Researchers have developed innovative technologies capable of producing drinking water from the arid desert air, addressing water scarcity in some of the world’s most water-stressed regions. Leveraging advanced materials and engineering techniques, these new systems are capable of extracting water vapor from the atmosphere even in low-humidity environments, providing a sustainable solution to a growing global crisis.
Technological Innovations in Water Extraction
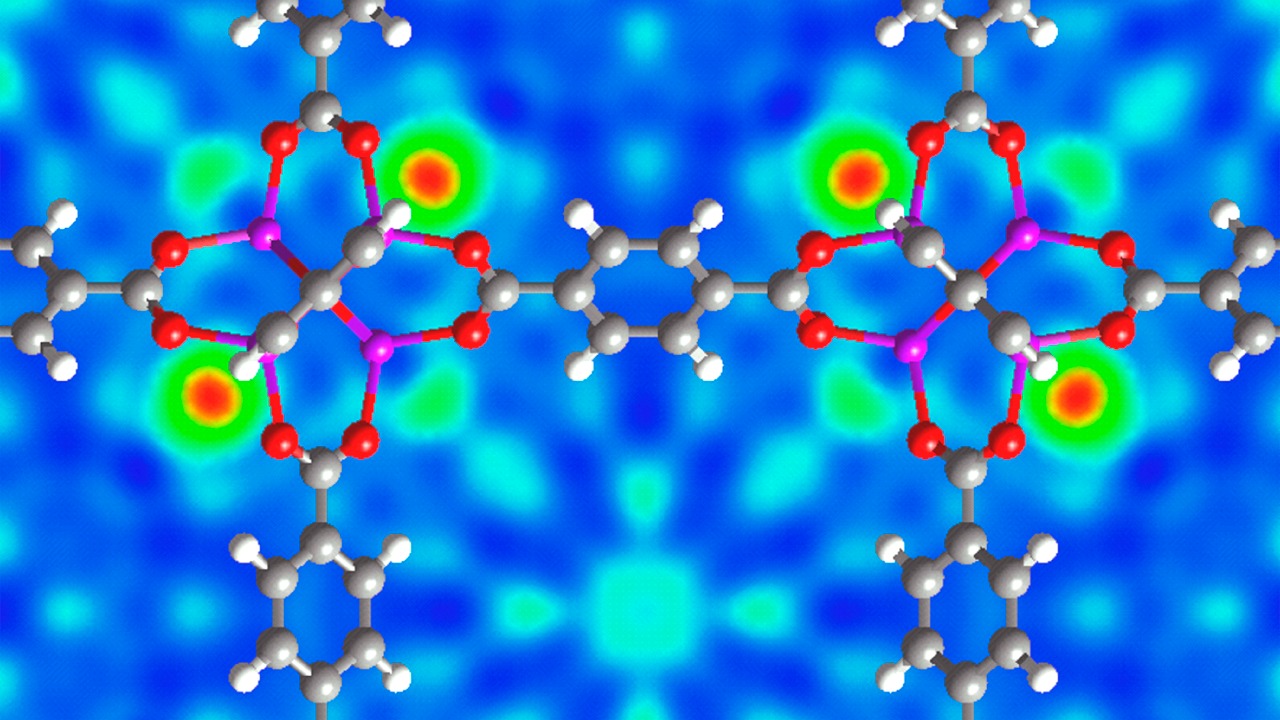
MOF-based Systems
Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) represent a breakthrough in the quest to extract water from the air. These highly porous materials are engineered to capture and hold water molecules from the atmosphere, even in low-humidity environments like deserts. The unique structure of MOFs allows them to trap moisture effectively, making them a cornerstone in the development of atmospheric water generation technologies.
Recent advancements have significantly improved the efficiency of MOFs in water absorption. Researchers are continually refining these frameworks to enhance their capacity and reduce energy consumption. One study demonstrated that MOFs could absorb and release water in a cyclical process, maximizing water yield. These innovations are paving the way for systems that can provide consistent water output in some of the world’s driest areas.
Solar-Powered Water Harvesting
Solar-powered devices are another promising technology for extracting water from desert air. By harnessing sunlight, these devices facilitate the conversion of atmospheric moisture into potable water. This method of water harvesting is particularly advantageous in desert regions, where sunshine is abundant and reliable.
The energy efficiency of solar-powered systems is a significant advantage, allowing them to operate sustainably without the need for external power sources. These systems can be integrated into existing infrastructures, such as solar farms, to provide a dual benefit of energy and water production. The use of renewable energy not only reduces the environmental footprint but also enhances the viability of deploying these technologies in remote desert locations.
Addressing Water Scarcity in Desert Regions

