NASA’s latest discovery has reignited the age-old question of whether we are alone in the universe. With the identification of a potential ancient alien haven within our solar system, scientists are delving deeper into the mysteries of extraterrestrial life. This breakthrough not only challenges our understanding of life beyond Earth but also opens new frontiers for exploration and study.
The Discovery: A New Frontier
NASA’s recent missions have unveiled a potential alien haven that could hold clues to ancient extraterrestrial life. Data from these missions, such as the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and the Cassini-Huygens mission, have provided substantial evidence pointing to unusual geological formations and chemical signatures. These findings suggest that certain celestial bodies, particularly some of the moons orbiting our gas giants, might have once harbored conditions suitable for life. The combination of icy crusts, subsurface oceans, and organic molecules presents a tantalizing prospect for researchers.
The role of advanced technology cannot be overstated in this discovery. Instruments like the Hubble Space Telescope and the James Webb Space Telescope have enabled scientists to peer deeper into the cosmos than ever before. Spectrometers and high-resolution imaging devices have been pivotal in identifying the unique characteristics of these potential havens. The use of autonomous rovers and landers has also allowed for in-situ analysis, providing a wealth of data to researchers back on Earth.
Initial reactions from the scientific community have been a mix of excitement and cautious optimism. Leading researchers, such as those from the SETI Institute, have expressed their enthusiasm about the implications of the discovery. Dr. Jill Tarter, a prominent astronomer, remarked on the significance of these findings, stating that they could redefine our understanding of life’s potential spread across the universe. The global scientific community is abuzz with discussions on how best to explore these sites further.
The Significance of the Haven
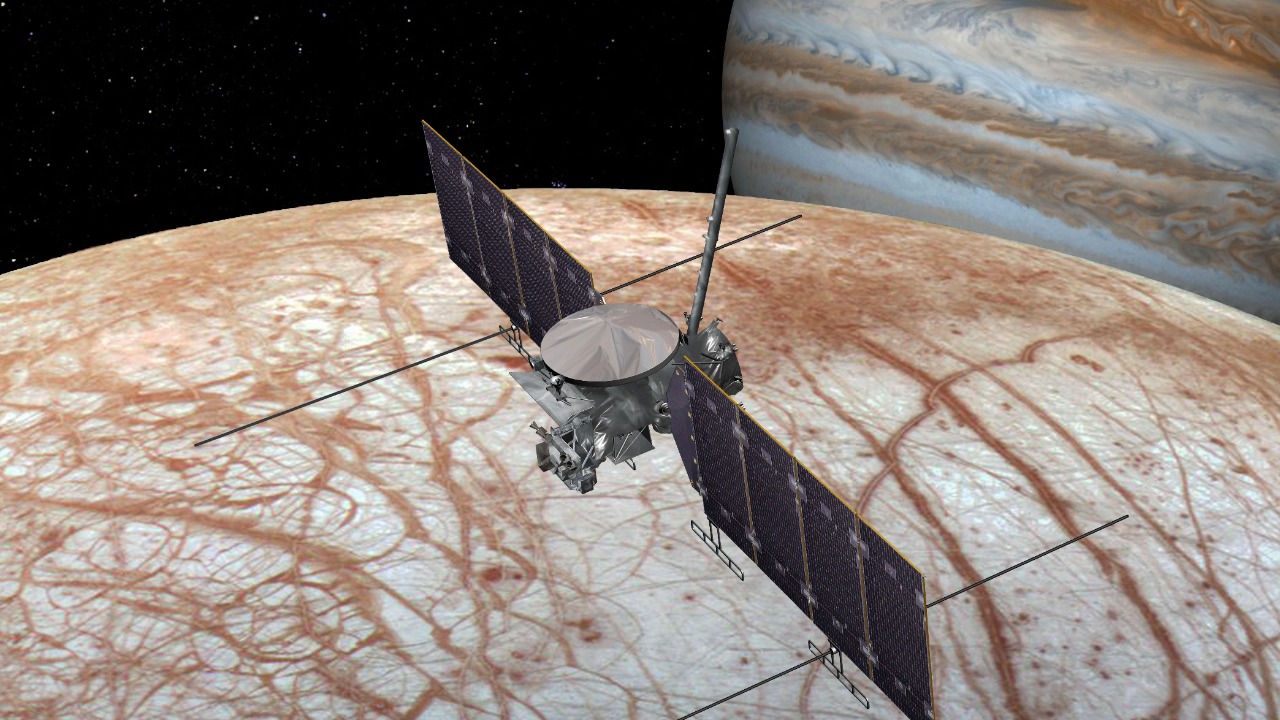

