Recent photographs captured by a spacecraft reveal the stunning phenomenon of ice geysers erupting on Enceladus, one of Saturn’s moons. This discovery not only adds to the intrigue surrounding Enceladus but also raises questions about potential life-supporting environments in our solar system. With its icy surface and mysterious plumes, Enceladus continues to captivate scientists and space enthusiasts alike.
The Enceladus Phenomenon
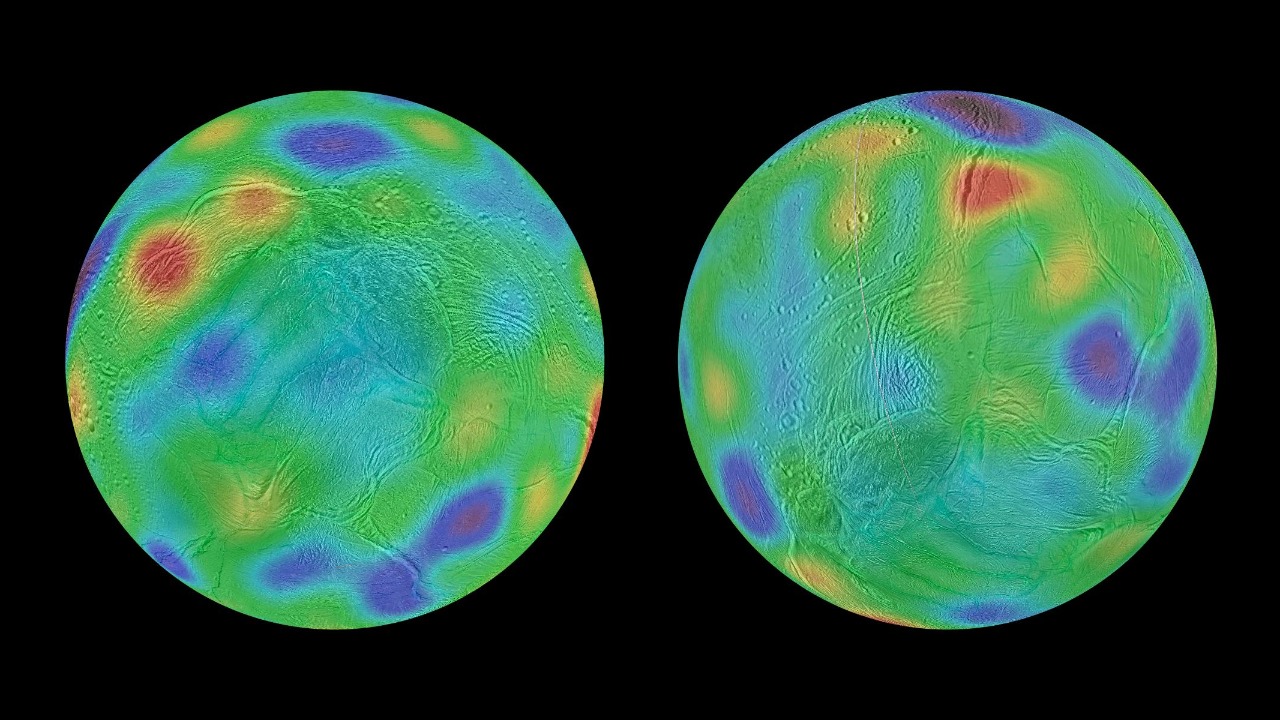
Understanding Enceladus
Enceladus, a relatively small moon of Saturn, has long been a subject of interest for astronomers and planetary scientists. It is the sixth-largest moon of Saturn and was first observed in detail by the Voyager missions in the early 1980s. However, it was the Cassini spacecraft that provided the most compelling data about this icy world. Cassini’s observations revealed that beneath its icy crust, Enceladus harbors a subsurface ocean, making it one of the most promising places in the solar system to search for life.
