Light-speed particles have long captivated scientists, presenting both a sense of wonder and a profound challenge. Despite extensive research efforts, the true nature and behavior of these particles remain elusive, sparking ongoing debates and investigations. The exploration into the world of particles that travel at the speed of light reveals both intriguing possibilities and significant implications for the realms of physics and cosmology.
The Speed Limit of the Universe

The concept of a universal speed limit, dictated by the speed of light, is foundational to our understanding of physics. Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity postulates that nothing can travel faster than light in a vacuum, a principle that has been extensively tested and verified in various scientific contexts. The speed of light, approximately 299,792,458 meters per second, serves as a critical constant in the equations governing space and time, shaping our comprehension of the universe’s structure.
Yet, why can’t particles be accelerated to this extraordinary speed? Xinghong Wang’s study offers insights into the prohibitive factors, such as the exponential increase in mass and energy requirements as particles approach light speed. This fundamental limitation underscores the immense energy barriers that inhibit achieving or surpassing light-speed acceleration.
Numerous experiments have sought to probe the boundaries of particle acceleration. Facilities like CERN’s Large Hadron Collider push particles to near-light speeds, approaching the theoretical limits set by physics. These experiments not only test our technological capabilities but also provide crucial data about fundamental particle interactions, expanding our grasp of the universe’s underlying principles.
Particles at the Speed of Light
Among the particles that naturally travel at light speed are photons, massless entities responsible for electromagnetic forces, including light itself. Photons’ unique ability to move at light speed without gaining mass allows them to traverse vast cosmic distances, playing an essential role in phenomena ranging from the basic transmission of information to the intricate dance of quantum mechanics.
Then there are neutrinos, once thought to potentially exceed light speed due to initial experimental errors at CERN’s OPERA project. However, subsequent recalibrations confirmed that neutrinos, like all particles with mass, travel slightly slower than light. This episode highlighted the complexities and precision required in experimental physics, emphasizing the challenges in confirming the behaviors of subatomic particles.
The speculative realm of hypothetical particles introduces entities such as tachyons, which are theorized to travel faster than light. While no empirical evidence supports their existence, tachyons offer intriguing theoretical possibilities, challenging physicists to reconsider the limits of our understanding and the potential consequences of superluminal particles.
Cosmic Implications and Dark Matter
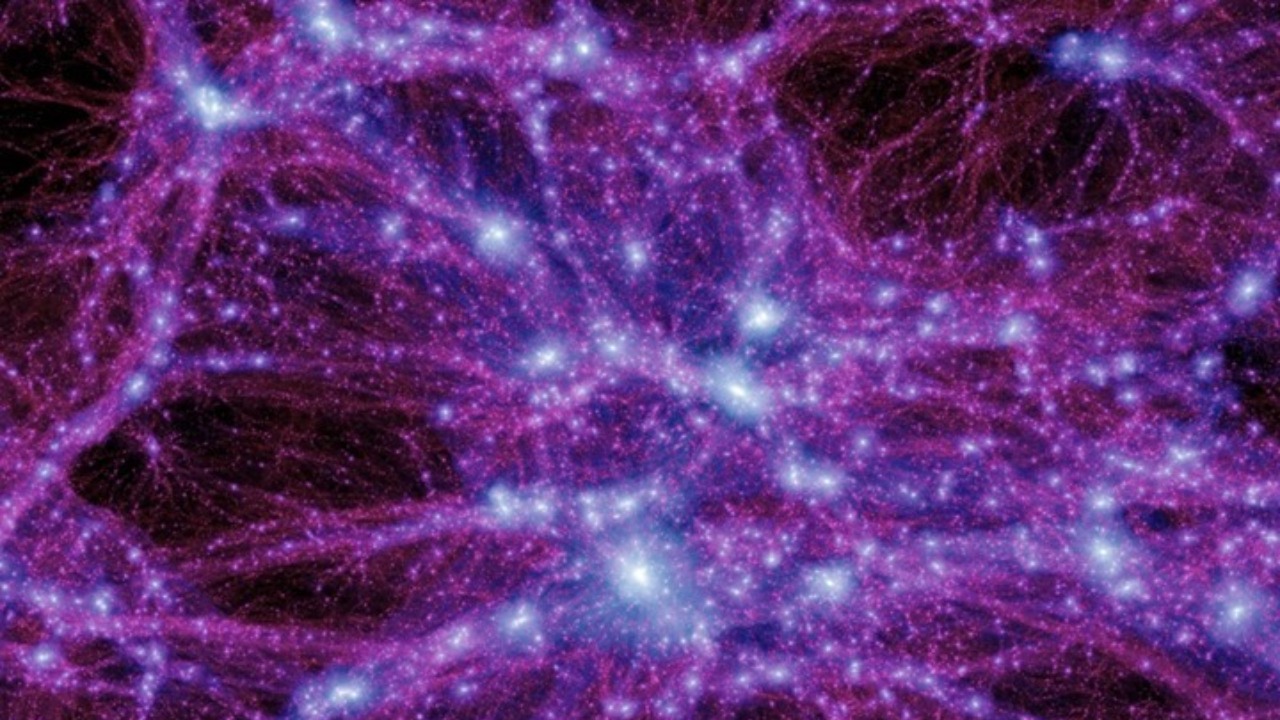