Impact on Local Communities
The introduction of atmospheric water generation technologies has the potential to revolutionize access to clean drinking water in desert regions. These systems can be deployed in remote areas, providing communities with a reliable source of water and reducing their dependence on external supplies. For instance, a community in the Sahara Desert could greatly benefit from solar-powered water harvesters, ensuring a stable and sustainable water supply.
Case studies highlight the transformative impact of these technologies on local populations. In desert regions of the Middle East, for instance, the deployment of MOF-based systems has improved water access for thousands. By reducing the need for extensive water transportation infrastructure, these technologies can significantly lower costs and improve the quality of life for residents in arid regions.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their promise, these technologies face several challenges in desert environments. The harsh climate can affect the durability and performance of water extraction systems. Sandstorms, extreme temperatures, and limited maintenance resources pose significant obstacles to the successful deployment of these technologies.
Cost is another critical factor. The initial investment required for installing and maintaining these systems may be prohibitive for some communities. Moreover, the ongoing need for technology refinement and adaptation to local conditions can further complicate deployment efforts. These challenges underscore the need for strategic partnerships and funding to facilitate widespread adoption.
Scientific Principles Behind Water Production
Understanding Atmospheric Water Vapor
Water vapor is a constant presence in the atmosphere, even in arid regions. The natural cycle of water vapor involves evaporation and condensation processes that occur globally. Technologies that harness atmospheric water vapor capitalize on this cycle by capturing and condensing moisture from the air.
The physics and chemistry behind water vapor extraction are complex but well-understood. By employing materials that absorb moisture effectively, these technologies can condense water from the air and channel it for human use. This process is analogous to natural phenomena, such as dew formation, but optimized through engineering advancements.
Role of Humidity and Temperature
The efficacy of atmospheric water generation systems is closely tied to ambient humidity and temperature. Higher humidity levels generally facilitate greater water collection, while temperature variations can affect the rate of condensation. Despite these variables, recent innovations have enabled these systems to operate effectively even in low-humidity conditions.
These technologies are designed to adapt to different desert climates, optimizing their performance based on local environmental conditions. For instance, a device developed by MIT researchers can extract water even in arid climates with as low as 10% humidity, showcasing the adaptability of modern water harvesting systems. More information about this technology can be found here.
Future Prospects and Innovations

Scaling Up and Commercialization
The potential for scaling these technologies is immense, offering prospects for broader commercial use. Partnerships between researchers, governments, and the private sector are crucial in driving development and deployment. By investing in research and fostering collaboration, stakeholders can accelerate the commercialization of water harvesting technologies.
Efforts are underway to refine these systems for mass production and distribution. With the right support, atmospheric water generators could become a staple in addressing water scarcity across arid regions worldwide. Such developments could significantly impact industries reliant on water, from agriculture to manufacturing, fostering economic growth in previously water-scarce areas.
Integration with Other Sustainable Practices
Integrating water harvesting systems with other renewable technologies can create a holistic approach to sustainability. For example, combining these systems with solar farms or greenhouses could optimize resource use and enhance efficiency.
This integrated approach could transform how desert regions harness natural resources, reducing reliance on traditional water sources and minimizing environmental impact. By aligning with broader sustainability goals, these innovations can contribute to a more resilient and self-sufficient future for communities in arid environments.
Environmental and Economic Implications

Sustainability and Environmental Impact
The environmental implications of deploying water harvesting technologies on a large scale are significant. By reducing the strain on traditional water sources, these systems can alleviate pressure on already stressed ecosystems. Additionally, the use of renewable energy to power these technologies minimizes their carbon footprint.
However, potential ecological risks must be considered. The widespread deployment of these systems could alter local environments, affecting flora and fauna. It is crucial to balance technological advancement with environmental stewardship to ensure sustainable development.
Economic Opportunities
The development and deployment of atmospheric water generation technologies present numerous economic opportunities. By creating new industries and jobs, these innovations can drive economic growth in water-scarce regions. The potential for exporting these technologies to other arid areas further enhances their economic impact.
Moreover, by improving water access, these technologies can support agricultural and industrial activities, boosting local economies. As these systems become more affordable and accessible, their potential to transform economies in arid regions will grow, opening new avenues for prosperity and development.