The historical context of Enceladus’s exploration is rich with fascinating discoveries. Prior missions have shown that Enceladus is geologically active, with a surface that is constantly being reshaped by tectonic forces and cryovolcanism. These early findings set the stage for further exploration, making the recent discovery of ice geysers even more significant in understanding the moon’s dynamic nature.
The Mystery of the Geysers
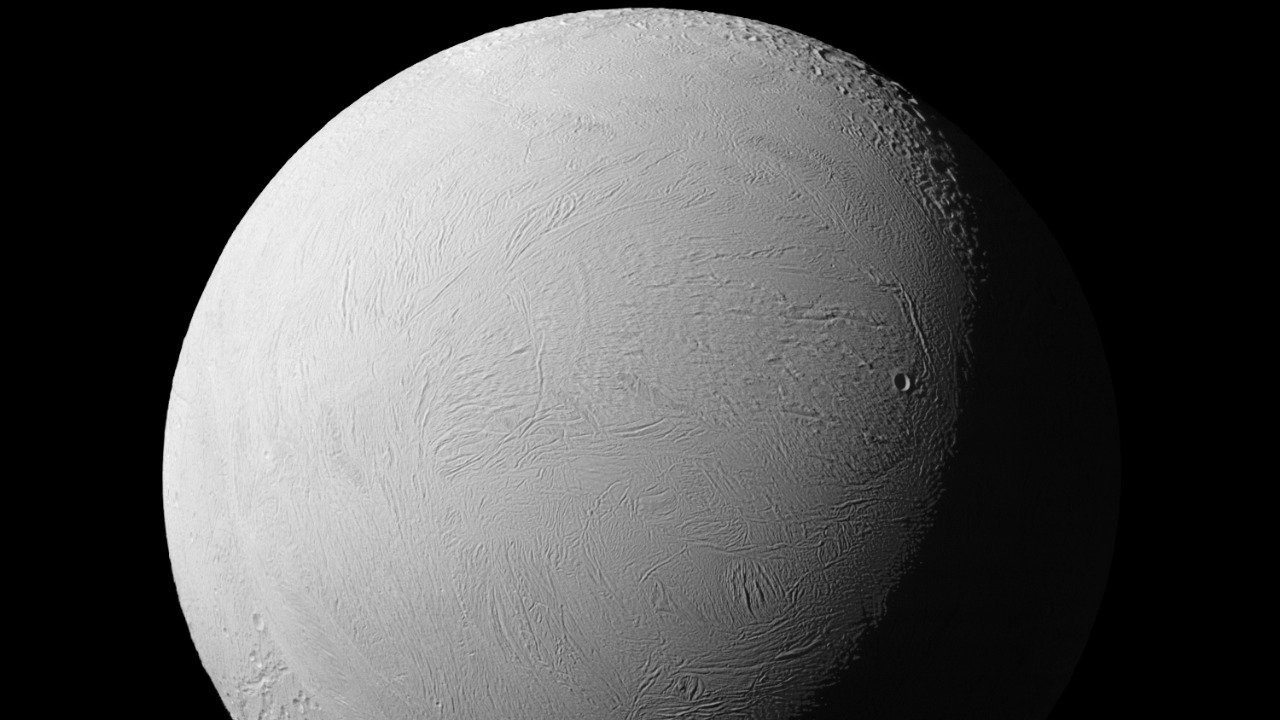
The recent photographs capturing the ice geysers of Enceladus have provided valuable insights into the moon’s geophysical processes. These images reveal plumes of water vapor and ice particles being ejected from cracks in the moon’s surface, primarily located at its south pole. Scientists believe that these geysers are the result of hydrothermal activity occurring in the subsurface ocean, where water is heated by tidal forces and then expelled through surface fissures.
Scientific explanations for this geyser activity suggest that the presence of these plumes could indicate favorable conditions for life. The ejected material contains a variety of chemicals, including organic compounds, which are essential ingredients for life as we know it. This discovery raises significant implications for astrobiology and the possibility of microbial life existing in environments beyond Earth.
