A recent analysis of moon dust has unveiled fascinating insights into the secrets of our solar system. By examining these extraterrestrial particles, scientists have gained a deeper understanding of the Sun’s history and its influence on planetary bodies. These groundbreaking findings hold significant implications for the future of space exploration.
Understanding Moon Dust
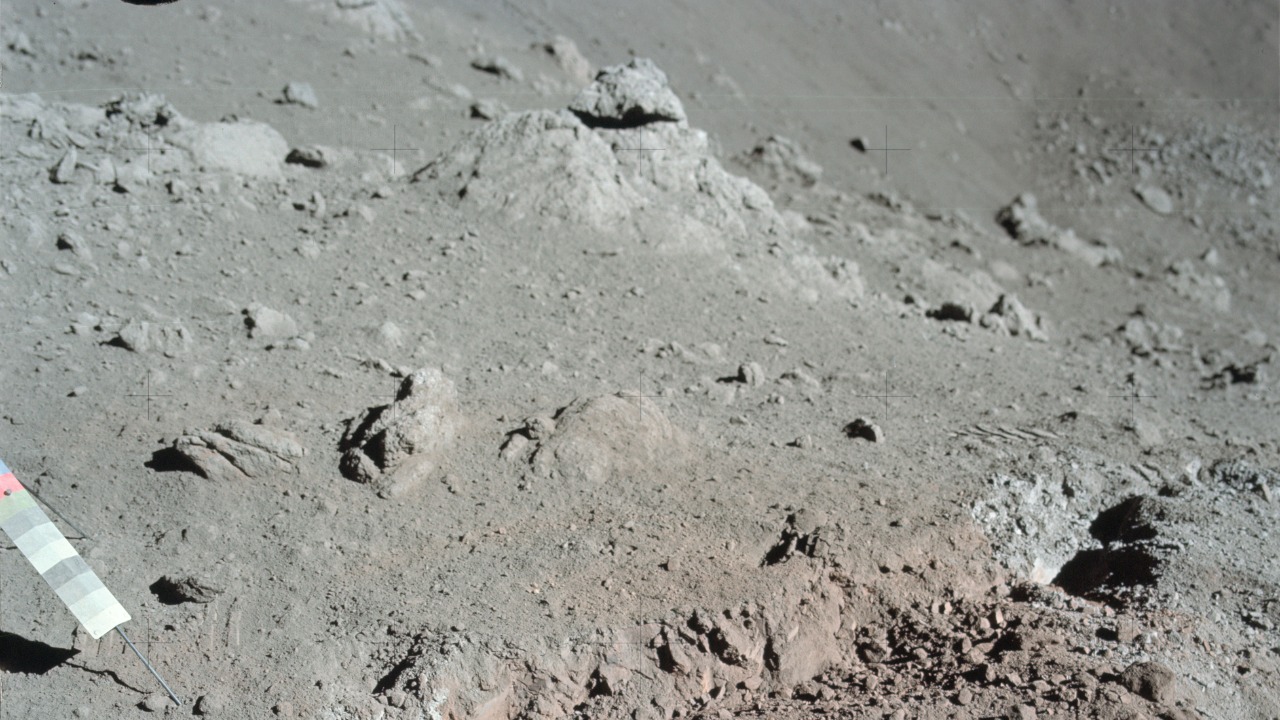

Composition and Origin of Lunar Dust
The study of lunar dust began in earnest with the Apollo missions, which were pivotal in collecting samples from the moon’s surface. These missions provided scientists with the first substantial quantities of extraterrestrial material to analyze. Lunar dust, known scientifically as regolith, is primarily composed of tiny fragments of rock and mineral particles. The fundamental components found in lunar dust include silicates, iron, and magnesium, each playing a unique role in the dust’s overall characteristics.
Unlike Earth’s soil, lunar dust has unique physical and chemical properties that make it an area of interest for scientists. It is highly abrasive and adheres to surfaces due to its electrostatic charge. The regolith’s composition is largely influenced by micrometeorite impacts and the solar wind, which continuously bombard the moon’s surface. This has resulted in a mineralogical makeup distinct from that of terrestrial soil, offering a unique opportunity to study geological processes in a low-atmosphere environment.
The Sun-Moon Connection
How Solar Wind Affects Lunar Surface
The interaction between the solar wind and the moon’s surface is a dynamic process that alters the properties of lunar dust. As charged solar particles collide with the moon, they become embedded within the regolith, leading to changes in its chemical composition. This process is crucial in understanding the long-term effects of solar radiation on lunar soil. Over time, the continuous bombardment of solar particles modifies the lunar surface, providing researchers with a historical record of solar activity.
One of the most intriguing aspects of moon dust is its ability to trap solar particles. These particles serve as a record of historical solar activity, offering insights into past solar cycles. By analyzing these trapped particles, scientists can reconstruct the Sun’s activity over millions of years, shedding light on the cyclical nature of solar phenomena and its potential impact on planetary environments.
Scientific Techniques for Analyzing Moon Dust

