The Himalayas, renowned as the world’s highest mountain range, have always been a focal point of significant geological research. These majestic peaks, often seen as the epitome of Earth’s structural majesty, have recently become even more intriguing. Groundbreaking scientific revelations suggest the geological theories that we’ve held true regarding the formation and stability of the Himalayas may need to be reevaluated.
The Traditional Understanding of Himalayan Geology

The long-established theories explaining the formation and support of the Himalayas primarily revolve around the concept of tectonic plate movement. For years, we’ve understood that the collision of the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates gave birth to these impressive mountains. This collision, resulting in what is often referred to as the ‘Himalayan uplift’, is a textbook example of the power of tectonic activity.
The theory of tectonic plates has been crucial in shaping our understanding of not just the Himalayas, but mountain ranges worldwide. It’s been accepted that these moving sections of the earth’s crust are responsible for the creation, and continued existence, of these natural wonders. However, recent findings suggest we may need to rethink these assumptions.
New Discoveries: Challenging the Established Beliefs

A recent scientific study has thrown a spanner in the works of traditional Himalayan geology. This research suggests a surprising link between Earth’s magnetic field and oxygen levels, a connection previously undetected. These findings challenge the established theories about the geological processes that hold up the Himalayas.
This new theory presents the idea that changes in the Earth’s magnetic field can impact the oxygen content in the Earth’s mantle, the layer just beneath the crust. As oxygen levels increase, the mantle becomes more rigid, providing additional support to the overlying crust and subsequently, the Himalayas. This unexpected discovery could radically alter our understanding of how mountain ranges are supported.
Implications of the New Geological Theory
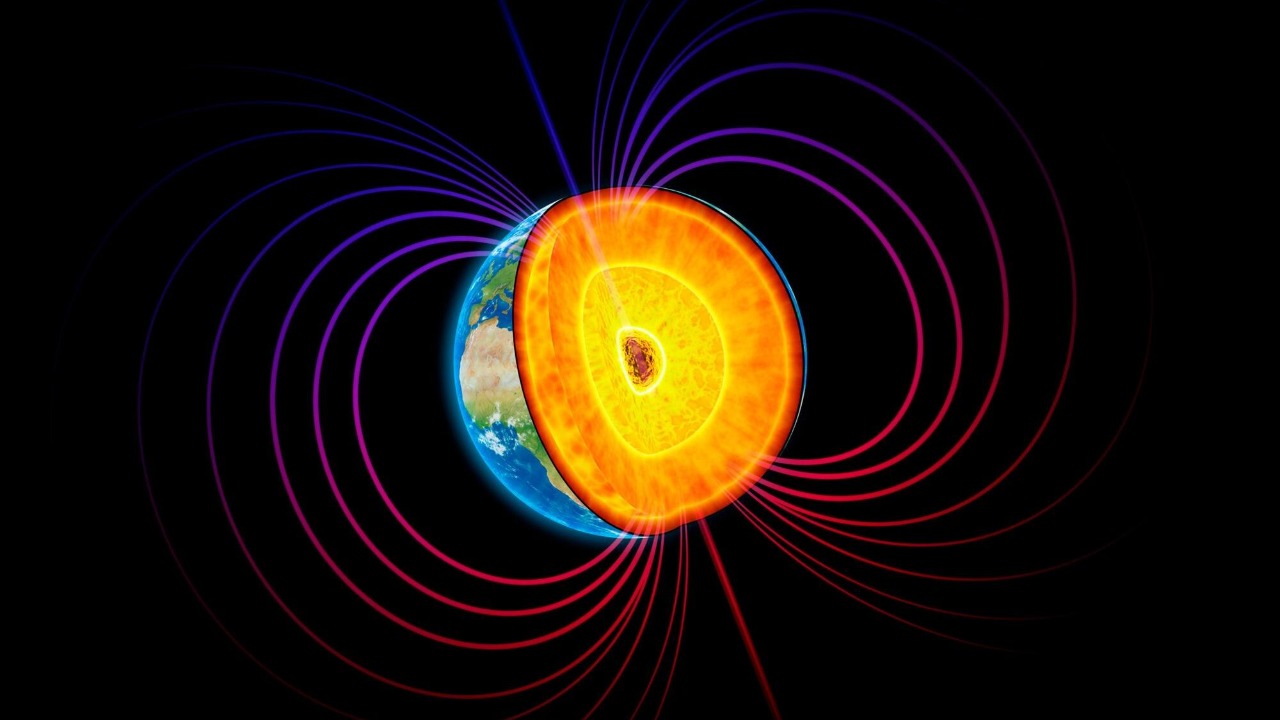