The Role of Spacecraft Observations

Technological Advances
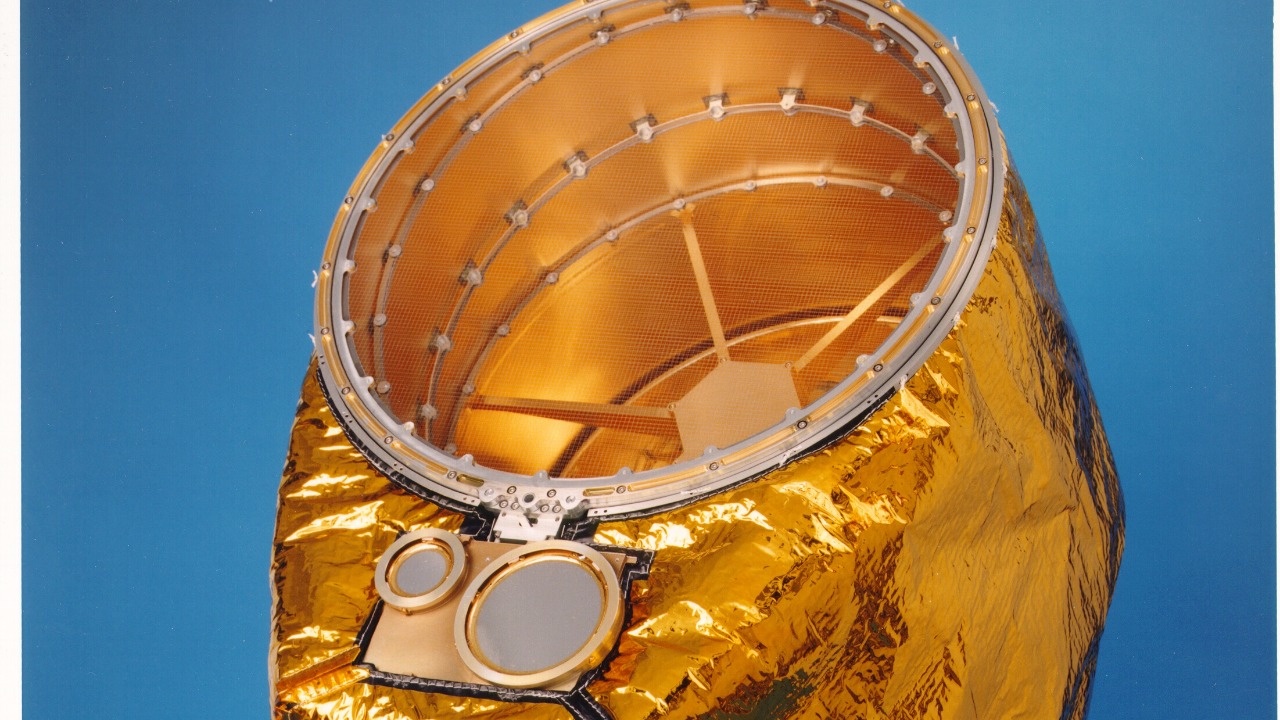
The advancements in space technology have played a pivotal role in capturing images of Enceladus’s ice geysers. The spacecraft responsible for these observations is equipped with state-of-the-art instruments capable of analyzing the chemical composition of the plumes. One such instrument is the Cosmic Dust Analyzer (CDA), which can identify the particles’ size and composition, providing crucial data about the moon’s geophysical processes.
These technological advances have significantly enhanced our ability to study distant celestial bodies. The precision and capability of modern spacecraft instruments allow scientists to gather detailed information about the moons and planets in our solar system. This, in turn, helps researchers to develop a more comprehensive understanding of the dynamics of these celestial objects and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Data Collection and Analysis
The methods used in analyzing the data collected from Enceladus are both sophisticated and meticulous. Scientists employ a combination of remote sensing techniques and computer modeling to interpret the information gathered by the spacecraft. This data analysis is crucial for understanding the complex interactions occurring beneath the moon’s icy crust.
