Researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences have made a significant advancement in the development of solid-state batteries by creating a novel electrolyte that enhances their performance. This breakthrough addresses critical challenges in ionic conductivity and stability, potentially accelerating the commercialization of solid-state batteries for electric vehicles. Meanwhile, Honda has committed to deploying solid-state batteries by 2030, aiming to double the electric vehicle range to 620 miles, underscoring the growing momentum in the industry.
The Electrolyte Innovation
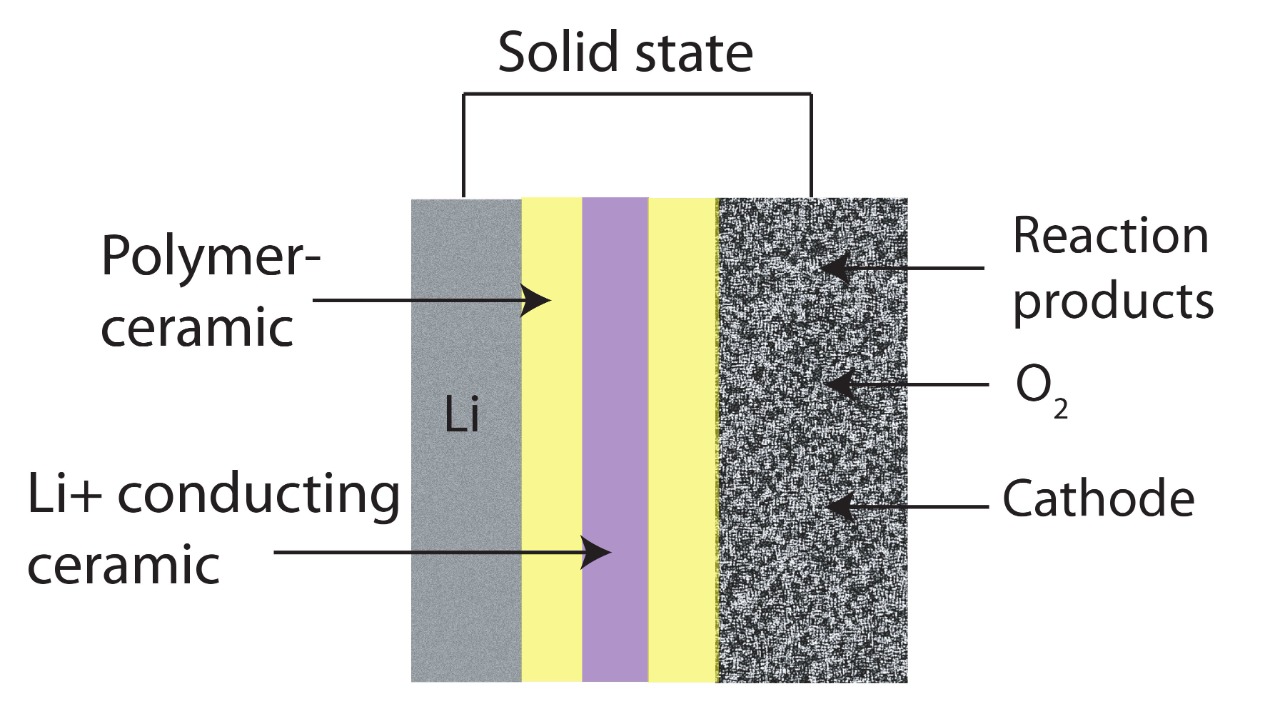
The new electrolyte formulation developed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences significantly improves lithium-ion transport efficiency in solid-state batteries. This advancement reduces internal resistance compared to traditional liquid electrolytes, which is a crucial factor in enhancing battery performance. According to Car News China, this innovation could lead to more efficient energy storage solutions, making electric vehicles more viable for widespread adoption.
Moreover, the material achieves higher energy density while maintaining safety by minimizing dendrite formation during charging cycles. This is a significant improvement over previous technologies, as dendrites can cause short circuits and battery failures. As reported by Interesting Engineering, the ability to maintain safety without sacrificing performance is a critical step forward in battery technology.
Testing has shown that the electrolyte enables batteries to operate at room temperature without compromising cycle life, which is essential for practical applications. This development, highlighted by China Daily, marks a critical milestone in making solid-state batteries a feasible option for everyday use, potentially transforming the electric vehicle market.
Challenges Addressed in Solid-State Technology

Solid-state batteries have historically faced significant challenges, particularly with interfacial stability between the electrolyte and electrodes. The Chinese breakthrough addresses this issue through a proprietary composite structure, as detailed by Interesting Engineering. This innovation could pave the way for more reliable and efficient battery systems, overcoming one of the major hurdles in solid-state technology.
Another challenge is manufacturing scalability, which remains a significant hurdle for the widespread adoption of solid-state batteries. However, the new electrolyte’s compatibility with existing production lines could lower costs and facilitate mass production. According to China Daily, this compatibility could be a game-changer in making solid-state batteries more accessible to manufacturers and consumers alike.
Safety risks associated with liquid electrolytes, such as leakage and flammability, are eliminated in this solid-state approach, enhancing reliability for high-demand uses. This improvement, as noted by Car News China, could significantly increase consumer confidence in electric vehicles, further driving their adoption.
Global Production and Adoption Efforts
In South Korea, researchers are advancing production methods for solid-state batteries, focusing on scalable sintering techniques to integrate advanced electrolytes like the Chinese innovation. As reported by The Cool Down, these efforts are crucial for overcoming production challenges and ensuring that solid-state batteries can be manufactured at scale.
Honda’s roadmap targets 2030 for mass production of solid-state batteries with a 620-mile EV range, leveraging electrolyte improvements to achieve faster charging times under 10 minutes. This ambitious plan, highlighted by Live Science, underscores the potential of solid-state technology to revolutionize the electric vehicle industry.
Collaborative international efforts, including knowledge sharing on electrolyte formulations, are accelerating commercialization timelines across Asia. According to China Daily, these collaborations are essential for overcoming technical and logistical challenges, ensuring that solid-state batteries can be brought to market efficiently and effectively.
Potential Impacts on Electric Vehicles

The electrolyte breakthrough could enable EV batteries with up to 50% higher energy density, directly supporting Honda’s 620-mile range goal by 2030. This increase in energy density, as reported by Live Science, could transform the electric vehicle market by making long-range electric cars more accessible to consumers.
Reduced battery weight from solid-state designs would improve vehicle efficiency and extend range without increasing size. This advantage, highlighted by Interesting Engineering, could lead to more efficient electric vehicles, reducing the overall environmental impact of transportation.
Widespread adoption might lower EV prices by 20-30% through longer-lasting batteries that require fewer replacements over a vehicle’s lifespan. According to Car News China, this cost reduction could make electric vehicles more affordable for a broader range of consumers, further accelerating the shift towards sustainable transportation.