The exploration of Mars by NASA’s rovers has led to the discovery of a variety of unusual Martian rocks, each with its own unique characteristics and potential implications for the history and habitability of the Red Planet. These discoveries have not only expanded our understanding of Mars but also raised new questions about the planet’s geology and potential for life.
Unusual Martian Spheres
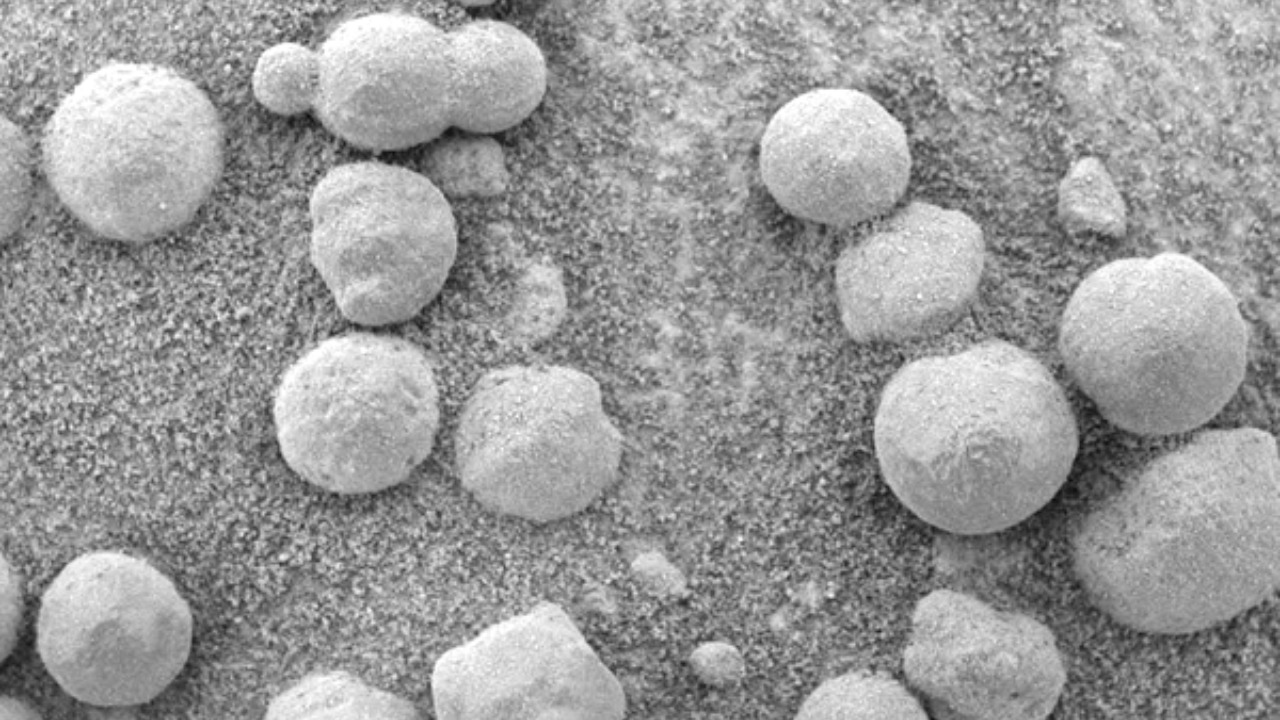
NASA scientists were left astonished by the discovery of spherical formations on Mars. These formations, discovered by the Mars rover, presented an intriguing mystery for researchers to unravel. The spheres, which were found in large numbers, were unlike anything previously seen on the Martian surface. The discovery of these unusual Martian spheres was reported by Newsweek.The unusual Martian spheres, often referred to as Martian blueberries due to their shape and size, have been a subject of intense study. According to Newsweek, these spheres are believed to have formed in wet conditions, suggesting that Mars may have once had a much wetter climate. The spheres are rich in hematite, a mineral that typically forms in water, further supporting this theory. However, the exact process of their formation remains a mystery, with theories ranging from volcanic activity to microbial life.
