
In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have identified what appears to be a new element on asteroid 33 Polyhymnia, challenging long-standing assumptions about the periodic table. This unexpected finding has sparked excitement and debate within the scientific community, as researchers work to understand its implications for both space exploration and fundamental physics.
The Discovery of the Impossible Element
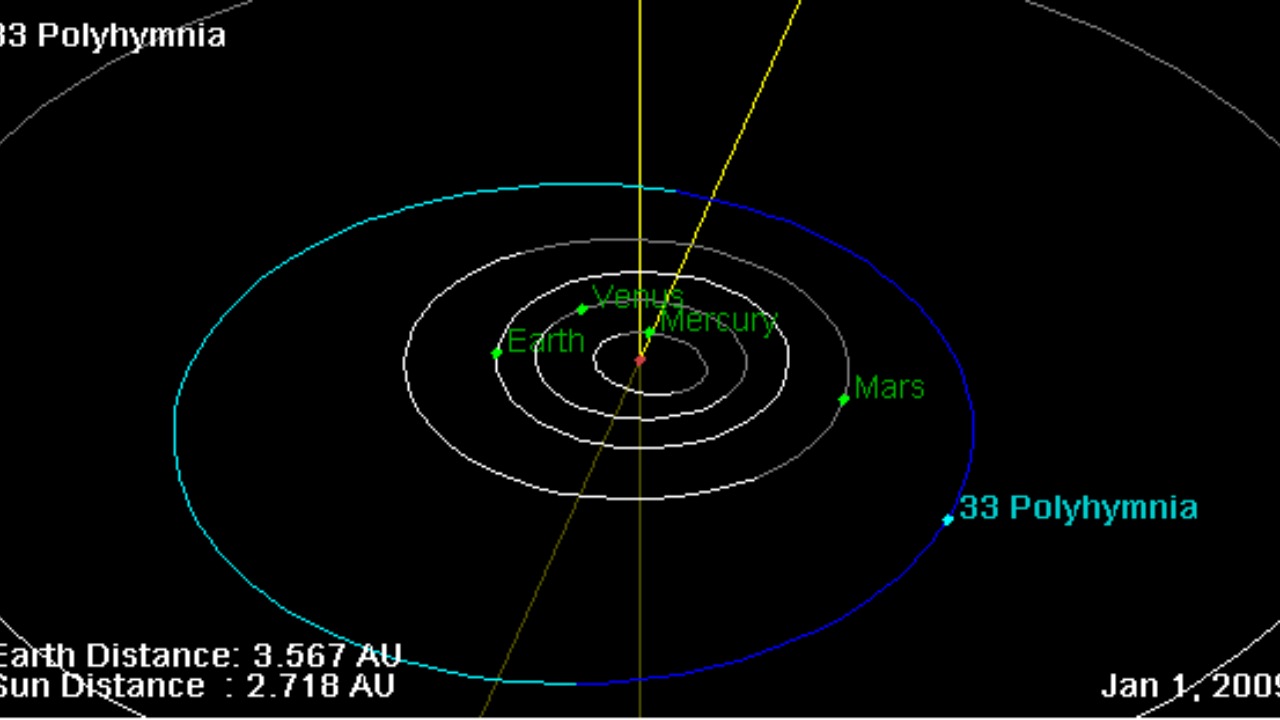
The research mission that led to this discovery was part of an extensive study aimed at analyzing the composition of celestial bodies within our solar system. The team employed a spacecraft equipped with state-of-the-art instruments to gather samples from the surface of asteroid 33 Polyhymnia. Upon returning to Earth, the samples underwent rigorous examination using advanced spectroscopic techniques. These methods allowed researchers to detect the presence of an element with properties unlike any known on the periodic table.
Upon the announcement of this discovery, the scientific community was abuzz with reactions and hypotheses. Some researchers suggest that this element might have formed under unique conditions present in the asteroid’s environment, while others propose that it could have originated from a different part of the universe and been deposited on the asteroid. The novelty of the element’s properties has led to a flurry of speculation about its potential uses and the processes that could have produced it.
Implications for the Periodic Table
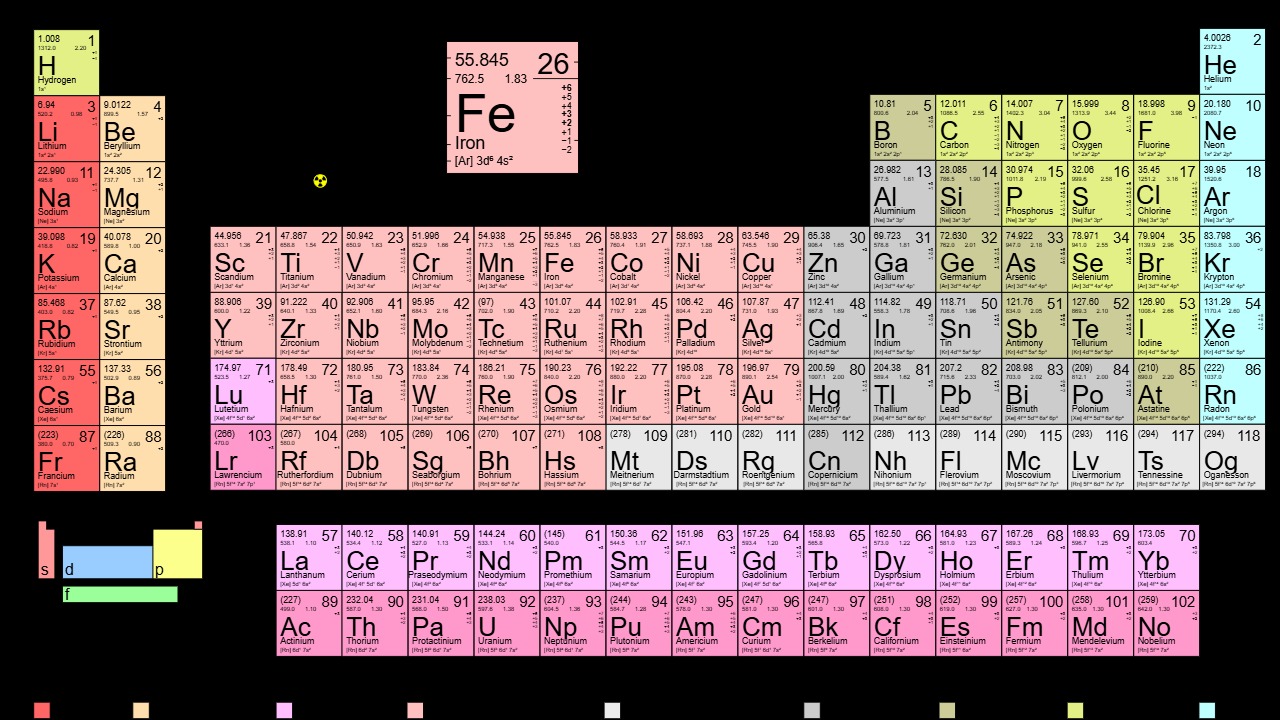
The discovery of this new element poses a significant challenge to existing scientific theories regarding the formation and stability of elements. Traditionally, the periodic table has been considered a comprehensive catalog of the universe’s building blocks, organized by atomic number and properties. However, this finding suggests that there may be other elements yet to be discovered, which could exist under conditions not previously considered.
Potential updates to the periodic table are being discussed, with scientists examining how this new element might be integrated. Such changes could have profound implications for the field of chemistry, prompting a reassessment of chemical properties and reactions. Historically, the addition of new elements has often been a catalyst for advancements in both theoretical and applied chemistry, and this case could be no different. As we look back at the history of elemental discovery, this new element might fit into a broader trend of uncovering the unseen and expanding our understanding of the universe.
Asteroids as Cosmic Laboratories