The exploration of light-speed particles extends into the enigmatic domain of dark matter. Some theories propose that light-speed particles might constitute this elusive substance, which makes up a significant portion of the universe’s mass yet remains undetectable through direct means. The hypothesis that dark matter could be composed of “frozen relics” of light-speed particles offers a tantalizing connection between the micro and macro scales of the cosmos, potentially linking particle physics with cosmological phenomena.
These “frozen relics” suggest a narrative where light-speed particles formed during the early universe remain trapped in a state that defies direct observation. Events such as the Big Bang could have set the stage for these particles to become integral components of dark matter, influencing cosmic evolution and structure without revealing their presence directly.
Detecting dark matter remains a formidable challenge due to its elusive nature. Scientists employ indirect methods, such as observing gravitational effects on visible matter and radiation, to infer the presence of dark matter. Despite advances, the quest for understanding these cosmic components continues, driven by the promise of unraveling the universe’s most profound mysteries.
Technological and Philosophical Considerations

Technological progress is crucial in the pursuit of understanding light-speed particles. Particle accelerators, such as those at CERN, and advanced space-based observatories are pivotal in detecting and analyzing these particles. Innovations in detection technologies are continually evolving, enabling scientists to delve deeper into the properties and interactions of particles traveling at extreme speeds.
The enigmatic nature of light-speed particles also poses philosophical questions about the fabric of reality. What does it mean for a particle to travel at the universe’s speed limit, and how does this challenge our perceptions of time and space? Such inquiries push the boundaries of science, inviting interdisciplinary dialogue that spans physics, philosophy, and cosmology.
Future research directions aim to address unanswered questions about light-speed particles. Scientists are exploring new experimental frameworks and refining theoretical models to gain insights into these elusive entities. The ongoing effort to unlock the secrets of light-speed particles could lead to groundbreaking discoveries, reshaping our understanding of the universe.
Implications for Modern Physics

Discoveries related to light-speed particles have profound implications for modern physics. Each breakthrough challenges or reinforces existing theories, prompting scientists to re-evaluate foundational principles. The interplay between empirical evidence and theoretical models is vital in advancing our comprehension of the universe.
Light-speed particles intersect with the domain of quantum mechanics, where the rules of classical physics often give way to more complex and counterintuitive behaviors. Understanding these intersections could lead to potential breakthroughs in areas like quantum computing, communication, and fundamental physics.
Interdisciplinary approaches are essential in unraveling the mysteries of light-speed particles. Collaborations across fields such as astrophysics, particle physics, and cosmology are crucial in piecing together the puzzle of these enigmatic entities. The pursuit of knowledge in this area exemplifies the interconnectedness of scientific disciplines, highlighting the collective effort required to explore the unknown.