Recent groundbreaking research into ape genomes has uncovered mysterious non-human DNA structures that challenge our traditional understanding of genetics. This discovery not only reshapes our knowledge of ape evolution but also raises questions about the complexity and variability of genetic sequences across species.
The Discovery of Non-Human DNA Structures
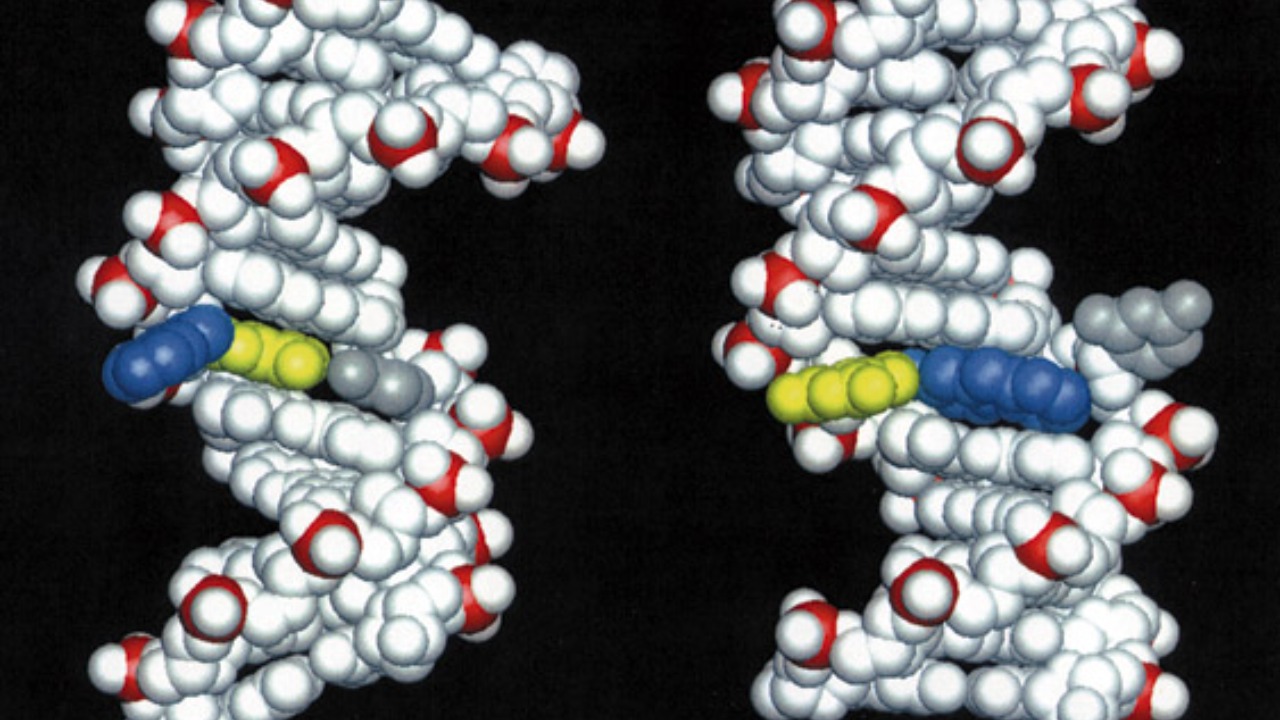
In a series of innovative studies, researchers have delved into the genetic makeup of various ape species, revealing unexpected DNA structures that differ significantly from those typically found in humans. By employing cutting-edge sequencing technologies and advanced bioinformatics tools, scientists have identified several non-standard DNA configurations within the ape genome. These findings, detailed in a study published in Genome Biology, highlight the complexity and diversity of genetic material beyond what was previously understood.
Among the most intriguing discoveries are the unusual DNA configurations such as quadruplexes and other complex forms. Quadruplex DNA structures, which consist of four strands rather than the usual two, have been observed in key areas of the ape genome. These structures, as outlined in recent reports, may play a crucial role in regulating gene expression and maintaining genomic stability. The identification of these configurations challenges the conventional view of DNA as merely a double helix and opens new avenues for understanding the diverse mechanisms of genetic regulation.
The implications of these findings for genetic research are profound. Unraveling the functions and impacts of these novel DNA structures could significantly advance our knowledge of genetic and evolutionary biology. Such insights may lead to a deeper understanding of how genetic diversity arises and is maintained within populations. As scientists continue to explore these non-standard DNA forms, the potential for new discoveries in the field of genetics seems boundless, paving the way for future breakthroughs.
