China’s Tiangong Space Station has officially entered a new era, marking a significant milestone in the nation’s space exploration journey. With ambitious plans and groundbreaking advancements, it is set to redefine the landscape of international space collaboration and competition. This new phase of Tiangong’s development is not just about technological prowess, but also about influencing and reshaping global dynamics in space exploration.
The Evolution of China’s Tiangong Space Station
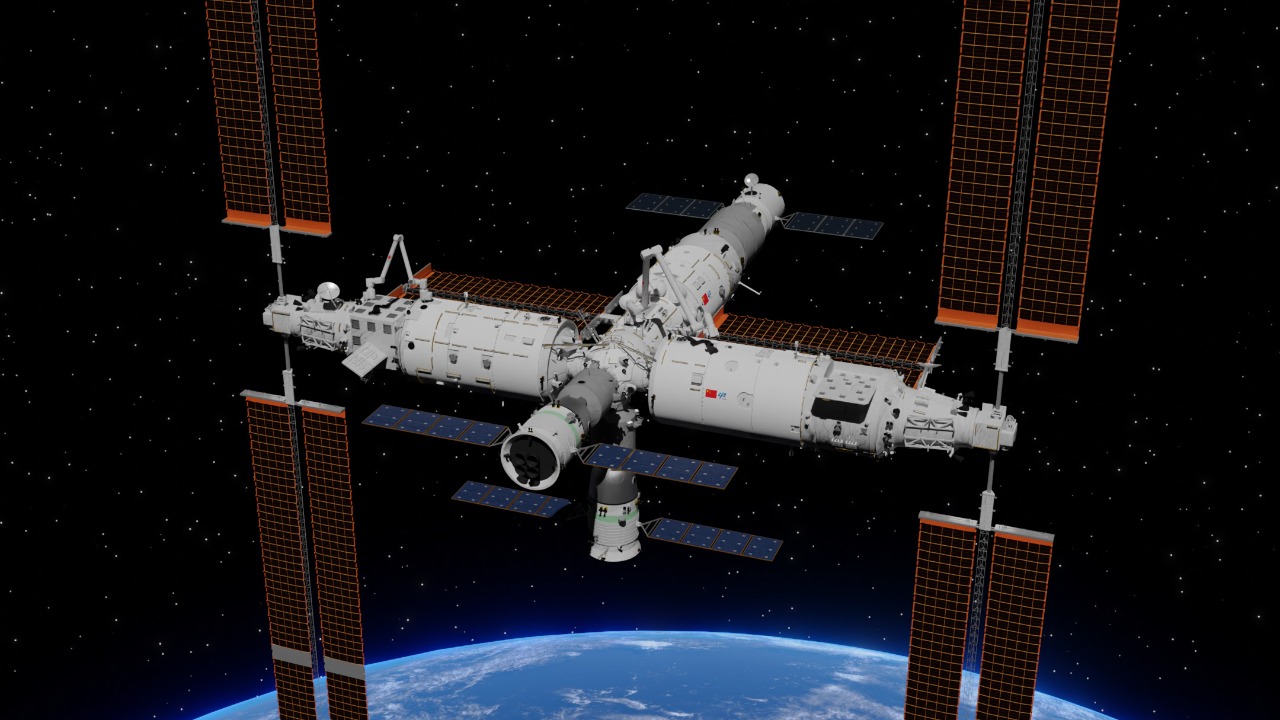

The Tiangong Space Station represents China’s audacious leap into the realm of advanced space exploration. Since its inception, Tiangong has evolved through several notable phases, with each phase marking a significant technological and strategic milestone. From Tiangong-1, the prototype module launched in 2011, to the current operational Tiangong station, China has demonstrated its ability to develop and deploy complex space structures independently. The successful launch of the core module Tianhe in 2021 laid the groundwork for the station’s current structure, incorporating cutting-edge technology to support long-term human habitation.
Technological advancements have been at the core of Tiangong’s development. The station integrates advanced life-support systems, autonomous docking technology, and robust communication systems. China’s use of automated cargo spacecraft like the Tianzhou series showcases its innovative approach to maintaining and supplying the station. These advancements not only enhance the station’s operational capabilities but also position China as a leader in space technology. Strategically, Tiangong is central to China’s long-term goals in space, including the establishment of a permanent human presence and the expansion of its influence in global space dynamics.
International Collaborations and Rivalries
Tiangong has become a focal point for international collaboration in space. China has opened its space station to scientists from across the globe, fostering a spirit of cooperation. Countries like Russia and Italy have already engaged in joint projects, conducting experiments aboard the station. This collaborative approach not only enhances scientific research but also strengthens diplomatic ties with participating nations. However, Tiangong’s rise also brings competitive aspects to the forefront, particularly in its competition with the International Space Station (ISS). While the ISS has been a symbol of international cooperation for decades, Tiangong offers an alternative platform for countries seeking to engage in space activities without the political constraints associated with the ISS.
The geopolitical impact of Tiangong cannot be underestimated. It serves as a tool for China to exert its influence in the realm of space diplomacy. By opening its station to international partners, China is not only building alliances but also challenging the status quo dominated by the US and its allies. This shift in dynamics has implications for global space policy, as countries reassess their alliances and partnerships in the face of China’s growing space capabilities.
Scientific Research and Discoveries
Tiangong offers unique opportunities for scientific research, enabling experiments that are not feasible on Earth. The microgravity environment of the space station allows for groundbreaking research in fields such as materials science, biology, and physics. Researchers have already conducted numerous experiments, investigating topics ranging from fluid dynamics to the effects of space radiation on biological organisms. These studies not only advance scientific understanding but also contribute to the development of technologies for future space missions.
The station has already yielded significant breakthroughs and discoveries. For instance, experiments on Tiangong have led to new insights into protein crystal growth, which has potential applications in drug development. The future research potential of Tiangong is immense, with plans to expand its scientific capabilities and host a broader range of international projects. As more countries collaborate on research aboard the station, the potential impact on various fields of study grows, promising advancements that could benefit humanity as a whole.
Public Access and Transparency