Advanced Spectroscopy Methods
Modern technology has revolutionized the way scientists study lunar samples. Advanced spectroscopy methods allow for the detailed analysis of moon dust, enabling researchers to identify its elemental and isotopic composition with unprecedented precision. These techniques are crucial for uncovering the solar secrets hidden within the lunar regolith. The use of sophisticated instruments, such as mass spectrometers, has been instrumental in revealing the presence of solar wind particles embedded in the dust.
Comparative analysis with meteorite samples further enriches our understanding of extraterrestrial materials. By examining both lunar and meteorite samples, scientists can identify similarities and differences in their compositions, providing a broader perspective on the processes that shape celestial bodies. Insights gained from asteroid research are particularly valuable, as they can be applied to lunar studies, enhancing our understanding of the solar system’s formation and evolution.
Implications for Space Exploration

Planning Future Lunar Missions
As new findings from moon dust analysis continue to emerge, they have a profound impact on the planning of future lunar missions. The insights gained from these studies help shape mission objectives, focusing on areas of scientific interest that promise the greatest potential for discovery. Developing technology for better sample collection is a priority, ensuring that future missions can gather high-quality materials for analysis. These advancements are crucial for maximizing the scientific return from lunar exploration.
The broader implications for solar system research are equally significant. Understanding the Sun’s influence on other celestial bodies can lead to the discovery of new planetary phenomena. By studying the interactions between solar activity and lunar surface materials, researchers can gain valuable insights into the processes that govern our solar system. This knowledge has the potential to inform our understanding of other planets and their moons, paving the way for future explorations beyond the moon.
Potential for Future Discoveries
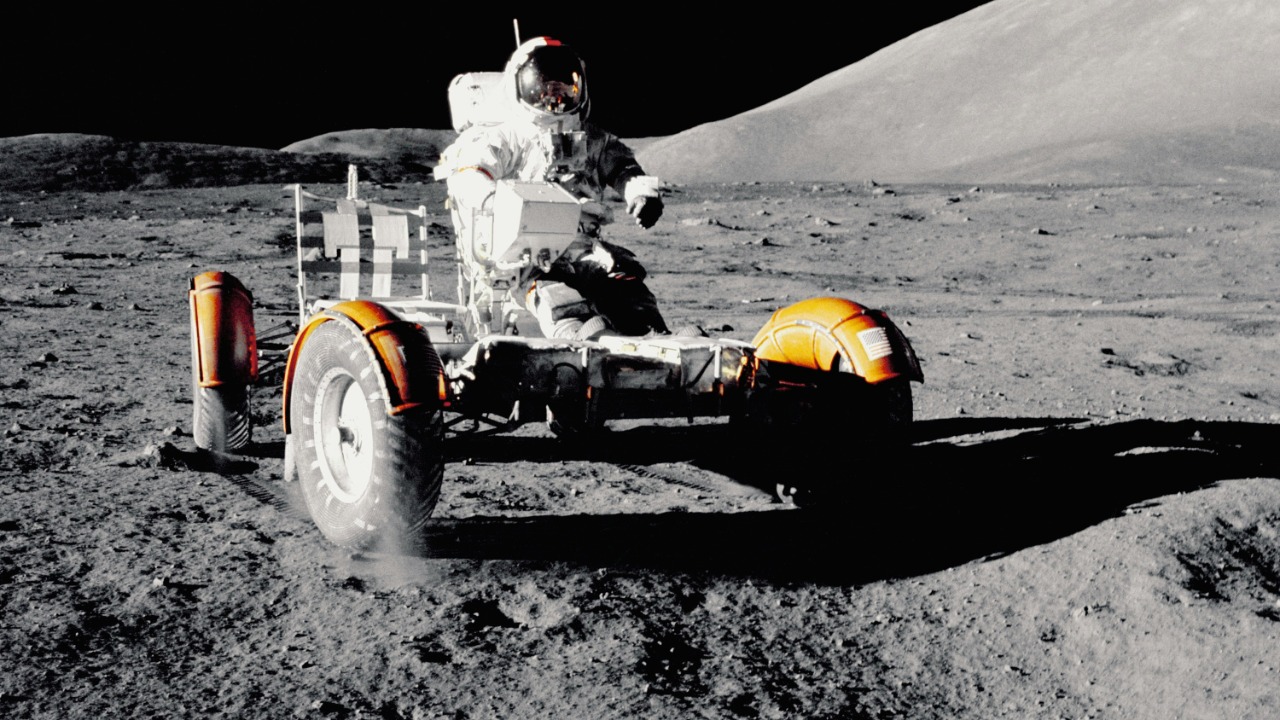

Unanswered Questions and Ongoing Research
Despite the progress made in understanding moon dust and its implications, there remain many unanswered questions and areas where more data is needed. Ongoing research is essential to fully grasp the complexities of lunar regolith and its interactions with solar particles. The continuous exploration of the moon is crucial for gathering the data necessary to address these questions, ensuring that our understanding of lunar science continues to evolve.
International collaboration plays a vital role in advancing lunar science. The sharing of knowledge and resources among global partners enhances the scope and impact of lunar research. By working together, countries can pool their expertise and technology to tackle the challenges of lunar exploration, fostering a spirit of cooperation that benefits the scientific community as a whole. As we look to the future, these partnerships will be instrumental in unlocking the full potential of moon dust analysis and the secrets it holds about our solar system.