Evolutionary Significance of Ape Genome Variations
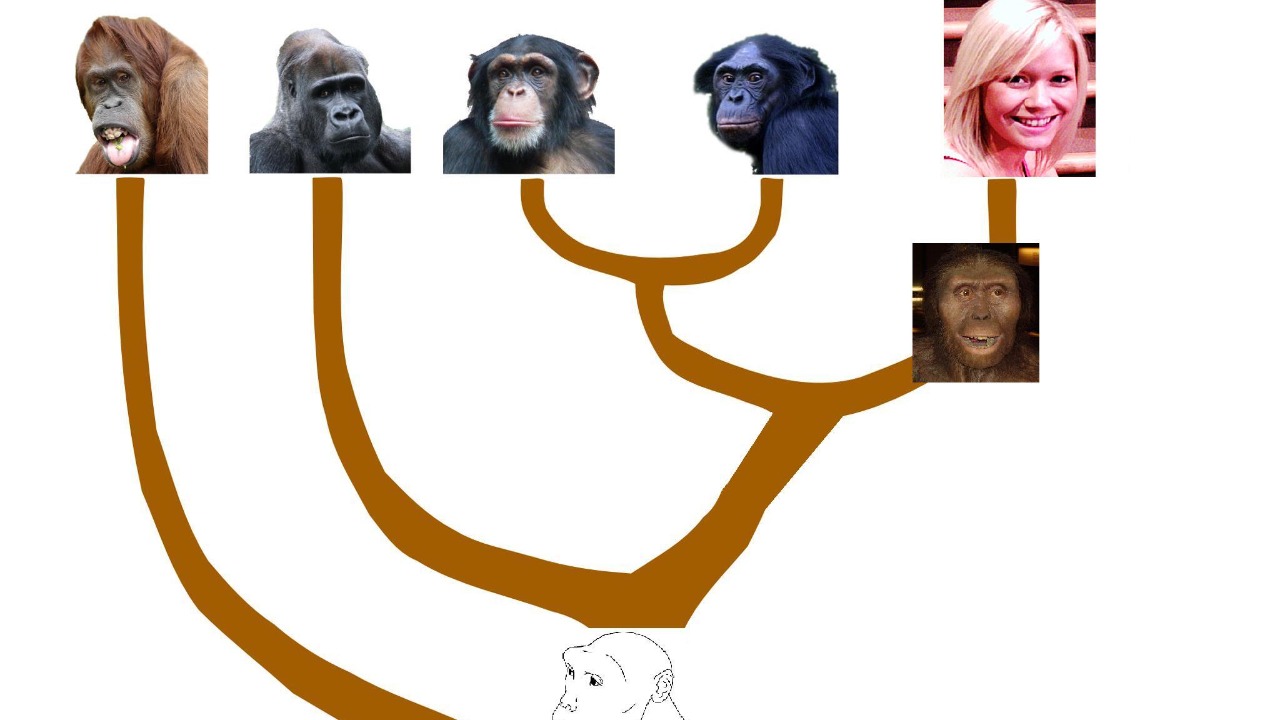

Comparative genomics has long been a valuable tool for understanding evolutionary relationships and differences among species. By comparing the newly discovered DNA structures in ape genomes to those in humans, researchers are gaining insights into the evolutionary paths that have shaped our lineage. Significant differences between human and ape genomes suggest that these unique DNA configurations may have provided adaptive advantages in certain environments.
The presence of quadruplex DNA structures and other variations could be a key factor in the evolutionary success of apes. These structures might enhance genetic flexibility, allowing apes to adapt more readily to changing environmental conditions. For instance, certain DNA configurations might facilitate rapid responses to new dietary resources or climatic shifts, providing a survival edge over other species. The possibility that these genetic features have played a role in shaping ape behavior and physical traits is a tantalizing area of study.
Moreover, the new genetic evidence necessitates a reevaluation of phylogenetic trees, which map the evolutionary relationships between species. The novel DNA structures identified in ape genomes could prompt a reassessment of the evolutionary links between apes and other primates. As outlined in a recent publication in Nucleic Acids Research, the integration of this new genetic data could refine our understanding of primate evolution and help clarify the origins of various species.
Potential Applications and Future Research

The discovery of non-human DNA structures in ape genomes holds significant promise for medical and biotechnological applications. Understanding these unique genetic features could lead to innovative approaches in medicine, particularly in the fields of gene therapy and personalized medicine. By studying how these DNA structures influence gene expression and stability, researchers may develop novel strategies for treating genetic disorders.
However, the manipulation and replication of these complex DNA configurations present challenges in genetic engineering. Scientists must consider the technical and ethical implications of editing or replicating these structures in laboratory settings. Addressing these challenges requires a nuanced understanding of the underlying genetics and the potential consequences of altering natural DNA forms.
Future directions in genome research could focus on exploring the functional roles of these novel DNA structures and their contributions to genetic diversity. As researchers continue to investigate the complexities of ape genomes, there is potential for groundbreaking discoveries that could reshape our understanding of DNA and its role in evolution. The integration of these findings into broader genomic studies may yield insights into the intricate mechanisms of life.
Ethical Considerations and Broader Implications
The manipulation and study of ape genomes raise important ethical questions that must be carefully considered. As researchers push the boundaries of genetic science, it is crucial to address the moral implications of such work. Issues surrounding the potential exploitation of genetic resources and the welfare of ape populations require thoughtful deliberation.
Conservation and biodiversity efforts could also be influenced by these findings. The insights gained from studying non-human DNA structures may inform strategies for protecting endangered ape species and preserving genetic diversity. Understanding the genetic makeup of apes could provide valuable information for conservation programs aimed at maintaining healthy populations in the wild and captivity.
On a broader scale, these discoveries have the potential to impact our understanding of human origins. By shedding light on the genetic similarities and differences between humans and apes, researchers can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex evolutionary processes that have shaped our species. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the ape genome, we are reminded of the interconnectedness of all life and the shared genetic heritage that binds us together.