Surprise in a Martian Rock

NASA’s Curiosity rover made an unexpected discovery in a specific Martian rock sample. The details of this discovery, while not disclosed, have added another layer to the complex puzzle of Mars’ geological history. This surprising find, as reported by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, underscores the ongoing importance of Mars exploration.
The surprise found in a Martian rock by NASA’s Curiosity rover has added a new dimension to our understanding of Mars. According to the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the rock sample contained an unexpected mineral composition that suggests a complex geological history. The discovery has prompted scientists to reevaluate previous theories about Mars’ past and consider new possibilities, such as the potential for seismic activity on the planet.
Potential Biosignatures in Martian Mudstones
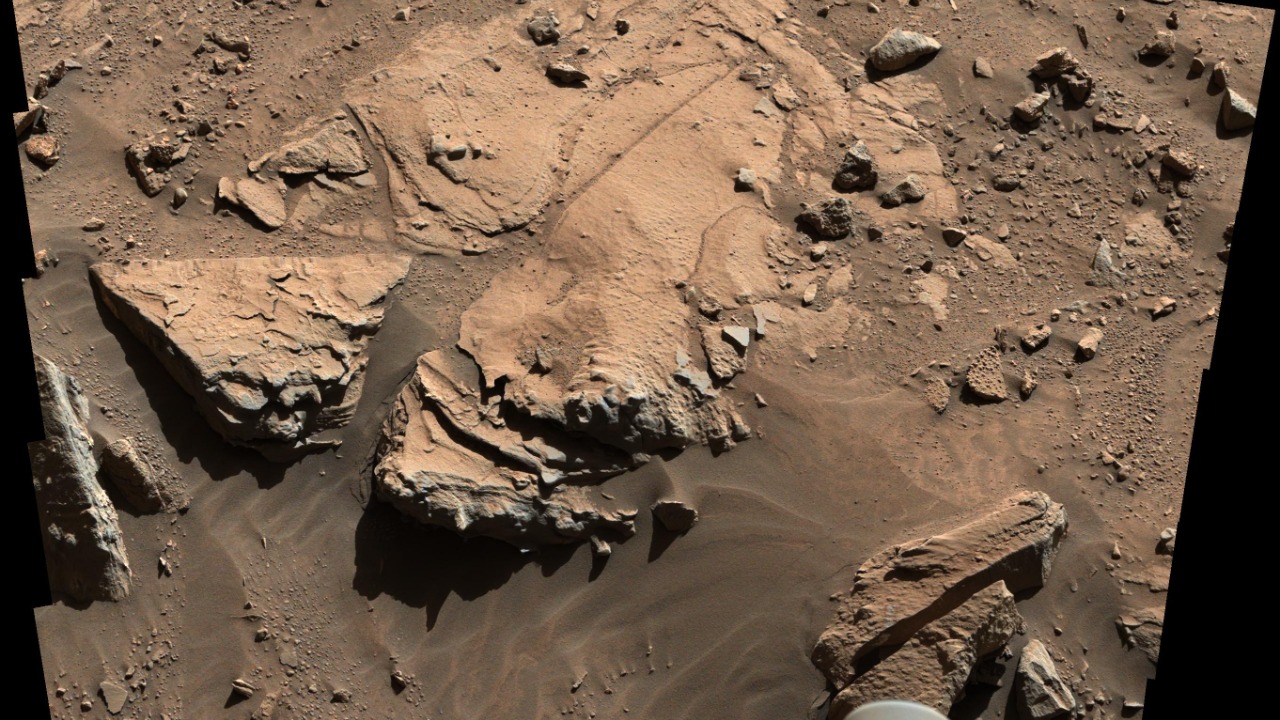

NASA’s exploration of Mars has also led to the discovery of potential biosignatures within mudstone formations. These biosignatures, if confirmed, could indicate the presence of ancient life on Mars, a possibility that has long intrigued scientists. This groundbreaking finding was reported by ScienceDaily.The potential biosignatures discovered in Martian mudstones represent a significant step forward in the search for life on Mars. As reported by ScienceDaily, these biosignatures, which are chemical or physical structures that could have been created by life, were found in rocks that are billions of years old. If confirmed, these biosignatures could provide evidence of ancient microbial life on Mars, fundamentally changing our understanding of the potential for life in our solar system.
