Scientists have recently detected a “donut-shaped” magnetic region within Earth’s core, a discovery that could redefine our understanding of the planet’s inner dynamics. This landmark finding, unveiled through advanced seismic and magnetic analyses, provides new insights into Earth’s magnetic field and its implications for geophysical processes.
The Discovery of the Donut-Shaped Magnetic Region
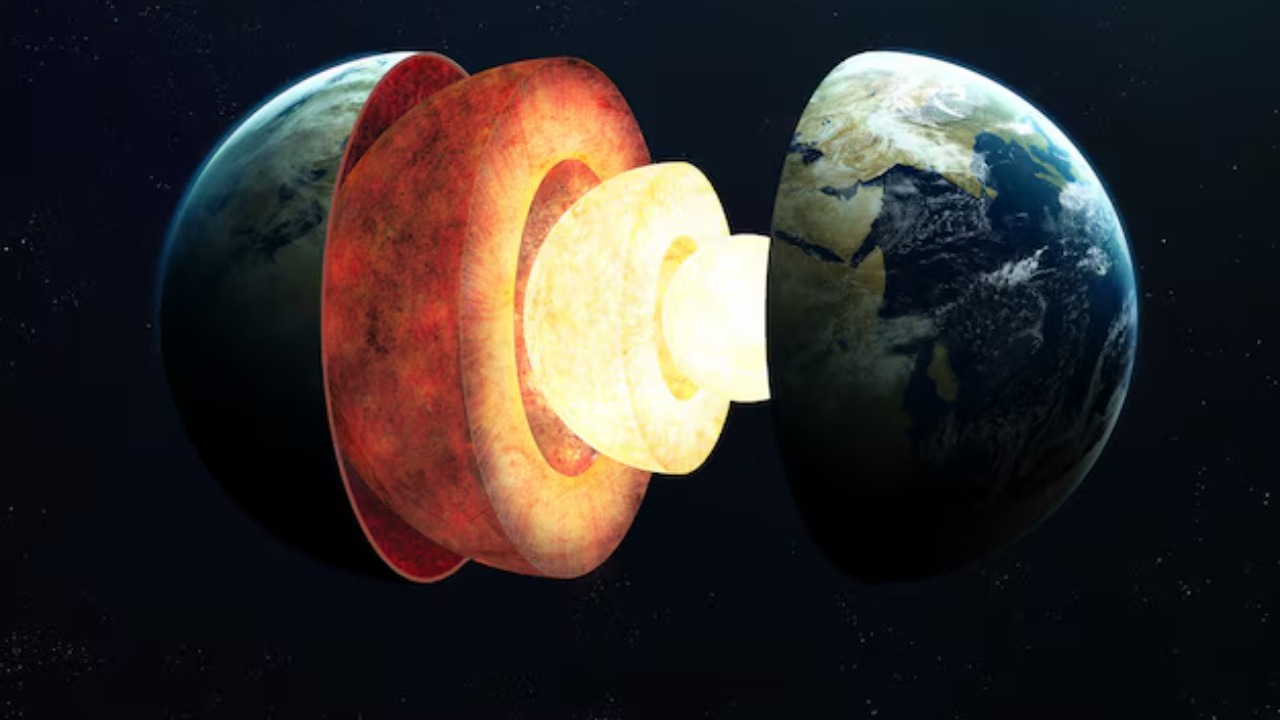
The unveiling of this donut-shaped magnetic region within Earth’s core is a testament to the advancements in seismic and magnetic technology. Researchers employed sophisticated seismic wave analysis and magnetic field modeling to detect this unusual structure. Seismic waves, which travel through Earth’s layers, were meticulously analyzed to map out the core’s complex dynamics. Simultaneously, magnetic field measurements helped to reveal the unique shape of this region, offering a deeper understanding of its characteristics.
The discovery of a donut shape within Earth’s core is intriguing because it defies previous assumptions about the core’s uniformity. This shape suggests the presence of complex, toroidal currents within the core, which may play a significant role in Earth’s magnetic processes. The shape’s symmetry and structure could indicate previously unknown movements or flows of molten iron, hinting at the dynamic nature of the core’s composition.
This groundbreaking discovery is the result of collaborative efforts by leading scientists and institutions worldwide. Researchers from the Australian National University and other prominent organizations have been at the forefront of this study, utilizing cutting-edge technology to peer deep into Earth’s interior. Their work, documented in various scientific publications, highlights the importance of international cooperation in advancing geophysical research.
