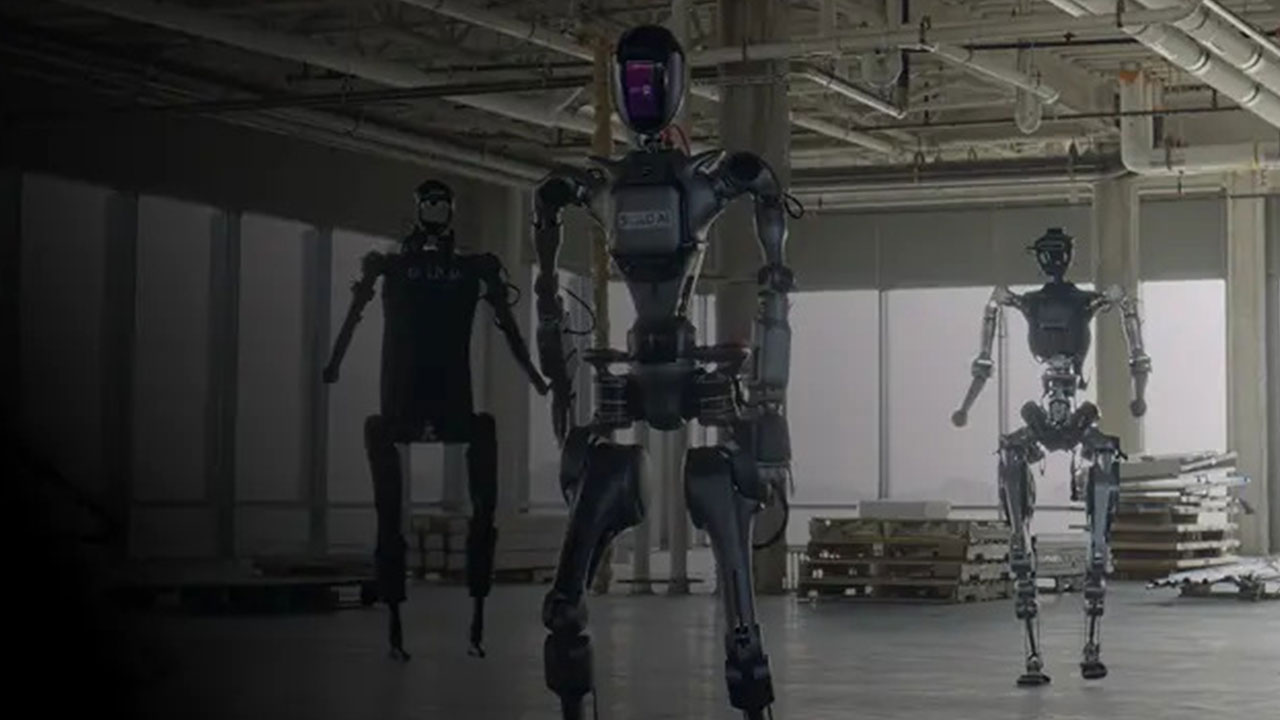
In a remarkable display of resilience and adaptability, Skild AI has developed an AI-powered robot that can withstand severe damage, including an attack with a chainsaw, and continue functioning. This development showcases the robustness of Skild AI’s versatile robotic intelligence.
1. Skild AI’s Advanced Robotic Intelligence

Skild AI, a pioneering company in the field of artificial intelligence and robotics, is dedicated to pushing the boundaries of what is possible in the realm of machine intelligence. The company’s mission is to create AI systems that are not only intelligent but also adaptable and resilient, capable of functioning in a variety of challenging environments and situations. The versatile robotic intelligence developed by Skild AI is a testament to this mission, demonstrating a level of adaptability and resilience that sets it apart from other AI applications in robotics (Startup Ecosystem).
Unlike many AI systems, which are designed for specific tasks and struggle to adapt to new situations, Skild AI’s advanced robotic intelligence is designed to be versatile. It can learn, adapt, and function in a variety of scenarios, making it more akin to a multitalented robot brain than a single-purpose AI system. This adaptability is a key differentiator for Skild AI, setting it apart from other companies in the field.
2. The Resilience of Skild AI’s Robot

Perhaps the most striking demonstration of Skild AI’s advanced robotic intelligence is the resilience of its AI-powered robot. This machine is capable of withstanding severe damage, including an attack with a chainsaw, and continuing to function. This level of resilience is unprecedented in the field of robotics and is a testament to the robustness of Skild AI’s technology (Wired).
The technology that enables this resilience is a combination of advanced AI algorithms and robust physical design. The AI system is capable of adapting to damage and finding new ways to accomplish its tasks, while the physical design of the robot is built to withstand severe damage. This combination of intelligent software and robust hardware is what allows the robot to keep functioning even under extreme conditions.
3. The Future of Resilient Robotics

The advancements made by Skild AI in the field of resilient robotics have significant implications for the future. As robots become more resilient and adaptable, they can be deployed in a wider range of environments and situations, from disaster relief operations to deep-sea exploration. The societal and industrial benefits of such resilient robots are immense, potentially revolutionizing industries and improving lives.
However, the development and deployment of such robust AI systems also raise important ethical considerations. As AI systems become more autonomous and resilient, questions about accountability, transparency, and control become increasingly important. These are challenges that the field of AI and robotics will need to address as it continues to advance.
Looking ahead, the potential applications of Skild AI’s resilient robotics are vast. For instance, in the field of disaster relief, these robots could be used to navigate dangerous terrains, locate survivors, and deliver essential supplies. Their ability to adapt to damage and continue functioning could be crucial in situations where human intervention is risky or impossible. This could significantly enhance the effectiveness of disaster response efforts, potentially saving lives and reducing the impact of disasters (Wired).
Similarly, in the realm of deep-sea exploration, Skild AI’s resilient robots could be used to explore the ocean’s depths, where the pressure and conditions are too harsh for human divers. These robots could collect data, take samples, and perform tasks that would otherwise be impossible, opening up new possibilities for scientific discovery and understanding of our planet’s oceans (Startup Ecosystem).
On the industrial front, resilient robots could be deployed in hazardous environments such as mines, nuclear power plants, or chemical factories, where they could perform maintenance and inspection tasks, reducing the risk to human workers. This could revolutionize these industries, improving safety and efficiency.
Yet, as these AI systems become more autonomous and resilient, they also become more complex, raising new ethical and regulatory challenges. For instance, how do we ensure that these systems are used responsibly and do not pose a risk to society? How do we maintain transparency and accountability in their operation? And how do we ensure that control over these systems does not fall into the wrong hands? These are questions that policymakers, ethicists, and technologists will need to grapple with as the field of resilient robotics continues to evolve.