The recovery of the Earth’s ozone layer, a crucial shield against harmful ultraviolet radiation, was once hailed as a significant environmental success. However, recent studies suggest that this recovery may have an unintended consequence: amplifying global warming by as much as 40%. Understanding the intricate dynamics of this surprising climate twist is essential for shaping future climate strategies.
The Science Behind Ozone Recovery
The ozone layer serves as Earth’s protective shield, absorbing the majority of the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation. This not only prevents damage to living organisms but also plays a vital role in climate regulation. The layer’s presence in the stratosphere influences atmospheric temperatures and circulation patterns, affecting weather and climatic conditions globally. Without it, the risk of skin cancer, cataracts, and other health issues would significantly increase, along with disruptions in ecological systems.
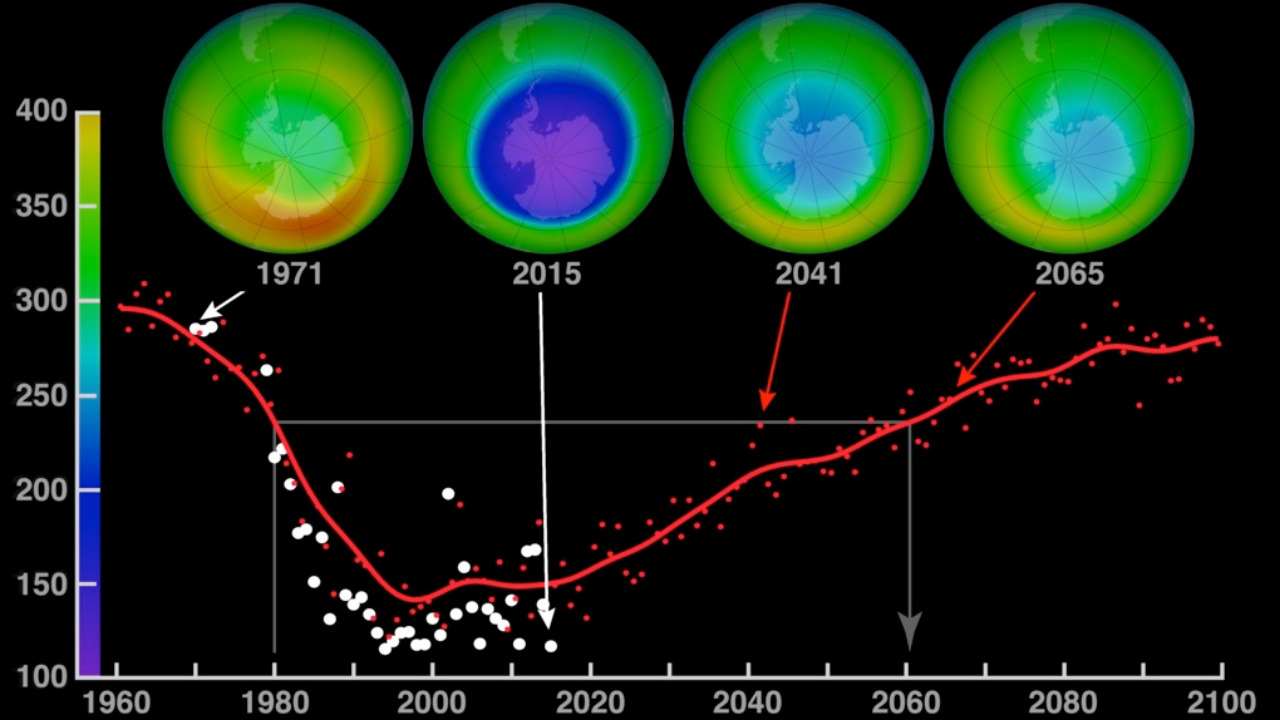
Historically, the ozone layer faced severe depletion due to human activity, primarily from chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) used in refrigeration, air conditioning, and aerosols. The issue gained global attention in the 1980s, leading to the Montreal Protocol in 1987. This international treaty successfully phased out the production of ozone-depleting substances, leading to a gradual recovery of the ozone layer. Scientific efforts and policy measures combined to set this environmental success in motion, highlighting the power of global cooperation.
The recovery process involves complex chemical reactions within the stratosphere. As CFCs were phased out, natural atmospheric processes began to heal the ozone layer. Ultraviolet radiation breaks down ozone molecules, but under normal conditions, they are replenished naturally. The reduction of CFCs has allowed these natural processes to restore the ozone layer’s integrity. However, as this healing continues, scientists are observing unexpected interactions with climate dynamics.
Linking Ozone Recovery and Global Warming
The interplay between ozone recovery and global warming is rooted in atmospheric science. Changes in ozone concentration can significantly impact atmospheric temperatures and circulation patterns. As the ozone layer heals, it alters the distribution of temperature in the stratosphere, which can cascade down to affect weather patterns in the troposphere. This is a critical area of study, as these changes can exacerbate the effects of climate change.
One of the primary concerns is the feedback loops that emerge from these atmospheric interactions. As ozone levels increase, they may enhance the greenhouse effect by trapping more heat in the atmosphere. This process could amplify global warming, creating a feedback loop that accelerates temperature rise. Such feedback mechanisms are complex and require sophisticated models to predict their outcomes accurately.
Recent studies and simulations have offered insights into these potential impacts. Scientists employ advanced models to simulate future climate conditions with varying ozone levels. These models suggest that the recovery of the ozone layer could lead to a substantial increase in global warming rates, potentially up to 40% more than previously estimated. This highlights the importance of considering ozone dynamics in climate projections and strategy development.
The Unexpected Climate Twist