Understanding Earth’s Core Dynamics
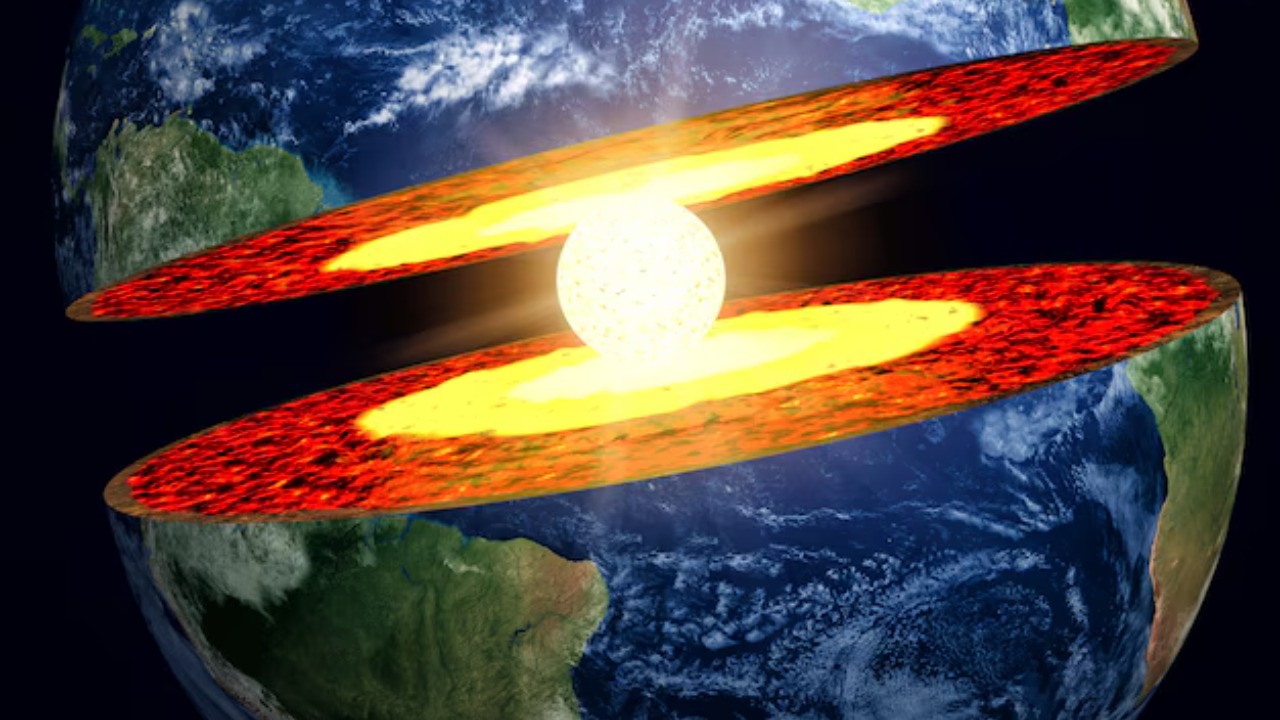

Earth’s core is composed of a solid inner core and a fluid outer core, primarily made of iron and nickel. These layers play a crucial role in the generation of Earth’s magnetic field. The movement of molten iron within the outer core creates convective currents, which, in turn, generate magnetic fields through a process known as the geodynamo effect. This newly discovered donut-shaped region adds another layer of complexity to our understanding of these processes.
The core’s dynamics are central to understanding Earth’s magnetism. The swirling motions and temperature variations within the core contribute to the ever-changing nature of Earth’s magnetic field. This discovery may provide insights into how these movements are organized and how they interact with each other. The donut shape could indicate a specific flow pattern that enhances or disrupts the overall magnetic field.
Previous theories about Earth’s core dynamics have often depicted the core as a relatively uniform structure. However, the detection of this donut-shaped region challenges those assumptions. It aligns with emerging theories that suggest more intricate patterns of movement and magnetic field generation within the core. These findings could lead to a reevaluation of existing models and inspire further research into the core’s enigmatic processes.