Corals on Mars Rocks
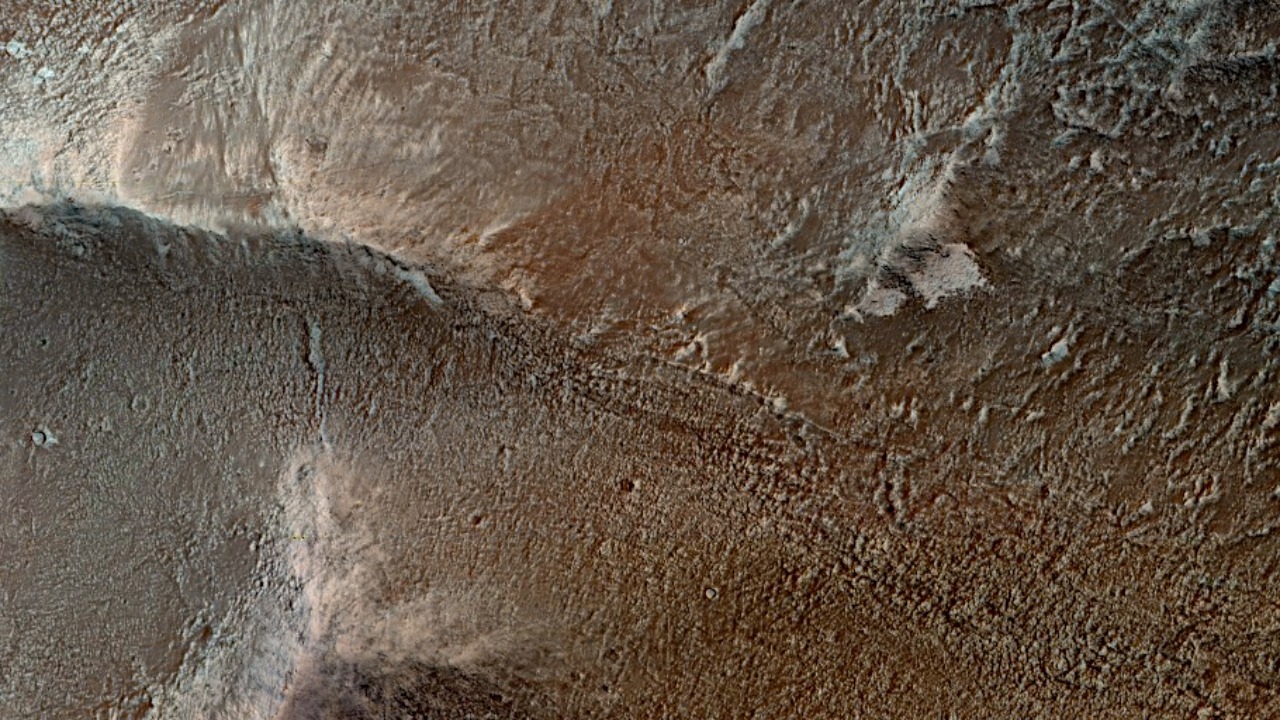

Another intriguing discovery made by NASA’s rovers involves rock structures on Mars that bear a striking resemblance to earthly corals. This discovery, as reported by EarthSky, has sparked speculation about the potential for past or present life on Mars.
