The Mariana Trench, the deepest part of the world’s oceans, has long captivated scientists and explorers alike. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, this mysterious underwater canyon reaches depths of over 36,000 feet. What exactly lies at the bottom of this abyss, and what secrets does it hold?
The Geography of the Mariana Trench
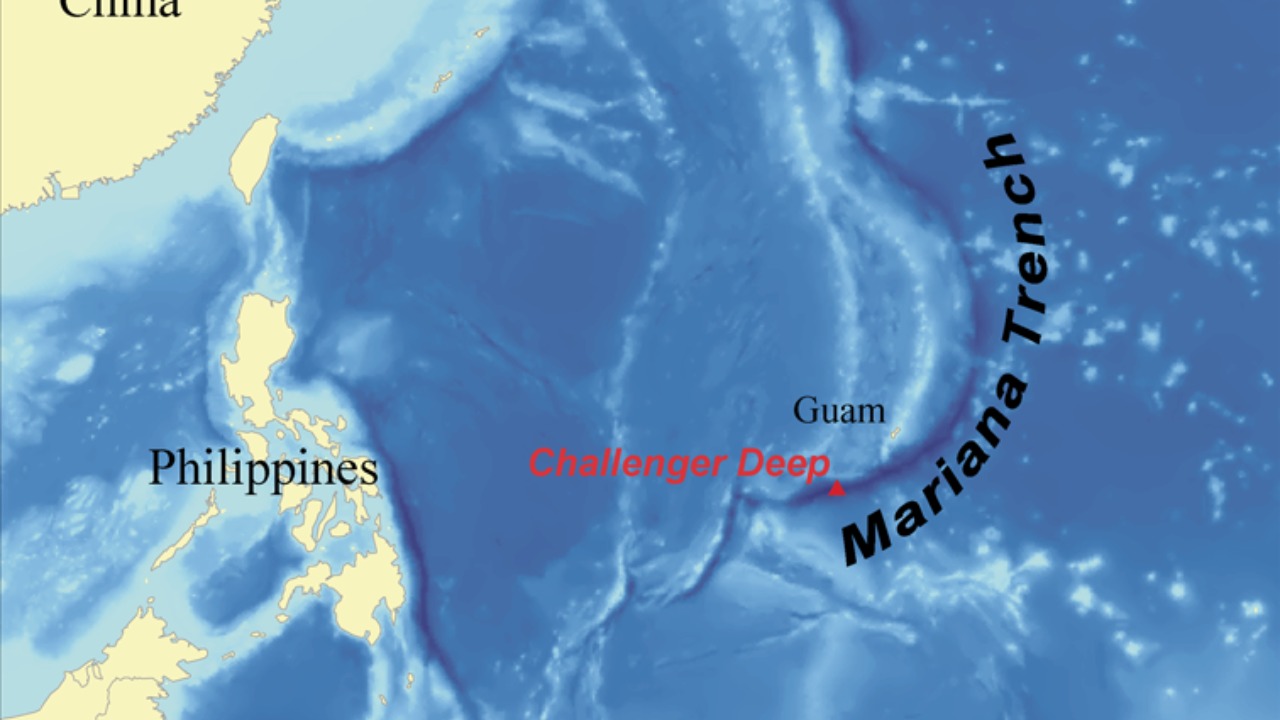
Location and Dimensions
Situated in the western Pacific Ocean, the Mariana Trench is a staggering natural wonder, stretching approximately 1,550 miles in length and averaging about 45 miles in width. Its most notable feature is the Challenger Deep, the deepest known point in the world’s oceans, plunging over 36,000 feet below the sea surface. The trench is a product of the Pacific Plate subducting beneath the smaller Mariana Plate, creating a dramatic underwater landscape that continues to intrigue scientists worldwide.
Formation and Geological Importance
The formation of the Mariana Trench can be attributed to the complex dance of tectonic plates. As the Pacific Plate is forced under the Mariana Plate, a process known as subduction, it creates a trench that provides valuable insights into Earth’s geological history. The trench offers a unique opportunity to study the processes that shape our planet, from seismic activity to the creation of new crust.
Challenger Deep
Challenger Deep holds a special place in scientific exploration, as it represents the deepest point in the trench, and indeed, the ocean. This remote location has been the site of numerous expeditions, each contributing to our understanding of the deep sea. The extreme conditions present unique challenges, but they also offer the potential for groundbreaking discoveries about life on Earth.
Unique Marine Life and Ecosystems

