Quantum entanglement, a bewildering phenomenon where particles become interconnected regardless of the distance separating them, challenges our fundamental understanding of reality. It has puzzled scientists and intrigued philosophers for decades, offering a glimpse into the underlying fabric of the universe. By exploring its implications and the ongoing scientific debates, one can begin to unravel the mysteries of this quantum enigma.
The Nature of Quantum Entanglement
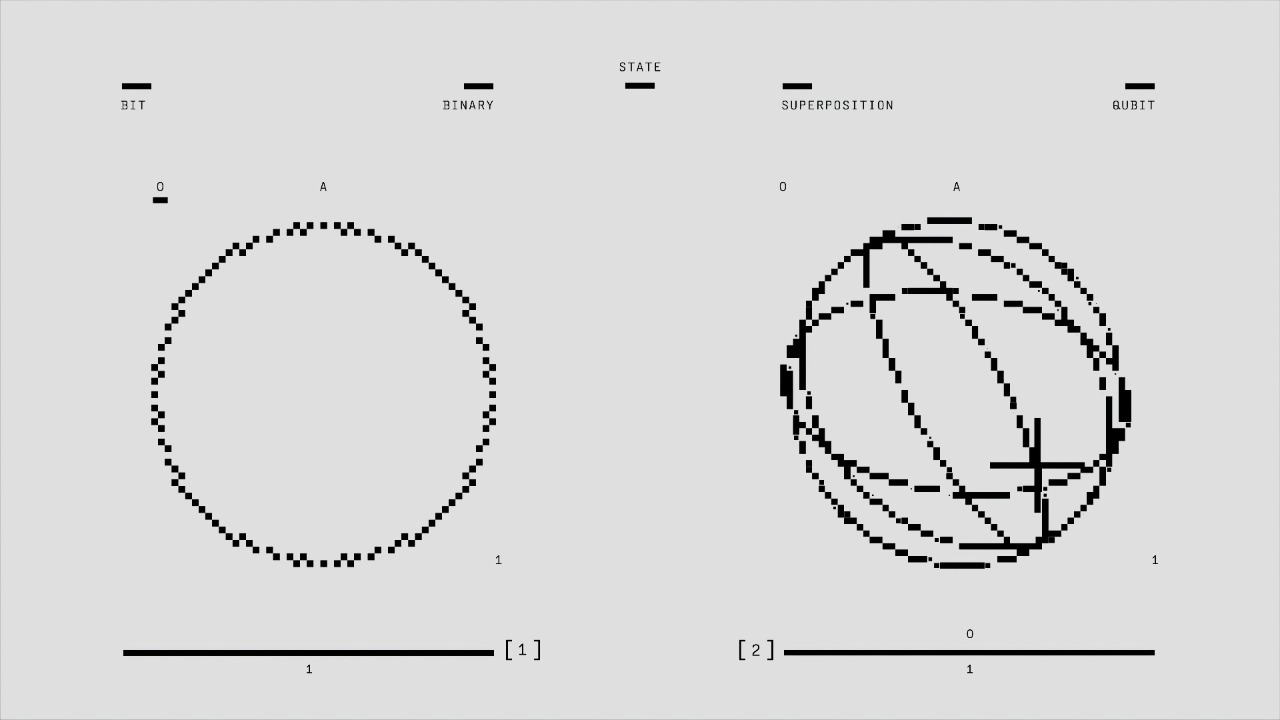
Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon that occurs when pairs or groups of particles interact in ways such that the quantum state of each particle cannot be described independently of the state of the others, even when the particles are separated by large distances. This interconnectedness defies classical intuition, where objects are expected to have independent and localized properties. Instead, entangled particles exhibit correlated behaviors instantaneously, no matter how far apart they are.
The concept of entanglement traces back to the early 20th century, when it was first proposed in the context of quantum mechanics. One of the pivotal moments in its history was the formulation of the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (EPR) paradox. This thought experiment challenged the completeness of quantum mechanics, suggesting that if quantum mechanics were correct, then particles could instantaneously affect each other, which seemed incompatible with the theory of relativity.
Over the decades, numerous experiments have validated the existence of entanglement. One of the most significant milestones was Bell’s theorem, which provided a framework for testing the predictions of quantum mechanics against those of classical physics. Experiments based on Bell’s theorem have consistently shown results in favor of quantum mechanics, confirming that entangled particles do indeed exhibit non-local correlations.
