NASA has recently detected metallic fragments entering Earth’s atmosphere, sparking intrigue and concern among scientists and the public alike. These fragments, originating from space debris, meteoroids, or man-made objects, pose potential risks and hold significant scientific interest. Understanding the nature of these fragments, their origins, and the implications for our planet is crucial for both scientific advancement and public safety.
The Nature of Metallic Fragments

Metallic fragments entering Earth’s atmosphere can be broadly categorized into two types: natural meteoroids and man-made space debris. Meteoroids are small rocky or metallic bodies traveling through space, which become meteors when they enter Earth’s atmosphere. In contrast, space debris consists of defunct satellites, spent rocket stages, and other fragments from human activities in space. These objects vary in size and composition, but all pose potential risks when they re-enter the atmosphere.
NASA and other space agencies employ advanced technologies to detect and track these fragments. Radar systems, telescopes, and satellite networks are used to monitor the skies for incoming objects. These tools allow scientists to predict the trajectory and potential impact sites of larger fragments, providing crucial data for risk assessment and mitigation strategies. The ability to track these fragments has improved significantly with advancements in technology, enabling more accurate predictions and timely warnings.
The potential impacts of metallic fragments on Earth are varied. While most small fragments burn up upon entering the atmosphere, larger pieces can reach the surface, posing risks to both people and property. Environmental concerns also arise from the chemical and physical changes these fragments can cause in the atmosphere. Understanding these impacts is essential for developing effective strategies to manage and mitigate the risks associated with falling space debris.
Origins of Metallic Fragments
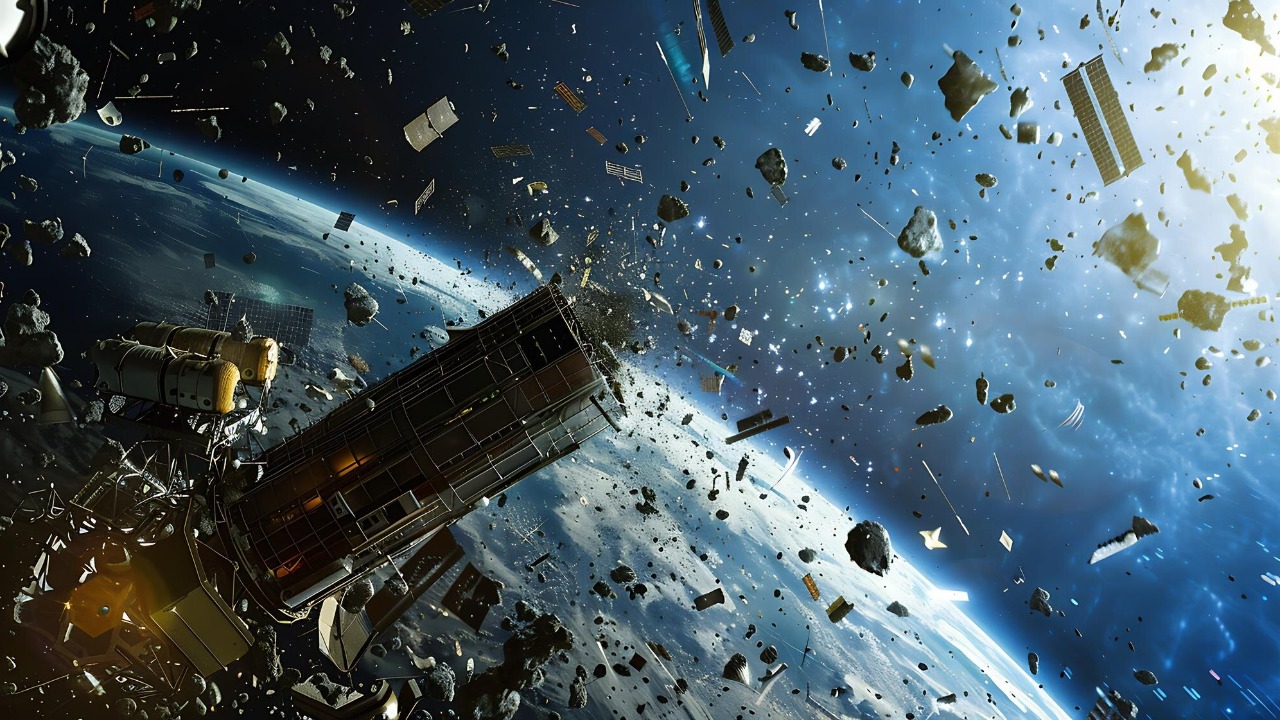

The growing problem of space debris is a significant contributor to the metallic fragments entering Earth’s atmosphere. As the number of satellites and other objects in orbit increases, so does the amount of debris. Recent incidents, such as the investigation into fallen space debris in Kenya, highlight the challenges posed by this issue (source).
In addition to man-made debris, naturally occurring space rocks, or meteoroids, also contribute to the influx of metallic fragments. These objects, often originating from asteroids or comets, differ from man-made debris in their composition and behavior. NASA’s tracking of near-Earth objects (NEOs), such as Asteroid 2024 YR4, is crucial for understanding and predicting the behavior of these natural fragments (source).
Human activities, such as satellite re-entry, also play a significant role in contributing to atmospheric metallic fragments. As satellites reach the end of their operational life, they often re-enter the atmosphere, creating debris that can pose environmental and safety risks. The environmental impact of satellite re-entry, including atmospheric pollution, has been identified as a potential future environmental problem (source).
Technological and Scientific Implications