In a bid to enhance transparency and public engagement, China has made efforts to provide rare insights into Tiangong. Recent video releases have offered the public a glimpse inside the station, showcasing the living and working conditions of astronauts aboard. This openness is part of a broader strategy to demystify space exploration and inspire interest in science and technology among the global populace.
Educational outreach is a key component of China’s strategy with Tiangong. The space station serves as a platform to educate and inspire the next generation of scientists and engineers. Initiatives like live broadcasts from the station and interactive educational programs aim to engage students and spark curiosity about space. China’s approach to public engagement is also shaping the global perception of its space program, positioning it as a transparent and collaborative player in the international space community.
Challenges and Future Prospects
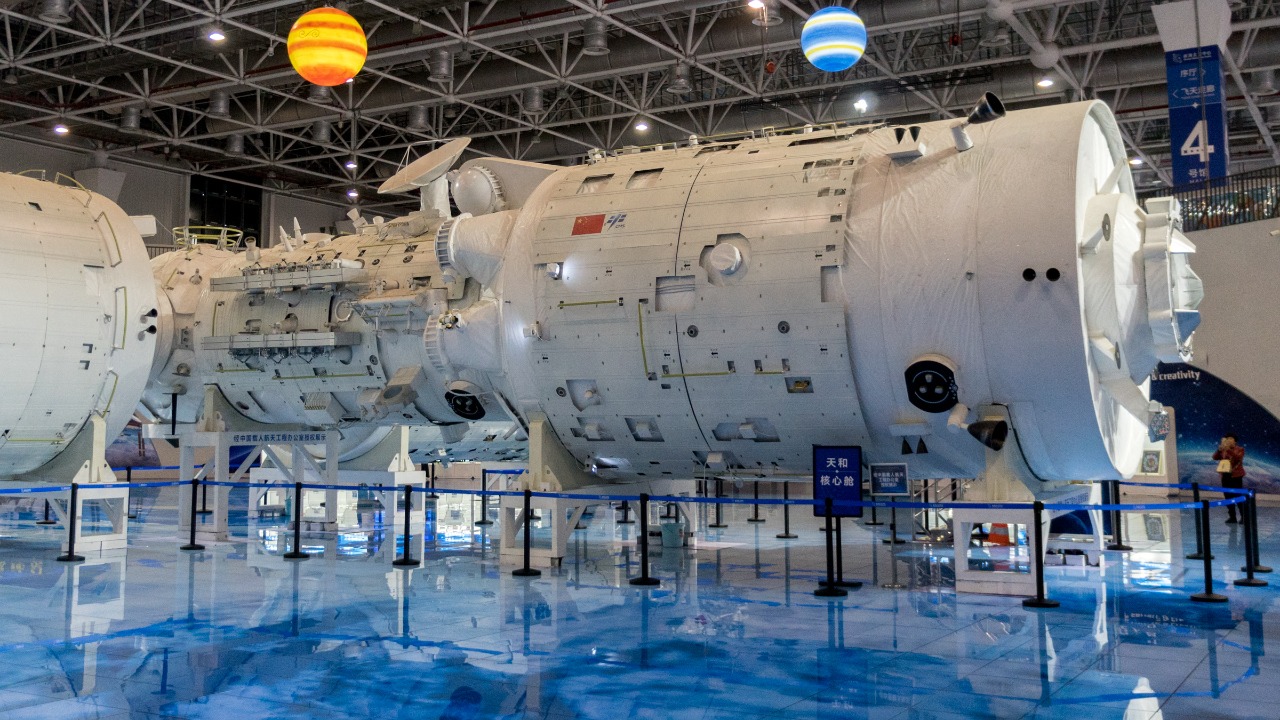

Despite its successes, Tiangong faces technical and operational challenges. The long-term maintenance of the station, including ensuring the reliability of its systems and managing the risks associated with space debris, remains a significant hurdle. Additionally, expanding the station’s capacity to accommodate more research and international collaborations requires continued investment and innovation. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the sustained success of Tiangong as a hub of scientific and technological advancement.
Sustainability is at the forefront of China’s plans for Tiangong. The country is committed to ensuring the station’s continuous operation, with strategies to enhance its resilience and adaptability. This includes plans to incorporate renewable energy sources and develop advanced recycling systems to minimize resource consumption. Looking ahead, China’s vision for Tiangong extends beyond its current capabilities. The station is poised to play a pivotal role in future space exploration missions, potentially serving as a launch pad for missions to the Moon and beyond. As humanity continues its quest to explore the cosmos, Tiangong’s contributions will be instrumental in shaping the future of space exploration.