically for 3D printing enhances the durability and functionality of rocket parts. Companies are continually researching and developing high-strength, lightweight materials suitable for space travel. These advanced materials not only improve the performance of rockets but also contribute to their safety and reliability. As a result, 3D printed rockets are increasingly seen as viable alternatives to traditionally manufactured ones, offering a promising future for the aerospace industry.
Environmental and Sustainability Benefits

In addition to its technical advantages, 3D printing also offers environmental and sustainability benefits. The streamlined manufacturing process of 3D printing contributes to a lower carbon footprint compared to conventional methods. With fewer manufacturing processes involved, there are reduced emissions and energy consumption. This aspect of 3D printed rockets aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility in the aerospace sector, making them an attractive option for companies looking to minimize their ecological impact.
The use of recyclable and sustainable materials in 3D printing further supports environmental sustainability initiatives. Innovations in bio-based and recycled materials are paving the way for greener aerospace practices. By incorporating these materials into their manufacturing processes, companies can reduce their reliance on non-renewable resources and promote a more sustainable approach to space exploration. As the industry continues to evolve, the integration of environmentally friendly practices will become increasingly important, ensuring that the pursuit of space exploration does not come at the expense of our planet’s health.
Challenges and Considerations in 3D Printed Rocket Development
Despite the promise of 3D printing in rocket development, technical challenges remain. One notable example is the inaugural launch of a fully 3D printed rocket by a private company, which ended in failure and highlighted the ongoing need for technical refinement. These setbacks underscore the importance of continued research and development to address the complex challenges of 3D printed rocket technology. As the industry moves forward, overcoming these technical hurdles will be crucial to realizing the full potential of 3D printing in aerospace.
Regulatory and safety concerns also pose significant challenges to the development and deployment of 3D printed rockets. The novel nature of this technology necessitates updated regulatory frameworks to ensure safety and reliability. Collaboration between regulatory bodies and aerospace companies is essential to address these concerns and establish standards that guarantee the safe and effective use of 3D printed rockets. As the technology matures, it will be important to balance innovation with the need for rigorous safety measures, ensuring that the benefits of 3D printing are realized without compromising safety.
The Future of Space Exploration with 3D Printed Rockets
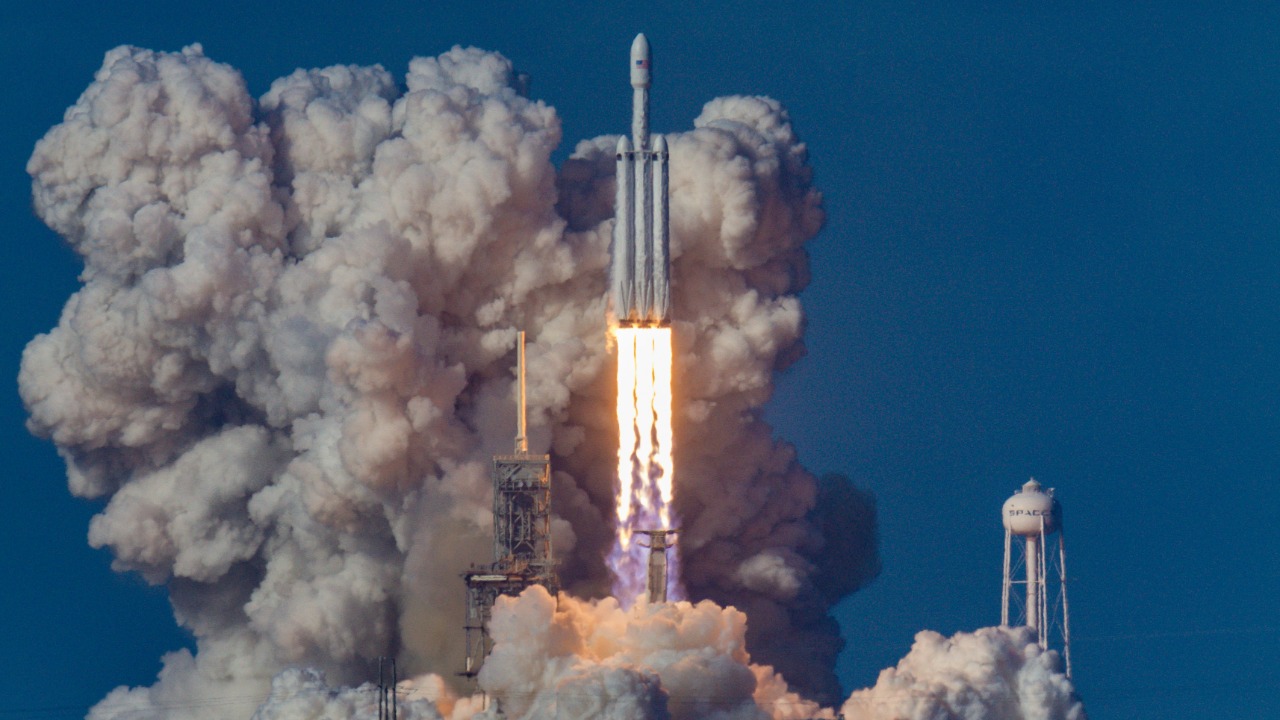

The efficiencies and cost reductions offered by 3D printed rockets hold the potential to democratize access to space, enabling more players to enter the arena. Smaller companies and nations may find new opportunities in space exploration due to lower barriers to entry. This increased accessibility could lead to a more diverse and competitive space industry, driving innovation and expanding the possibilities for scientific research and commercial ventures.
Another exciting prospect is the potential for on-demand manufacturing of rocket parts, even in space. This capability could transform future missions by allowing for more adaptive and responsive space exploration strategies. By printing parts as needed, missions could be more flexible, reducing the need for extensive pre-launch preparations and enabling real-time problem-solving. This transformative potential of 3D printed rockets is already being explored, as seen in various demonstrations and experiments. For example, getting up close and personal with 3D printed rockets showcases the possibilities.
In conclusion, the genius of 3D printed rockets lies in their ability to revolutionize the aerospace industry through efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and technological innovation. Despite the challenges that remain, the potential benefits of this technology are immense, promising a future where space exploration is more accessible, sustainable, and adaptable than ever before. As the industry continues to evolve, 3D printed rockets are set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of space exploration.