Recent advancements in detection technology have significantly improved our ability to track and analyze metallic fragments. Enhanced radar systems, improved satellite tracking, and sophisticated computer models allow scientists to monitor space debris and meteoroids with greater accuracy. These technological advancements not only aid in risk assessment but also open up new opportunities for scientific research.
Studying metallic fragments provides valuable insights into the composition of celestial bodies and the history of our solar system. By analyzing the chemical and physical properties of these fragments, scientists can gain a better understanding of the processes that shaped our cosmic neighborhood. This research can also inform the development of new materials and technologies for space exploration.
International collaboration and data sharing are crucial for effectively monitoring and managing space debris. By working together, space agencies can pool resources and expertise to improve detection capabilities and develop coordinated strategies for debris mitigation. This cooperation is essential for ensuring the long-term sustainability of space activities and protecting our planet from the risks posed by falling debris.
Environmental and Safety Concerns

The environmental impact of metallic fragments burning up in the atmosphere is a growing concern. Studies on satellite re-entry have highlighted the potential for atmospheric pollution, which can have far-reaching effects on climate and air quality. Understanding these impacts is essential for developing effective strategies to minimize environmental harm.
Risk assessment and management are critical components of addressing the challenges posed by space debris. By predicting the trajectories and potential impact sites of falling fragments, scientists can develop strategies to mitigate risks to people and property. This includes improving public communication and education to address fears and misconceptions about space debris.
Public awareness and education play a vital role in addressing the challenges posed by space debris. By informing the public about the risks and realities of space debris, scientists and policymakers can foster a better understanding of the issue and promote informed decision-making. This is essential for building public support for policies and initiatives aimed at reducing and managing space debris.
Future Outlook and Challenges
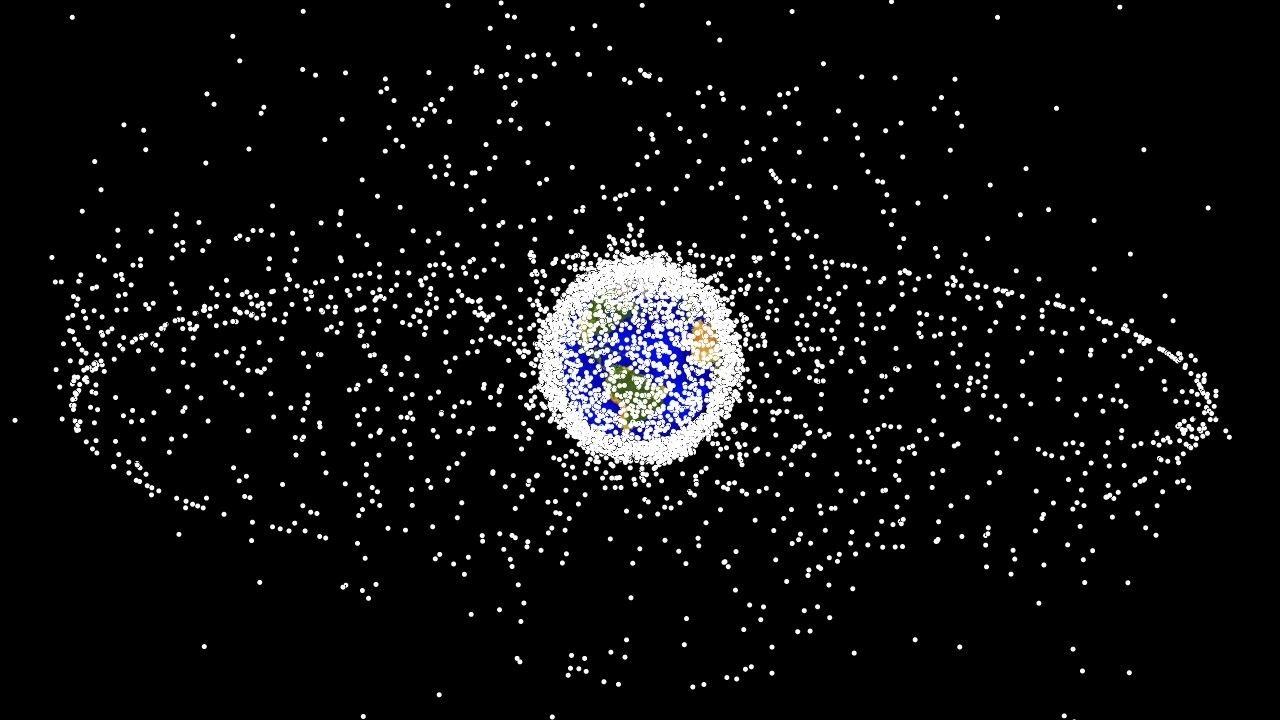
Current international policies governing space debris are often insufficient to address the growing challenges posed by metallic fragments. There is a need for more stringent regulations and enforcement mechanisms to ensure the responsible use of space and the protection of our planet. This includes developing guidelines for satellite design, launch, and disposal to minimize the creation of new debris.
Efforts to create a sustainable space environment are underway, with initiatives aimed at reducing and managing debris. These efforts include the development of technologies for debris removal and the implementation of best practices for satellite operations. By prioritizing sustainability, space agencies can help ensure the long-term viability of space activities.
Innovations in space technology are crucial for addressing the challenges posed by space debris and metallic fragments. New technologies, such as advanced propulsion systems and autonomous debris removal vehicles, offer promising solutions for reducing the risks associated with falling debris. By investing in these innovations, space agencies can help protect our planet and ensure the continued exploration and utilization of space.