NASA’s Perseverance rover has made a significant discovery on Mars, identifying a leopard-spotted rock that could potentially hold signs of ancient microbial life. This finding is described as the strongest evidence yet of potential ancient life, providing the most compelling hints to date.
The Perseverance Rover’s Mission on Mars

Actively exploring the Martian surface, NASA’s Perseverance rover is on a mission to find signs of ancient life. The rover’s findings have been intriguing, with one of the most notable being a rock spotted in an area potentially named Sapphire Canyon. This discovery contributes to the ongoing search for microbial evidence on Mars. Since its landing, Perseverance has been operational and making significant discoveries, with the latest findings announced around September 10, 2025.
Perseverance’s mission, aptly named Mars 2020, is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the red planet. The primary goal of the Mars 2020 mission is to investigate astrobiologically relevant ancient environments on Mars, and to investigate the surface geological processes and history, including the assessment of its past habitability and potential for preservation of biosignatures within accessible geological materials. The rover is equipped with a suite of scientific instruments that allow it to analyze the Martian environment and send back data to Earth for further analysis. The rover’s findings, including the leopard-spotted rock, are significant steps in achieving the mission’s goals.
Perseverance’s landing site, Jezero Crater, was chosen after extensive study by planetary scientists. It is believed that the 28-mile-wide crater once contained a lake, and within it, life may have existed. The rover’s exploration of this area, including the discovery of the leopard-spotted rock, is part of the mission’s larger goal of understanding Mars’ geological history and the planet’s potential for having hosted life.
Discovery of the Leopard-Spotted Rock

The Perseverance rover has spotted a rock on Mars that features leopard-like spots, which may indicate signs of ancient microbial life. This rock was identified as a potential carrier of ancient life evidence during the rover’s operations on Mars. The discovery was made in a Martian location tied to geological features suggestive of past habitability, further strengthening the possibility of the rock holding signs of ancient life.
The leopard-spotted rock was discovered during Perseverance’s exploration of a region of Mars known as Sapphire Canyon. This area is of particular interest to scientists due to its unique geological features, which suggest it may have once been habitable. The rock was spotted by the rover’s Mastcam-Z, a pair of zoomable cameras that can capture color images and video. The cameras allow the rover to document the Martian landscape and its geological features in detail, leading to the discovery of the leopard-spotted rock.
The rock’s unique appearance immediately caught the attention of the rover’s science team. The spots on the rock are unlike anything previously observed on Mars, leading scientists to hypothesize that they could be signs of ancient microbial life. The discovery of the rock and its subsequent analysis is a testament to the rover’s capabilities and the effectiveness of its mission strategy.
Key Features of the Rock Suggesting Life
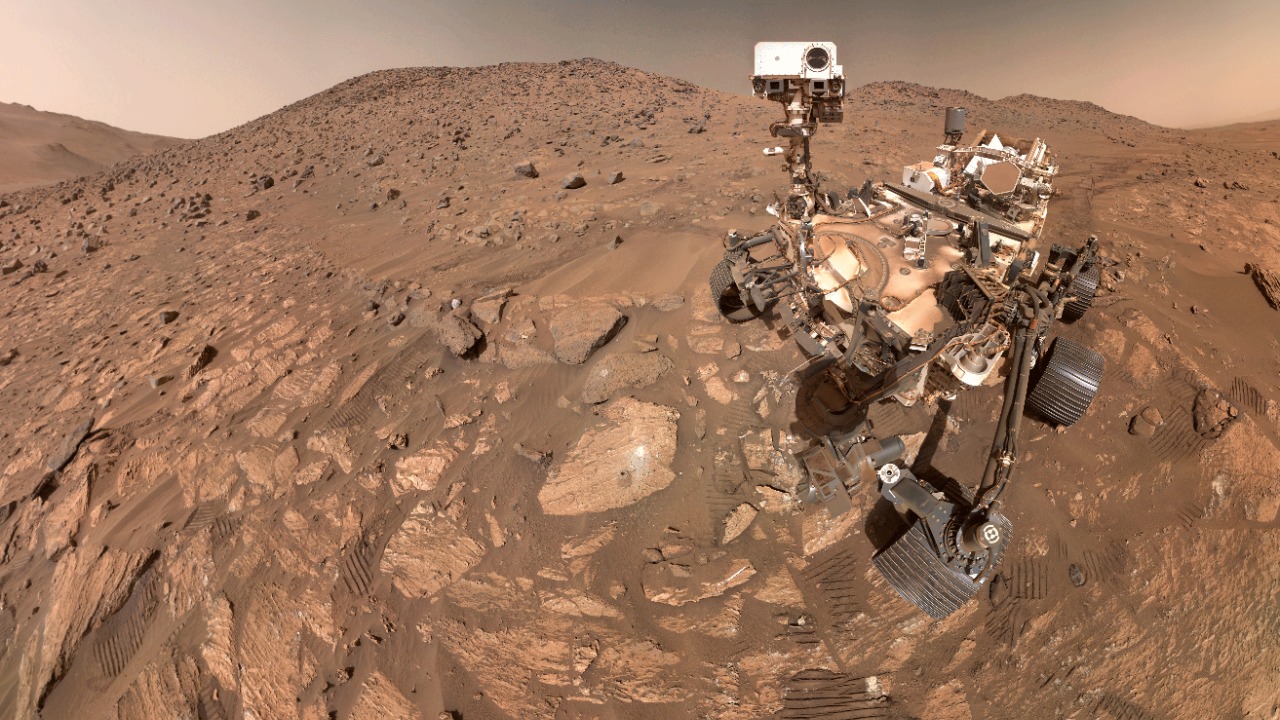