The discovery of coral-like structures on Mars has added a new layer of complexity to our understanding of the Red Planet. As reported by EarthSky, these structures, which resemble the corals found in Earth’s oceans, suggest a history of liquid water on Mars. The structures are believed to have formed in a wet environment, further supporting the theory that Mars once had a much wetter climate. However, the exact process of their formation and their potential implications for life on Mars remain subjects of ongoing research.
Remarkably Weird Rocks
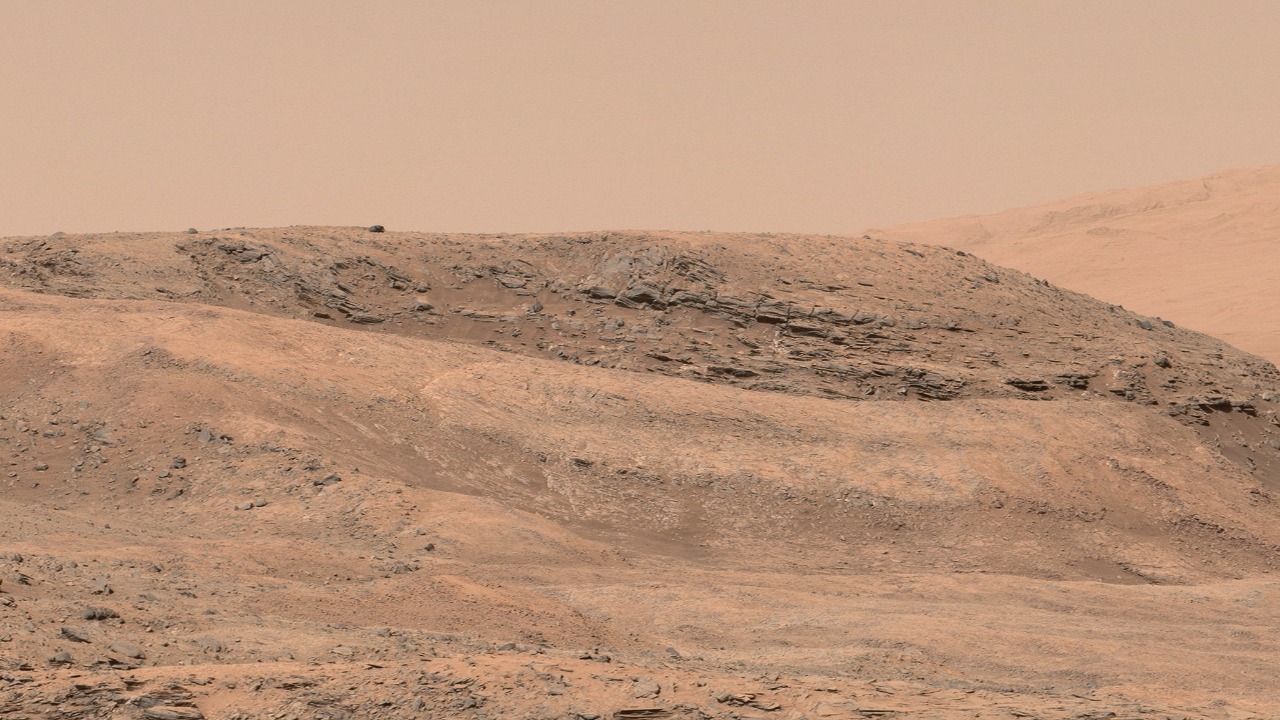

In addition to the coral-like structures, NASA’s rovers have encountered a variety of other bizarre rock formations on Mars. These formations, each with its own unique shape and composition, add to the diversity and complexity of the Martian landscape. These remarkably weird rocks, as reported by EarthSky, continue to captivate scientists and the public alike.
The variety of bizarre rock formations discovered on Mars by NASA’s rovers continues to fascinate scientists. According to EarthSky, these formations range from smooth, spherical rocks to jagged, irregularly shaped structures. Each formation provides a unique window into Mars’ geological history, revealing information about the planet’s past climate, volcanic activity, and potential for water. These discoveries underscore the diversity and complexity of the Martian landscape, and continue to fuel our curiosity about the Red Planet.