The importance of continuous observation and data accumulation cannot be overstated. Regular monitoring of Enceladus allows researchers to track changes over time, providing insights into the moon’s geological activity and potential habitability. This ongoing research is essential for planning future missions to Enceladus and other icy moons, as it helps to identify the most promising areas for exploration.
Potential for Life on Enceladus

Chemical Ingredients for Life
The chemical composition of the geysers on Enceladus has significant implications for the potential for life. The plumes contain a mixture of water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and ammonia, among other compounds. These ingredients are analogous to those found around Earth’s hydrothermal vents, where microbial life thrives despite extreme conditions.
This comparative analysis suggests that similar forms of life could exist in the subsurface ocean of Enceladus. The presence of organic molecules and the energy provided by hydrothermal activity create a potentially habitable environment beneath the moon’s icy exterior. This discovery fuels the hope that Enceladus could harbor life, making it a prime target for future astrobiological studies.
The Ocean Beneath
Insights into Enceladus’s subsurface ocean reveal its alkaline properties, which are conducive to life. Research indicates that the ocean is rich in sodium chloride, similar to Earth’s oceans, and has a pH level that could support biological processes. This environment provides a stable medium for the development of life, with the potential for complex chemical interactions occurring in its depths.
The exploration of Enceladus’s ocean is a key focus for scientists seeking to understand the moon’s potential to support life. The combination of water, organic compounds, and energy sources makes it one of the most intriguing places in the solar system to search for extraterrestrial life. The possibility of life existing in these hidden depths challenges our understanding of habitability and encourages further exploration.
Implications for Space Exploration

Expanding Horizons
The discoveries on Enceladus have far-reaching implications for the search for extraterrestrial life. The presence of an ocean beneath its icy surface and the chemical composition of its geysers suggest that life could exist in environments previously deemed inhospitable. This expands the horizons of astrobiology, prompting scientists to consider the potential for life on other icy moons and planets.
The potential for future missions to Enceladus is a topic of great interest among the scientific community. These missions could provide more detailed data about the moon’s environment, furthering our understanding of its potential habitability. As technology advances, the possibility of exploring Enceladus and other icy bodies becomes increasingly feasible, offering exciting opportunities for discovery.
Interdisciplinary Impact
The role of planetary science in understanding broader astrobiological questions is critical. The findings from Enceladus have implications for various scientific fields, including geology, chemistry, and biology. These interdisciplinary impacts highlight the interconnectedness of scientific research and the importance of collaboration in advancing our knowledge of the universe.
The discoveries on Enceladus have also sparked interest in the study of Earth’s geological processes. By comparing the moon’s geophysical activity with similar processes on Earth, scientists can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of our planet. This research not only informs our understanding of other celestial bodies but also enhances our knowledge of Earth’s geological history.
Enceladus in the Context of the Solar System
Comparative Planetology
Comparing Enceladus with other icy bodies in the solar system provides valuable insights into the moon’s unique features. Unlike other moons, Enceladus exhibits significant geological activity and has a subsurface ocean, making it a prime candidate for exploration. The study of Enceladus in conjunction with other celestial bodies helps scientists to develop a more comprehensive understanding of the solar system’s dynamics.
The unique features of Enceladus, such as its geysers and subsurface ocean, distinguish it from other moons and planets. These characteristics make it an intriguing target for future missions, as they offer the potential to uncover new information about the potential for life beyond Earth. The study of Enceladus and its icy counterparts continues to inform our understanding of planetary habitability and the potential for life in the cosmos.
The Broader Implications
The findings from Enceladus have significant implications for our understanding of the solar system’s formation and evolution. The study of its geysers and subsurface ocean provides insights into the processes that shape celestial bodies and the potential for habitability in extreme environments. These discoveries contribute to a broader understanding of the conditions necessary for life to exist.
The significance of Enceladus in the context of planetary habitability and astrobiology cannot be overstated. As we continue to explore this fascinating moon, we gain valuable insights into the potential for life beyond Earth and the dynamic processes that shape our solar system. The study of Enceladus challenges our perceptions of habitability and encourages us to expand our search for life in the cosmos.