The leopard-spotted appearance of the rock is highlighted as a possible indicator of microbial activity from ancient times. Further analysis shows that the rock may contain the strongest signs of life on Mars yet, based on its unique spotting and composition. NASA’s evaluation points to this rock as providing hints of potential ancient life through its preserved structures, making it a significant find in the search for life on Mars.
The leopard-spotted rock’s unique appearance is not its only intriguing feature. The rock’s composition also suggests that it may have been formed in an environment that was once habitable. The rock is believed to be sedimentary in nature, which means it could have formed in the presence of water. On Earth, similar rocks often contain fossils and other signs of past life. The leopard spots on the rock could be mineral deposits left behind by ancient microbes, similar to stromatolites on Earth.
Further, the rock’s location in Sapphire Canyon, an area believed to have once contained water, adds to the possibility that it could hold signs of past life. The combination of the rock’s unique appearance, its composition, and its location all point to it being a potential treasure trove of information about Mars’ past.
Scientific Analysis and Evidence Strength
New findings by the NASA Mars rover offer the strongest hints yet of potential signs of ancient life in the spotted rock. The evidence is described as the strongest yet for ancient life on Mars, surpassing previous rover observations. Scientists have identified this as potentially the strongest sign of ancient life discovered to date, pending further confirmation.
The leopard-spotted rock is currently the subject of intense study by the Perseverance science team. Using the rover’s suite of instruments, scientists are able to analyze the rock’s composition and structure in detail. The rover’s SuperCam instrument, for example, can identify the chemical and mineral makeup of the rock from a distance, providing valuable data about its formation and history. The rock’s leopard spots are of particular interest, as they could be mineral deposits left behind by ancient microbes.
While the evidence is promising, scientists caution that further analysis is needed to confirm the presence of biosignatures. The rock samples will be collected and stored by the rover for potential future return to Earth, where they can be analyzed in more detail using advanced laboratory techniques. This will allow scientists to confirm whether the leopard spots are indeed signs of ancient life, or if they were formed by other geological processes.
Implications for Mars Exploration
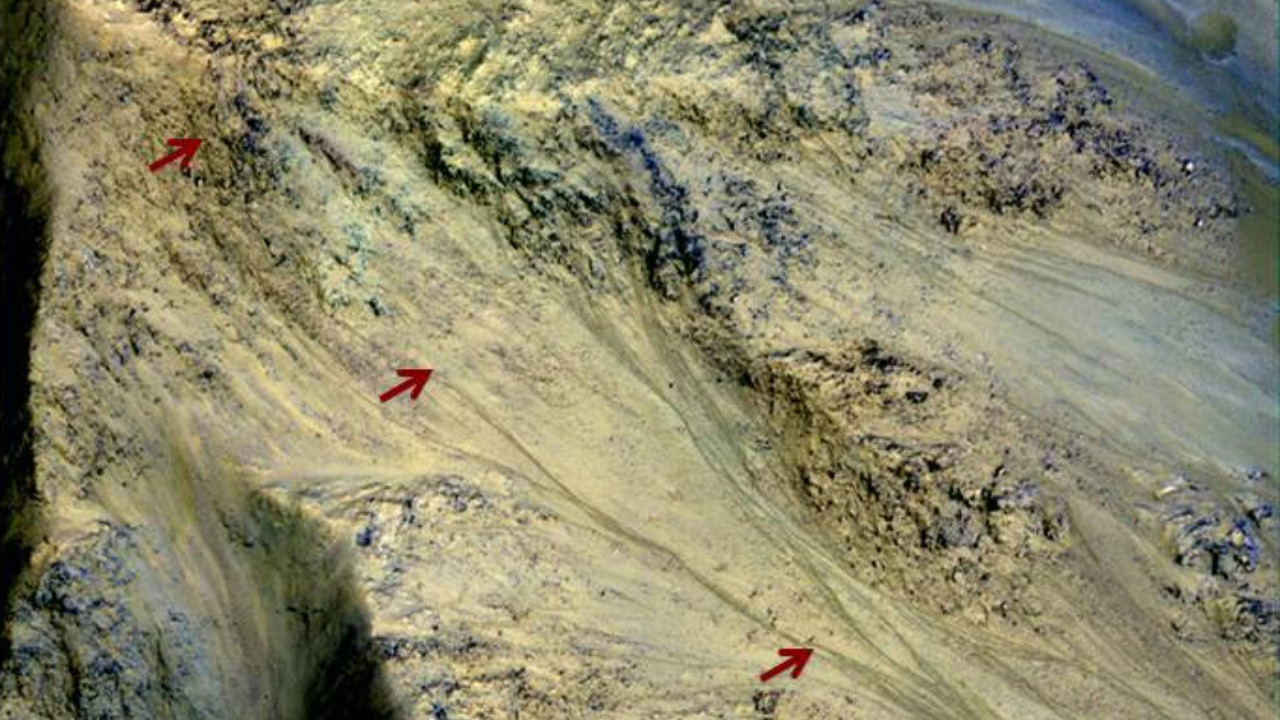