Quantum Entanglement and Relativity
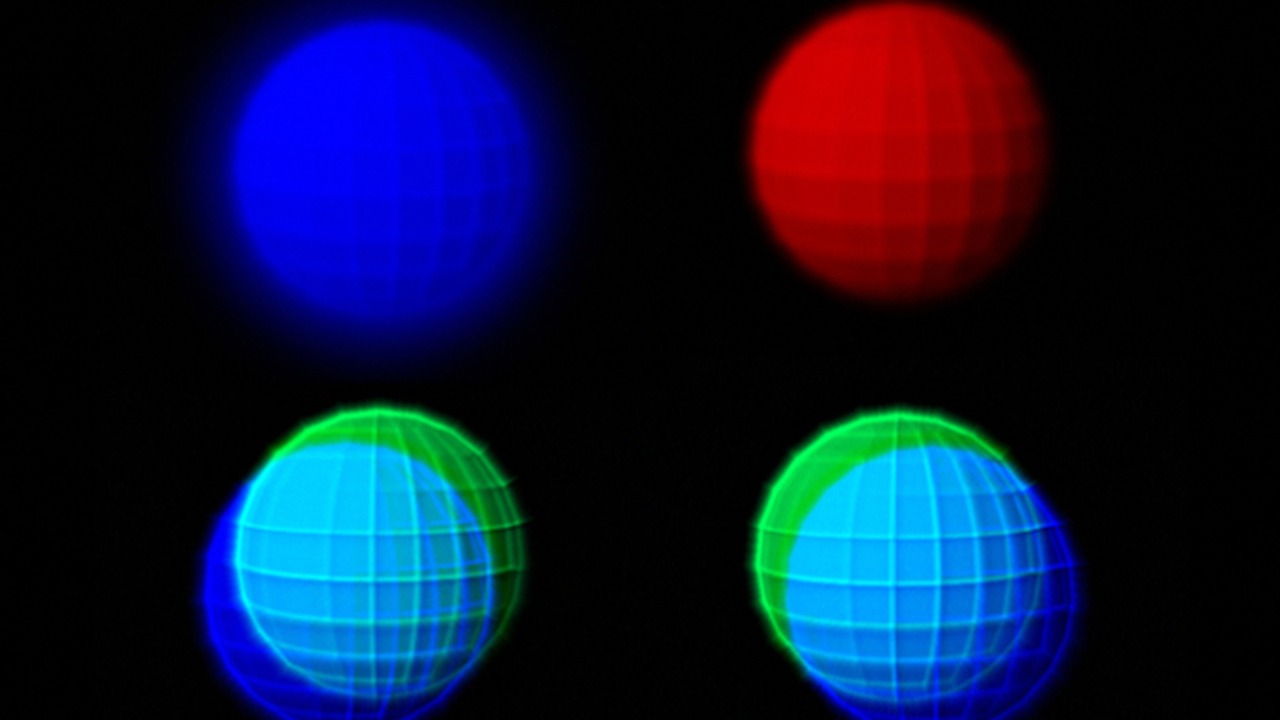

Albert Einstein famously referred to quantum entanglement as “spooky action at a distance.” His skepticism stemmed from the apparent contradiction between the instantaneous nature of entanglement and the principles of relativity, which assert that no information can travel faster than the speed of light. Despite his reservations, subsequent research has shown that entanglement does not violate relativity, as it involves correlations rather than direct transmission of information.
Efforts to reconcile quantum mechanics and relativity have led to new theoretical frameworks. One intriguing approach involves the role of Schrödinger’s cat, a thought experiment that highlights the paradoxes of quantum superposition and measurement. Recent studies have explored how such paradoxes might bridge the gap between the two theories, suggesting that entanglement could play a crucial role in a unified understanding of the universe.
The implications of entanglement extend beyond theoretical physics, challenging our understanding of time and space. By demonstrating that particles can remain interconnected across vast distances, entanglement suggests that the universe may be more interconnected than previously thought. This raises profound questions about the nature of reality and the limits of human perception.
Applications and Technologies

Quantum entanglement is not just a theoretical curiosity; it has practical applications that are transforming technology. One of the most promising areas is quantum computing, where entanglement is harnessed to perform computations at speeds unimaginable with classical computers. By exploiting the unique properties of entangled qubits, quantum computers can solve complex problems, such as factoring large numbers or simulating molecular interactions, more efficiently than traditional computers.
Another exciting application is quantum cryptography, which leverages entanglement to create secure communication channels. Unlike classical encryption methods, which can be vulnerable to eavesdropping, quantum cryptography relies on the principles of quantum mechanics to ensure that any attempt to intercept the communication alters the state of the entangled particles, alerting the communicators to the breach. This has the potential to revolutionize data security, making it virtually unbreakable.
Future technologies may also arise from a deeper understanding of entanglement. As researchers continue to explore its potential, we may see innovations in fields ranging from medicine to materials science. For instance, advances in quantum sensing could lead to more precise diagnostic tools, while entanglement-based materials could exhibit novel properties with applications in energy storage and conversion.