The revelations derived from this study carry profound implications for our understanding of Earth’s geological history. If the Earth’s magnetic field and oxygen levels in the mantle impact the stability of mountain ranges, then our understanding of how these structures form and persist could be in for a significant overhaul.
Moreover, these findings could have implications for other mountain ranges worldwide. If the principles discovered here apply elsewhere, we might have to revisit our understanding of mountain geology on a global scale. The potential impacts of this new line of thinking are immense, and it’s an exciting time to be delving into Earth’s geological mysteries.
Understanding the Role of Earth’s Mantle
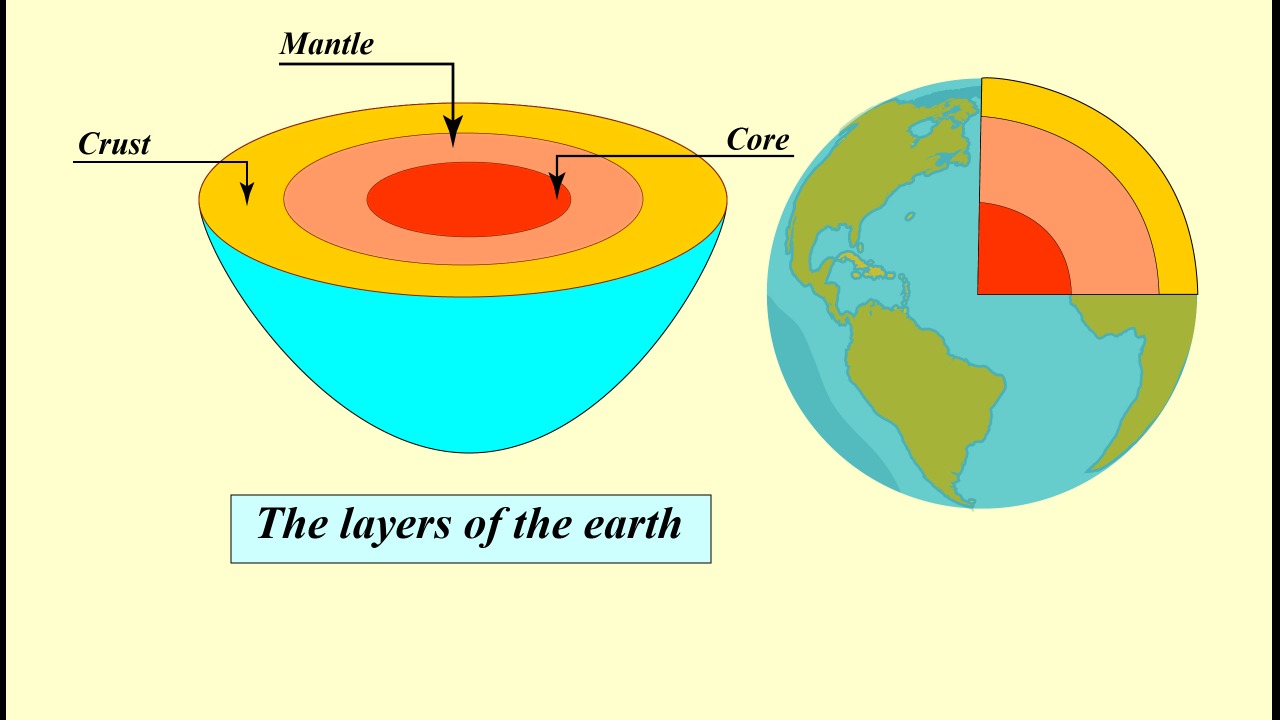
The Earth’s mantle has always been known to play a crucial role in global geology, but its contribution to the stability of the Himalayas is something that’s now being reevaluated. These new findings suggest that the rigidity of the mantle, influenced by oxygen levels, may be a significant factor in supporting this mountain range.
Additionally, a recent discovery of massive, billion-year-old blobs in Earth’s mantle further emphasizes its complex and crucial role in shaping our planet’s geology. These ancient structures, found deep within the Earth, are another piece of the puzzle in understanding the processes occurring beneath our feet.
What Does the Future Hold for Himalayan Geology?

As we continue to unearth new information about the geology of the Himalayas, the future direction of this research field becomes even more fascinating. With these new findings challenging our established beliefs, it’s clear that there are still many secrets within these majestic peaks waiting to be discovered.
Moreover, the potential impacts of these discoveries extend beyond just geology. They could have significant influences on environmental conservation and climate change research in the Himalayan region. As we continue to explore the connections between the Earth’s magnetic field, oxygen levels in the mantle, and the stability of the Himalayas, we’re not only rewriting textbooks but also potentially influencing policies and strategies for dealing with our changing climate.