Adaptations to Extreme Pressure
Life in the Mariana Trench is unlike any other on Earth. The extreme pressure, which can exceed 1,000 times atmospheric pressure at sea level, requires marine organisms to develop extraordinary adaptations. These adaptations include flexible cell membranes and specialized proteins that help organisms survive where few others can.
Mysterious Species Discoveries
The trench is home to a variety of mysterious species that have evolved to thrive in its dark, high-pressure environment. Among these are the snailfish, which holds the record for the deepest living fish, and giant amoebas, single-celled organisms that defy expectations with their large size. These discoveries continue to challenge our understanding of life and adaptation.
Bioluminescence in the Deep
Bioluminescence is a common trait among organisms in the trench, used for communication, camouflage, and predation. This fascinating adaptation allows creatures to produce light in the pitch-black depths, creating a mesmerizing display that serves various ecological roles and enhances their chances of survival.
Human Impact and Pollution
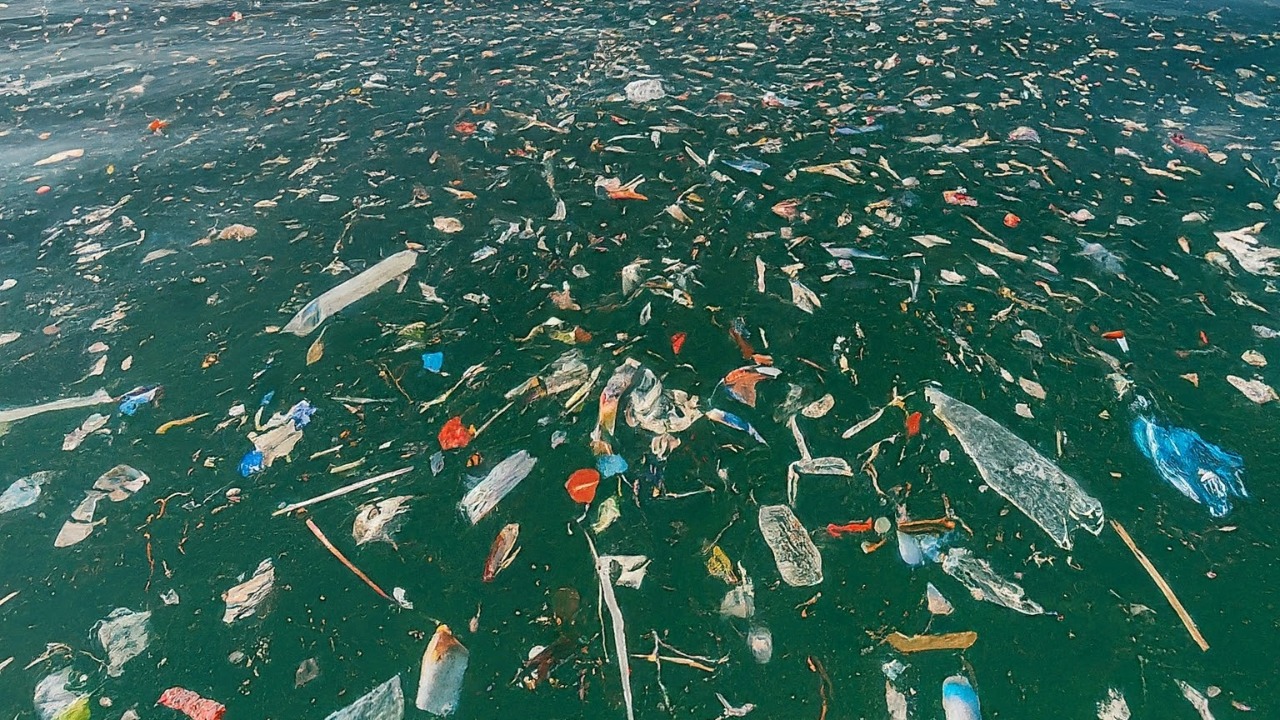

Plastic Pollution and Debris
Unfortunately, even the remote depths of the Mariana Trench are not immune to human impact. Scientific expeditions have uncovered human-made debris, including plastics, littering the trench floor. This pollution poses a threat to the unique ecosystems and highlights the global reach of human activities.
Scientific Expeditions and Their Findings
Recent expeditions have shed light on the extent of pollution in the trench, revealing alarming levels of contamination. Studies have found plastic fibers in deep-sea organisms and chemical pollutants in sediment samples. These findings underscore the urgent need for action to protect our oceans from further degradation.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation initiatives are crucial to preserving the unique marine environment of the Mariana Trench. Efforts to reduce plastic pollution and promote sustainable practices are essential to safeguard the trench’s fragile ecosystems. Supporting these initiatives can help ensure that future generations can continue to explore and learn from this remarkable natural wonder.
Technological Advances in Deep-Sea Exploration

Submersibles and ROVs
Exploring the depths of the Mariana Trench requires advanced technology. Submersibles and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) are essential tools for scientists, allowing them to navigate the extreme conditions and capture valuable data. These technologies have enabled us to reach previously inaccessible areas and make groundbreaking discoveries.
Challenges of Deep-Sea Exploration
Despite technological advances, deep-sea exploration remains fraught with challenges. The immense pressure, frigid temperatures, and complete darkness make it one of the most hostile environments on Earth. Scientists must overcome these obstacles to unlock the secrets hidden beneath the ocean’s surface.
Future of Exploration
The future of deep-sea exploration holds great promise, with potential technological advancements on the horizon. Innovations in robotics, artificial intelligence, and sensor technology may pave the way for more efficient and comprehensive exploration, revealing the trench’s hidden wonders and enhancing our understanding of the deep ocean.
Cultural and Scientific Significance

Historical Expeditions
The Mariana Trench has a rich history of exploration, with key expeditions contributing significantly to our knowledge. From the early 20th-century voyages to modern-day missions, these endeavors have expanded our understanding of deep-sea environments and inspired generations of scientists and explorers.
The Trench in Popular Culture
The trench has also captured the public’s imagination through its depiction in literature, films, and media. It serves as a backdrop for stories of adventure and mystery, fueling curiosity and fascination with the unknown depths of our planet’s oceans.
Importance to Science and Discovery
The Mariana Trench continues to be a vital area for scientific discovery, offering insights into Earth’s past and future. Its unique ecosystems and geological features provide invaluable information for understanding the planet’s history and the processes that shape it. As exploration continues, the trench holds the potential to reveal even more secrets of our world.