In today’s digital age, smartphones have become indispensable, offering convenience and connectivity. However, these devices are also adept at collecting and transmitting data about us, often without our explicit knowledge. Understanding how smartphones track us can help users make informed decisions about privacy and security.
1. Location Services
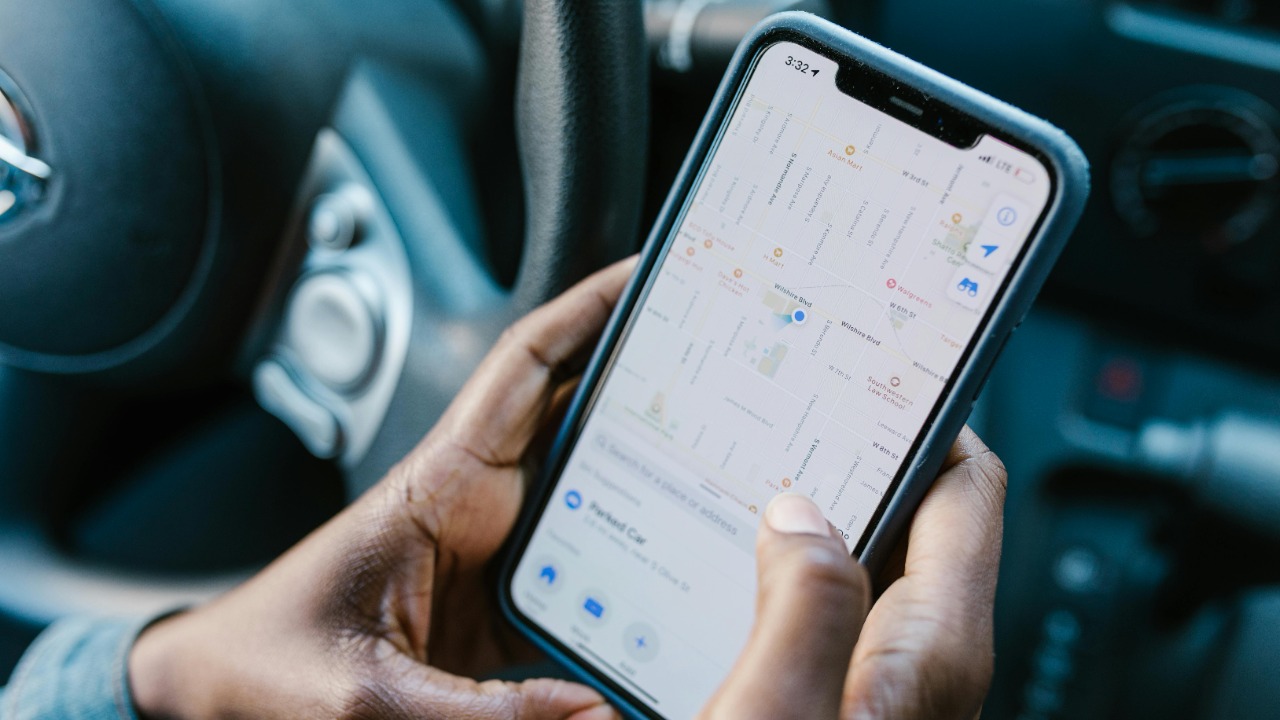

Many apps on your smartphone continuously track your location data to provide personalized experiences, such as navigation and local weather updates. While this can be convenient, it also means that apps can pinpoint exactly where you are at any given moment. Disabling location services when not needed can help protect your privacy.
Popular apps like Google Maps and Uber require location access to function optimally. However, even apps that don’t need your location might request it, as this data is valuable for advertising and analytics purposes. Always review app permissions to control which apps can access your location.
2. App Permissions
When installing new apps, you often grant them permissions to access certain features on your device, such as your contacts, camera, or microphone. Some apps require more permissions than necessary, raising potential privacy concerns. Regularly reviewing and managing app permissions is essential to ensure that apps only have access to data relevant to their functionality.
For instance, a flashlight app shouldn’t need access to your contacts. By going into your phone’s settings, you can adjust permissions for each app, limiting their access to sensitive information. This practice not only protects your privacy but also enhances your device’s security.
3. Bluetooth Connectivity

Bluetooth technology allows devices to connect wirelessly over short distances. While it’s useful for connecting headphones or car systems, it can also be a gateway for tracking. Retailers often use Bluetooth beacons to track shoppers’ movements and send targeted ads based on their location within a store.
To protect your privacy, keep Bluetooth turned off when not in use. This simple step can prevent unwanted tracking and potential security breaches. It’s also a good idea to regularly review and forget devices that you no longer use.
4. Wi-Fi Networks

Connecting to public Wi-Fi networks can expose your device to various tracking and security risks. Public networks are often unsecured, making it easier for malicious actors to intercept data or track your online activities. Even your device’s Wi-Fi scanning feature can reveal your location history as it constantly searches for known networks.
To mitigate these risks, use a VPN when connected to public Wi-Fi, and disable automatic network connections. Also, consider turning off Wi-Fi when it’s not needed to prevent your device from constantly scanning for networks.
5. Cookies and Tracking Pixels
Websites often use cookies and tracking pixels to monitor your online behavior and gather data for targeted advertising. These small pieces of code can follow you across different sites, creating a comprehensive profile of your interests and habits.
To enhance your online privacy, regularly clear your browser cookies and consider using privacy-focused browser extensions. Some browsers also offer built-in tools to block tracking cookies and enhance your online privacy.
6. Gyroscope and Accelerometer Data

Your smartphone’s gyroscope and accelerometer sensors track movement and orientation, enabling features like auto-rotate and fitness tracking. However, these sensors can also be exploited to infer sensitive information, such as keystrokes or even your location, by analyzing movement patterns.
Research indicates that such sensor data can potentially be used for unauthorized tracking and surveillance. To safeguard your privacy, be cautious about granting apps access to motion sensors, especially if the app doesn’t need that data for its core functionality.
7. Voice Assistants

Virtual assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa are designed to listen for voice commands, but this means they are always listening for their wake word. This constant listening raises privacy concerns, as snippets of your conversations could be sent to servers for processing and storage.
To protect your privacy, review the voice assistant settings on your device and consider disabling the always-on feature. Additionally, regularly delete stored voice recordings from the assistant’s settings to maintain control over your personal data.
8. Camera Access

Many smartphone apps request access to your camera for legitimate reasons, such as photo editing or video conferencing. However, granting access to apps you don’t trust can lead to unauthorized use of your camera, potentially capturing images or videos without your knowledge.
Always scrutinize the apps that request camera access, and regularly review the permissions granted to each app. If an app seems suspicious or requests more access than necessary, it might be worth reconsidering its installation on your device.
9. Biometric Data

Biometric features, such as fingerprint scanners and facial recognition, offer enhanced security and convenience. However, storing biometric data on your device raises privacy and security concerns, as this information can be targeted by hackers.
Ensure that your device’s biometric data is encrypted and stored securely. Additionally, stay informed about potential vulnerabilities and security risks associated with biometric technology to better protect your personal information.