Philosophical and Theoretical Implications
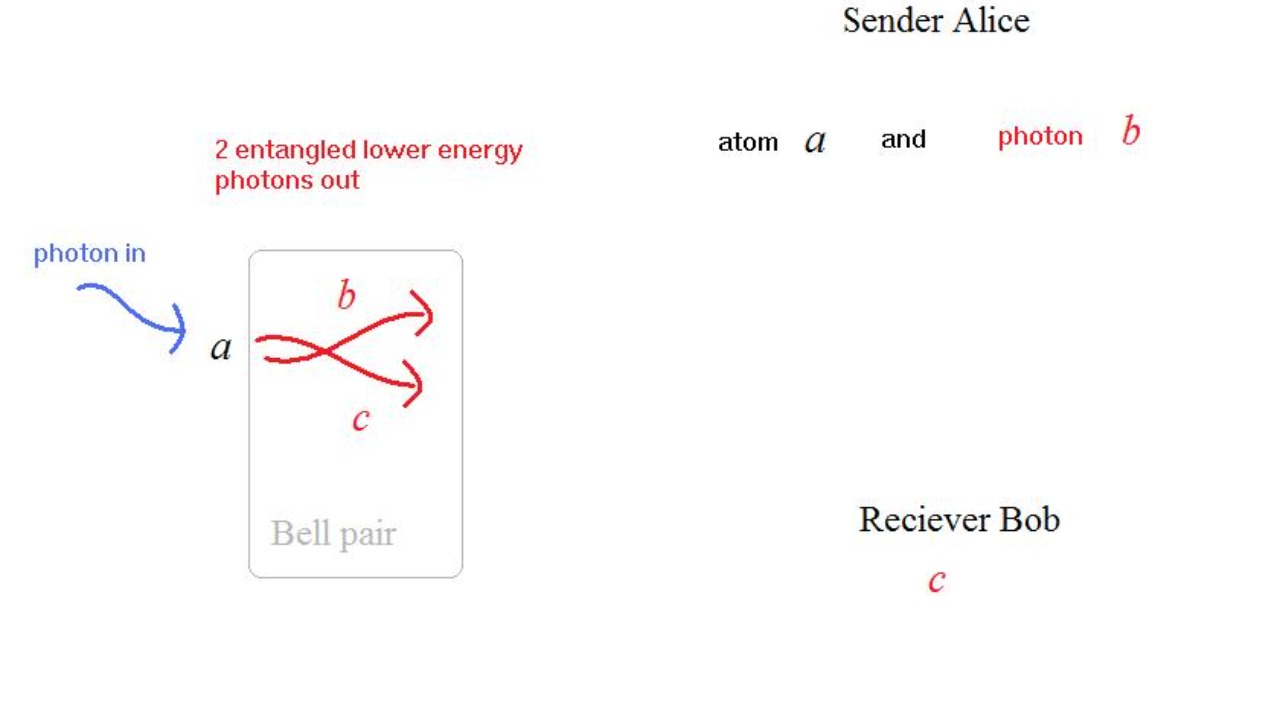
Beyond its practical applications, quantum entanglement has profound philosophical and theoretical implications. One area of interest is the multiverse theory, which posits that entanglement plays a crucial role in the branching of parallel universes. According to this interpretation, every quantum event results in a split, creating multiple realities where different outcomes occur. This challenges our perception of reality, suggesting that our universe is just one of many possible worlds.
The measurement problem is another area where entanglement poses significant challenges. In quantum physics, the act of measurement collapses a superposition of states into a single outcome, but the exact mechanism of this process remains elusive. Recent research has focused on unraveling this enigma, exploring how entanglement might influence the collapse of the wave function and the role of the observer in determining reality. For more on this topic, visit Berkeley’s exploration of measurement in quantum physics.
Ongoing debates continue to surround the interpretation of entanglement, with scientists and philosophers offering diverse perspectives. Some argue for a realist interpretation, where entanglement reflects an underlying reality independent of observation. Others advocate for an instrumentalist view, where entanglement is merely a mathematical tool for predicting outcomes. As research progresses, these debates will likely evolve, shaping our understanding of the quantum world.
Challenges and Future Directions

Despite the progress made in understanding quantum entanglement, significant challenges remain. Experimental limitations, such as maintaining coherence in entangled systems and minimizing environmental interference, pose technical hurdles for scientists. Developing reliable methods for generating and measuring entangled states is crucial for advancing both theoretical research and practical applications.
The quest for a deeper understanding of entanglement continues to drive research in quantum physics. Unanswered questions remain about the nature of entanglement, its role in the universe, and its potential to unify disparate areas of physics. As scientists explore these frontiers, they may uncover new insights that challenge our current paradigms and lead to transformative discoveries.
Ultimately, the future of quantum entanglement research holds the promise of bridging the gap between quantum mechanics and relativity. By unraveling the mysteries of entanglement, scientists hope to develop a more comprehensive understanding of the universe, one that transcends the limitations of classical physics and paves the way for a new era of scientific exploration.