General Unusual Martian Rocks Compilation
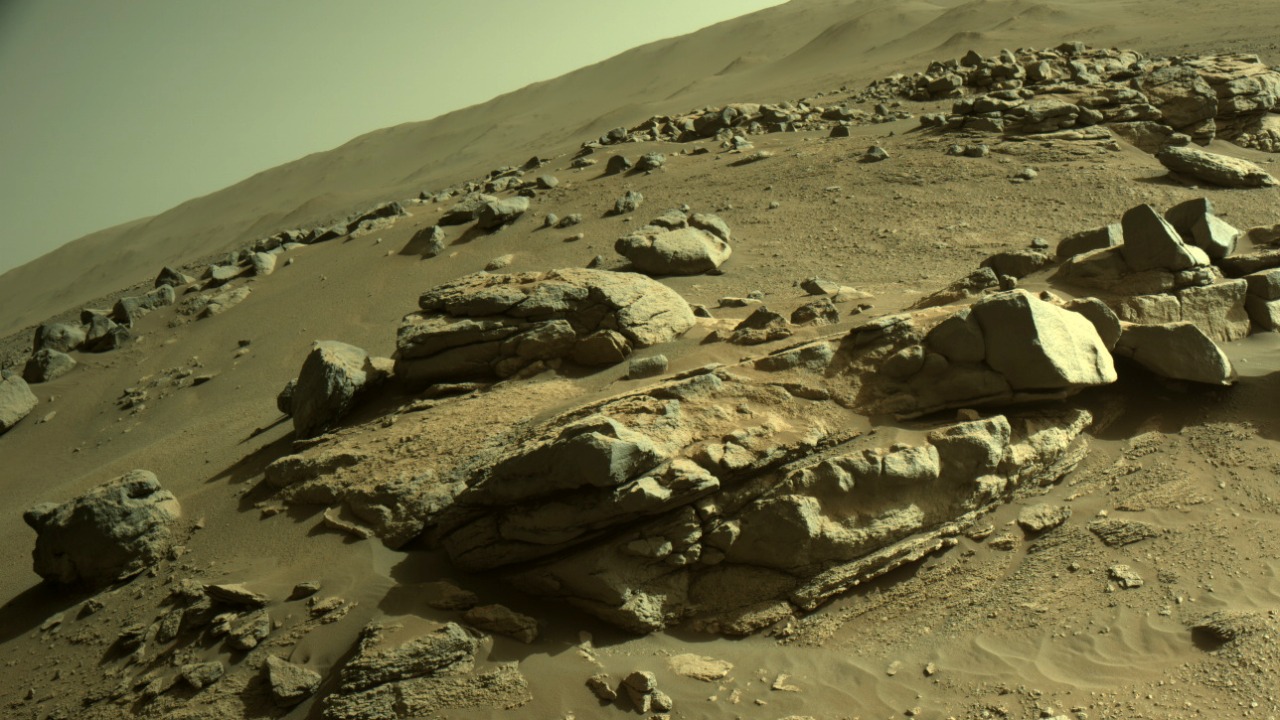

These five distinct unusual rocks represent just a fraction of the broader discoveries made by NASA on Mars. Each rock, with its own unique characteristics and potential implications, contributes to our growing understanding of the Red Planet. The compilation of these discoveries, as reported by India.com, underscores the importance of ongoing Mars exploration.
The compilation of unusual Martian rocks discovered by NASA represents a broad spectrum of Martian geology. As reported by India.com, these rocks range from spherical formations to coral-like structures, each with its own unique characteristics and potential implications. The discoveries have not only expanded our understanding of Mars’ geological history but also raised new questions about the planet’s past climate and potential for life. The ongoing exploration of Mars continues to yield fascinating insights, underscoring the importance of continued research and discovery.