Implications for Earth’s Magnetic Field
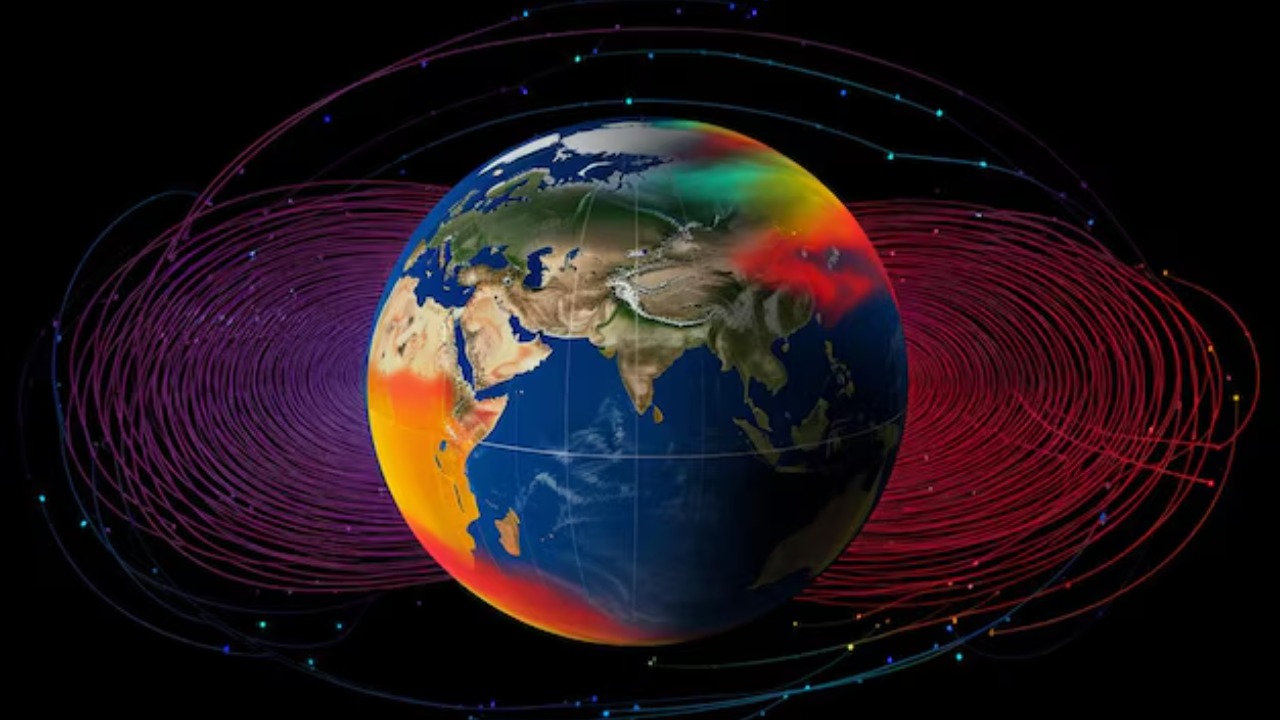
The presence of a donut-shaped magnetic region within the core has profound implications for understanding geomagnetic reversals. These reversals, where the magnetic poles switch places, have occurred throughout Earth’s history. The discovery suggests that the donut shape may influence the timing and frequency of these reversals. Understanding the role of this region could help predict future reversals and their impact on global systems.
Earth’s magnetic field acts as a shield against harmful solar and cosmic radiation. Any changes within the core, such as the dynamics of this donut-shaped region, could affect the strength and stability of this protective barrier. While the immediate impact of the discovery on Earth’s magnetic shield is yet to be fully understood, it underscores the need for continuous monitoring and research to anticipate potential changes in our planet’s radiation protection.
Future research will likely focus on exploring the magnetic interactions within the core. Scientists are keen to understand how the donut-shaped region interacts with other parts of the core and how it contributes to the overall magnetic field. This research could lead to new insights into the geodynamo process and improve our ability to model and predict magnetic field behavior.
Technological and Methodological Breakthroughs
The discovery of the donut-shaped magnetic region was made possible by significant advances in seismic technology. High-resolution seismic imaging techniques allowed researchers to visualize the core’s interior with unprecedented clarity. These methods, combined with magnetic field analysis, provided the tools necessary to uncover the intricate structures within Earth’s core.
The success of this research highlights the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration. Geophysicists, seismologists, and other experts worked together to combine their knowledge and expertise, leading to this groundbreaking discovery. Such collaborative efforts are crucial for advancing our understanding of complex geophysical phenomena and paving the way for future breakthroughs.
With these technological and methodological advancements, scientists are optimistic about the potential for new discoveries within Earth’s interior. The techniques used in this study could be applied to investigate other aspects of the core and mantle, revealing more about the planet’s internal dynamics. This ongoing research promises to deepen our knowledge of Earth’s inner workings and their influence on surface processes.
Broader Impacts on Geophysics and Earth Science

The discovery of the donut-shaped magnetic region is poised to have a significant impact on educational and scientific fields. It challenges existing curricula and theories, encouraging educators and researchers to incorporate these findings into their work. As our understanding of Earth’s core deepens, it will influence the teaching of geophysics and related disciplines, inspiring the next generation of scientists.
Global collaborative efforts have been instrumental in this discovery, underscoring the importance of international cooperation in advancing scientific knowledge. By working together, researchers from different countries and backgrounds have been able to achieve breakthroughs that might not have been possible in isolation. This spirit of collaboration is essential for tackling complex global challenges and expanding our understanding of planetary sciences.
The implications of this discovery extend beyond Earth, offering insights into the study of other planetary bodies. Understanding the dynamics of Earth’s core can inform research on the cores of other planets and celestial bodies. By applying similar methodologies, scientists may uncover unique features within the interiors of planets like Mars or Mercury, shedding light on their magnetic fields and geological histories.