The discovery of the leopard-spotted rock reinforces NASA’s focus on searching for signs of microbial life in Martian geology. This finding, reported in late September 2025, could reshape our understanding of Mars’ ancient habitability. As part of ongoing rover missions, there are plans to collect samples from similar rocks for Earth-based analysis, which could provide even more insights into the possibility of life on Mars.
The discovery of the leopard-spotted rock has significant implications for future Mars exploration. If confirmed to contain signs of ancient life, it would provide strong evidence that Mars was once habitable, reshaping our understanding of the red planet’s history. This would also guide future mission planning, as scientists would likely focus on similar environments in their search for life.
Furthermore, the discovery underscores the importance of robotic exploration in our quest to understand Mars. The Perseverance rover’s ability to explore the Martian surface, analyze geological samples, and store them for future return to Earth is a testament to the value of these missions. Future missions, including potential human exploration of Mars, will build on these findings, furthering our understanding of the red planet and its potential for life.
Broader Context of Life on Mars
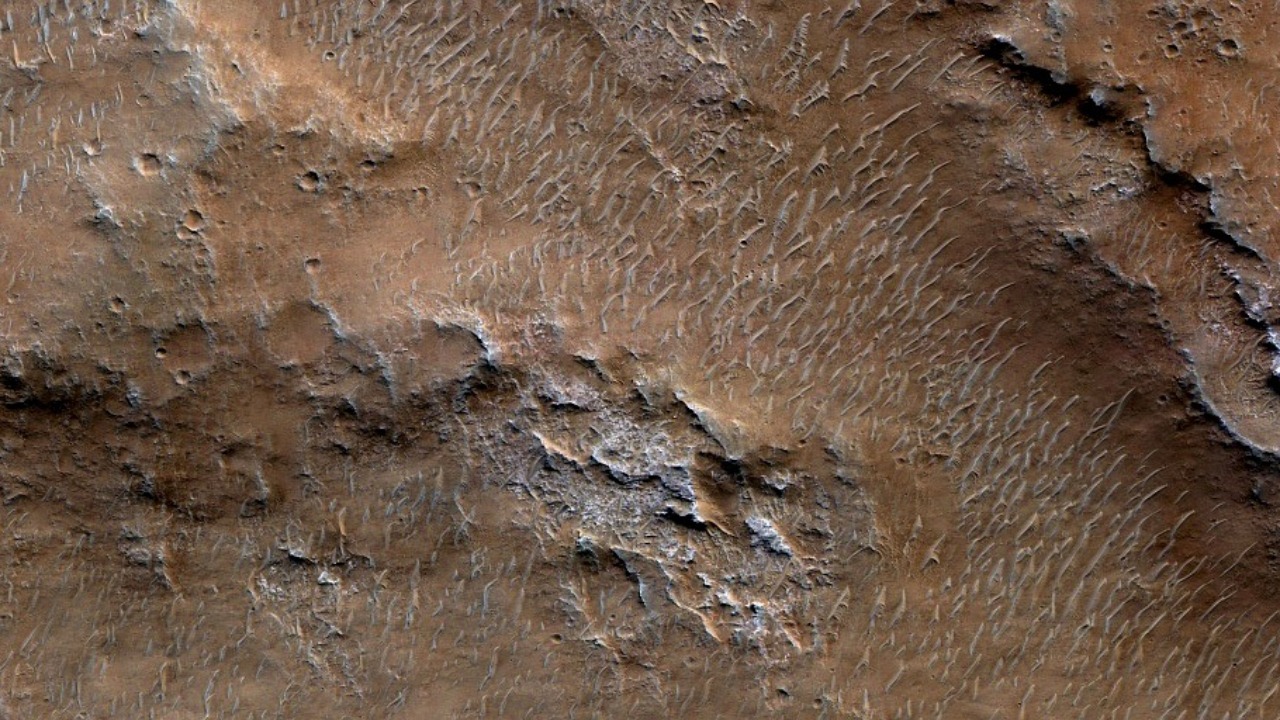

The rock discovered by the Perseverance rover provides what scientists call the strongest signs of life on Mars yet, building on the findings of prior missions. NASA’s rover has found evidence that may confirm ancient life, with the spotted rock serving as a pivotal example. This development, covered in reports from September 10 to October 1, 2025, highlights the accelerating progress in the field of astrobiology.
As we continue to explore Mars and other planets, these discoveries bring us one step closer to answering the age-old question: Are we alone in the universe?
Sources: BGR, Interesting Engineering, CBC, AP News, Science Daily