Asteroids are often viewed as time capsules, preserving the conditions of the early solar system. This makes them invaluable sources for understanding the origins and evolution of our cosmic neighborhood. The discovery on asteroid 33 Polyhymnia is not the first time asteroids have yielded significant scientific insights. For example, the detection of water on asteroids has provided new theories about how water may have arrived on Earth.
Previous missions have uncovered a wealth of information about asteroids, including the presence of organic compounds and minerals that were once considered rare or nonexistent in space. These findings have significantly contributed to our understanding of planetary formation and the distribution of elements across the solar system. With the advent of asteroid mining and exploration, there is a growing potential for discovering new elements and materials that could revolutionize various scientific fields.
Impact on Space Exploration and Technology

The discovery of new elements has the potential to greatly enhance material science and engineering, particularly in the realm of space exploration. New materials derived from such elements could lead to the development of stronger, lighter, and more resilient spacecraft components, enabling longer and more ambitious missions. Furthermore, these materials could also improve our capabilities in constructing habitats and tools for sustaining human life in space.
In technology and industry, the properties of the newly discovered element might offer novel applications, ranging from advanced electronics to cutting-edge medical technologies. As researchers continue to study this element, the potential applications could expand, influencing industries worldwide. The broader implications for future space missions are significant, as this discovery underscores the importance of international collaboration in space research, fostering partnerships that can lead to shared advancements and exploration goals.
The Future of Elemental Research

Looking ahead, upcoming missions and technologies are being planned to further investigate asteroid 33 Polyhymnia and similar celestial bodies. These missions aim to refine our understanding of the conditions that give rise to new elements, using enhanced analytical tools and sensors to gather more detailed data. The goal is to not only confirm the existence of this new element but also to explore its potential interactions and applications.
Interdisciplinary collaboration will be crucial in advancing our understanding of new elements. Chemists, physicists, astronomers, and engineers will need to work together to explore the implications of these discoveries. Such collaboration can lead to breakthroughs that have the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the universe, pushing the boundaries of what we know and opening new frontiers for exploration.
As we continue to explore the cosmos, the prospect of discovering more “impossible” elements remains ever-present. These future breakthroughs hold the promise of expanding our knowledge and capabilities, ultimately reshaping our approach to both science and technology. For those interested in the ongoing developments, more information can be found in studies like the Springer publication on asteroidal research and related scientific discussions.