The characteristics of the identified site are compelling. The presence of water ice, coupled with geothermal activity beneath the surface, suggests that these environments could have supported life forms in the past. Additionally, the detection of organic compounds—considered the building blocks of life—adds to the intrigue. These features are reminiscent of environments on Earth where life thrives despite harsh conditions, such as hydrothermal vents in the deep ocean.
Historically, discoveries related to extraterrestrial life have often been met with skepticism. However, this current discovery, highlighted by NASA and corroborated by independent studies, echoes previous findings, like the potential microbial life detected on Mars. Such discoveries have incrementally built a case for the possibility of life beyond Earth. The implications of this new potential haven are profound, as it may guide the design and objectives of future missions, focusing on in-depth exploration and sample collection.
Future research could be significantly shaped by this discovery. Missions like the Europa Clipper, set to launch in the next few years, are already aimed at exploring the icy moons of Jupiter. This discovery could refine their objectives, prioritizing areas with the highest potential for uncovering signs of past life. Collaborative efforts with other international space agencies may also see a renewed focus on these promising sites.
Understanding Extraterrestrial Life

Extraterrestrial life is defined as life that originates outside of Earth. Various scientific theories propose different scenarios for its existence, ranging from microbial organisms to more complex life forms. The Drake Equation, for instance, attempts to estimate the number of civilizations in our galaxy with which humans could communicate. While no definitive evidence of intelligent extraterrestrial life has been found, the possibility continues to intrigue scientists and the public alike.
Past discoveries have significantly shaped our understanding of life beyond Earth. In 1996, the announcement of possible microbial fossils in a Martian meteorite sparked a global debate. Although later contested, it emphasized the importance of continued exploration. Similarly, the discovery of extremophiles—organisms that thrive in extreme conditions on Earth—has broadened our perspective on where life could potentially exist elsewhere.
Studying alien life presents numerous challenges. The vast distances involved in space travel require significant advancements in propulsion technology. Additionally, the harsh environments of other planets and moons necessitate robust and versatile tools for exploration. The scientific and technological hurdles are indeed formidable but not insurmountable, as ongoing innovations continue to push the boundaries of what is possible.
The Search for Life Beyond Earth

NASA’s ongoing missions are at the forefront of the search for extraterrestrial life. Projects such as the Mars 2020 mission, which includes the Perseverance rover, are designed to search for signs of ancient life and collect samples for potential return to Earth. Future missions, like the planned exploration of Saturn’s moon Enceladus, aim to probe its subsurface ocean, believed to be one of the most promising locations for life in the solar system.
Collaboration with international space agencies is crucial in this endeavor. The European Space Agency, Roscosmos, and other partners have joined forces in ambitious projects like the ExoMars program, which aims to explore Mars’ surface and atmosphere. Such partnerships enhance the scientific community’s ability to conduct more complex missions, sharing expertise, resources, and data for mutual benefit.
The role of private companies in space exploration is increasingly significant. Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin are developing technologies that could make space travel more affordable and accessible. Their involvement accelerates the search for extraterrestrial life by providing the means for more frequent and cost-effective missions. The synergy between public and private sectors is proving to be a catalyst for innovation in space exploration.
Public Fascination and Cultural Impact

The discovery of a potential ancient alien haven is likely to have a profound impact on popular culture’s portrayal of alien life. Movies, books, and media narratives often draw inspiration from real-world scientific discoveries. This breakthrough could influence upcoming sci-fi productions, bringing a renewed sense of realism and excitement to the portrayal of extraterrestrial environments and life forms.
Public engagement and interest in space exploration are at an all-time high. Discoveries such as this captivate the public imagination, as evidenced by the buzz on social media platforms like X (formerly Twitter), where discussions about alien life are both widespread and enthusiastic. The allure of the unknown and the potential for groundbreaking discoveries keep people worldwide invested in the progress of space exploration.
Educational opportunities abound in the wake of such significant findings. Schools and universities can leverage this discovery to inspire the next generation of scientists and explorers. By integrating these topics into curricula and fostering a sense of curiosity and wonder, educators can motivate students to pursue careers in STEM fields, ensuring that the quest for knowledge and exploration continues well into the future.