The potential amplification of global warming due to ozone recovery presents an unexpected twist in climate science. Research indicates that as the ozone layer heals, the resulting atmospheric changes could lead to a significant rise in global temperatures. This increase, possibly up to 40%, could have far-reaching consequences for climate patterns worldwide.
Different regions may experience varying impacts due to this amplification. Some areas could see intensified weather events, such as more severe storms or prolonged droughts, while others might experience shifts in climatic zones. For instance, regions that are already vulnerable to climate change could face heightened risks, affecting agriculture, water resources, and overall economic stability.
The implications for international climate policy are profound. As new findings emerge, there may be a need to reassess and update existing strategies to address the dual challenges of ozone recovery and climate change. Policymakers must consider these interactions when designing future environmental policies to ensure they are both effective and comprehensive.
Future Research and Mitigation Strategies

Continued scientific research is crucial to monitor ozone levels and their climatic effects. By gathering data and refining models, researchers can better understand the ongoing dynamics and predict future changes. This information is vital for crafting effective climate policies and mitigation strategies.
Innovative solutions are needed to address the unintended consequences of ozone recovery.
Technological advancements, such as geoengineering or carbon capture, could play a role in mitigating the enhanced greenhouse effect. Additionally, policy measures that promote renewable energy and reduce carbon emissions remain essential components of global climate efforts.
International collaboration is more important than ever. Addressing the complex challenges of ozone recovery and climate change requires a coordinated global response. Countries must work together to share knowledge, resources, and strategies to ensure a sustainable future for all. The path forward involves both scientific innovation and political will.
Public Awareness and Education

Raising public awareness about the complex relationship between ozone recovery and global warming is essential. The media and educational institutions have a key role in disseminating information and fostering understanding among the general public. By being informed, individuals can make conscious choices that contribute to environmental protection.
Encouraging behavioral changes at the individual and community levels can have a positive impact. Simple actions, such as reducing energy consumption, supporting sustainable practices, and advocating for environmental policies, can collectively contribute to mitigating climate impacts. Public engagement is crucial in driving the change needed to address these global challenges.
Engaging stakeholders from various sectors, including policymakers, scientists, and the public, is vital for developing effective environmental strategies. Collaborative discussions and decision-making processes can lead to innovative solutions that address the complexities of ozone recovery and climate change. By working together, we can create a more resilient and sustainable future.