Quantum computing, on the cusp of a technological revolution, is set to significantly alter the way we process and interact with data. The latest quantum computer has implications far beyond the realms of academia and industry, reaching into the everyday lives of ordinary users.
Understanding Quantum Computing

Quantum computing operates on a fundamentally different level than classical computing. While classical computers utilize bits to process information in a binary format (1s and 0s), quantum computers employ quantum bits, or qubits. Qubits, leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics, can exist in multiple states at once, a phenomenon called superposition. This means that a quantum computer can process a vast number of possibilities simultaneously, potentially solving complex problems much faster than a classical computer.
This potential speed advantage stems from another quantum principle known as entanglement. It allows qubits that are entangled to be linked, such that the state of one directly influences the other, no matter how far apart they are. This phenomenon increases computational efficiency and is one of the key advantages of quantum computers.
The Newest Quantum Computer: A Snapshot
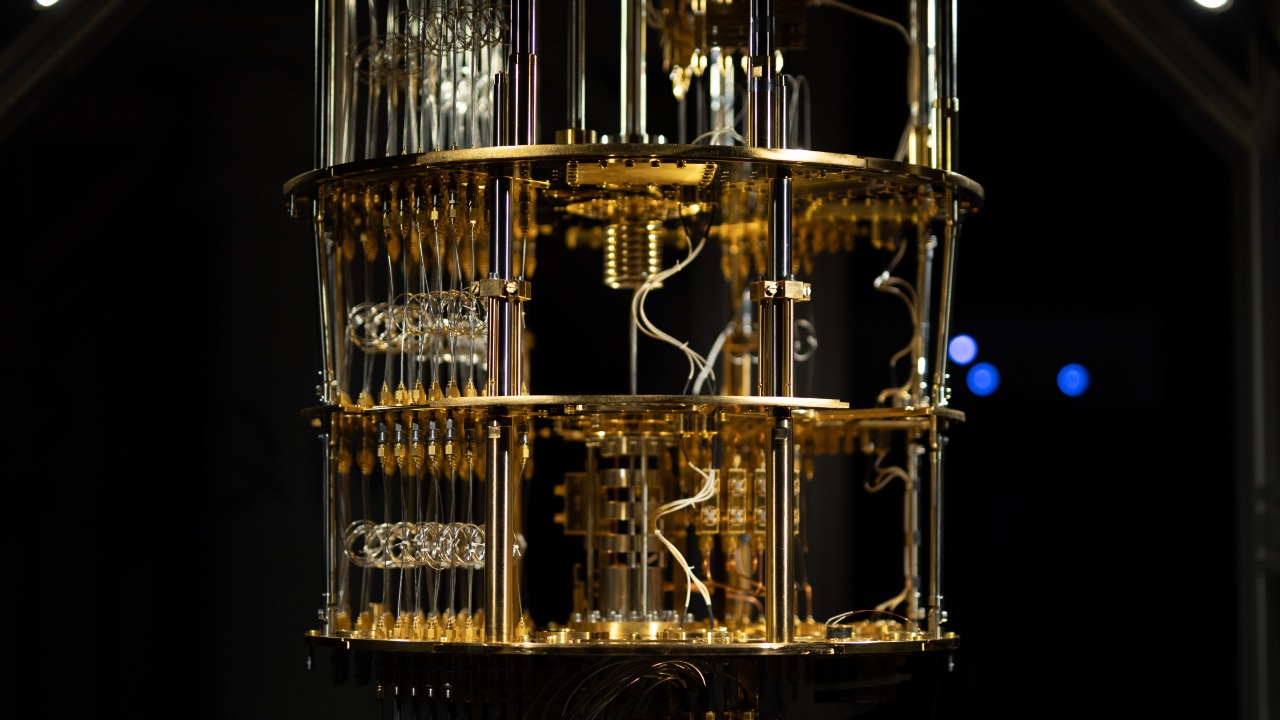

The latest models of quantum computers continuously push the boundaries of what’s possible. They are becoming increasingly powerful, with more qubits and improved error correction techniques. These advancements allow them to perform more complex calculations and tackle real-world problems that were previously considered computationally infeasible.
One of the key differences between the latest quantum computer and its predecessors is the increase in quantum volume. Quantum volume, a measure of the overall computational power, takes into account the number of qubits, their connectivity, and the error rates. The higher the quantum volume, the more complex problems the quantum computer can solve. This improvement is a key step towards quantum supremacy, the point where a quantum computer can outperform a classical computer for a specific task.
Implications for Everyday Technology
With these advancements, quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize everyday technology. The speed and computational power of quantum computers could significantly enhance machine learning algorithms, leading to smarter and more responsive AI. It could also revolutionize the field of cryptography, making current encryption methods obsolete and paving the way for more secure communication systems.
Another intriguing application of quantum computing is in the field of materials science. Quantum computers could simulate and analyze complex chemical reactions, potentially leading to the development of new materials and drugs. This could have a profound impact on industries such as pharmaceuticals, energy, and transportation. For example, a quantum computer could help design more efficient solar panels or high-capacity batteries.
The Potential Impact on Privacy and Security
While the power of quantum computing offers many benefits, it also poses potential risks, particularly in the area of security and encryption. Existing cryptographic systems rely on the difficulty of factoring large numbers, a task that could be made trivial with a sufficiently powerful quantum computer. This could potentially lead to the breaking of many current encryption methods, posing significant privacy concerns.
However, this also opens the door for quantum cryptography, a new form of secure communication that leverages the principles of quantum mechanics. Quantum key distribution, a technique in quantum cryptography, guarantees secure communication by making it impossible for a third party to intercept the key without being detected. This could provide a new level of security in the digital age.
Challenges and Future Outlook

Despite the promise of quantum computing, there are significant challenges to overcome. Quantum computers are extremely sensitive to environmental noise, which can cause errors in calculations. Additionally, qubits need to be maintained at extremely low temperatures, close to absolute zero, making the development of practical, scalable quantum computers a complex task.
However, the potential of quantum computing is undeniable, and research in this field is progressing at an impressive pace. With continued advancements, we are moving closer to the day when quantum computers will be part of everyday technology. The implications for ordinary users are vast, from enhanced AI and secure communications to groundbreaking developments in materials science and beyond. The age of quantum computing is just around the corner, promising to reshape the landscape of technology as we know it.