IBM and Moderna have achieved a groundbreaking milestone by simulating the longest mRNA pattern without the use of AI, instead leveraging the power of quantum computing. This collaboration marks a significant leap in computational biology, showcasing the potential of quantum technology in advancing medical research and development.
Understanding the Power of Quantum Computing

Quantum computing represents a paradigm shift from classical computing, fundamentally altering how we process and analyze information. Unlike classical computers, which use bits as the smallest unit of data, quantum computers use quantum bits or qubits. These qubits have the unique ability to exist in multiple states simultaneously, thanks to the principles of superposition and entanglement. This allows quantum computers to tackle complex calculations at unprecedented speeds, solving problems that would take classical computers years to unravel.
The potential applications of quantum computing extend far beyond computational biology. In finance, for example, quantum algorithms are being developed to optimize trading strategies and manage risks more effectively. In the realm of cryptography, quantum computers promise to revolutionize data encryption by creating virtually unbreakable codes. As research progresses, we can anticipate even more groundbreaking developments in quantum computing technology, potentially transforming industries such as logistics, artificial intelligence, and climate modeling.
The Collaboration Between IBM and Moderna
The partnership between IBM and Moderna brings together two giants renowned for their contributions to technology and medicine. IBM, a global leader in technology, has a storied history of innovation, from its early days as a pioneer in computing to its current focus on cutting-edge technologies such as quantum computing. You can explore more about this legacy here. On the other hand, Moderna has been at the forefront of mRNA technology, revolutionizing the pharmaceutical industry with its successful development of mRNA-based vaccines, most notably for COVID-19.
The collaboration aims to harness the power of quantum computing to advance medical research, particularly in the simulation and understanding of mRNA patterns. By simulating complex mRNA structures, IBM and Moderna hope to accelerate the development of new vaccines and therapeutics. Their shared vision is to push the boundaries of what is possible in medical science, leveraging the unique capabilities of quantum computing to gain deeper insights into biological processes and disease mechanisms.
The Impact of Simulating mRNA Patterns
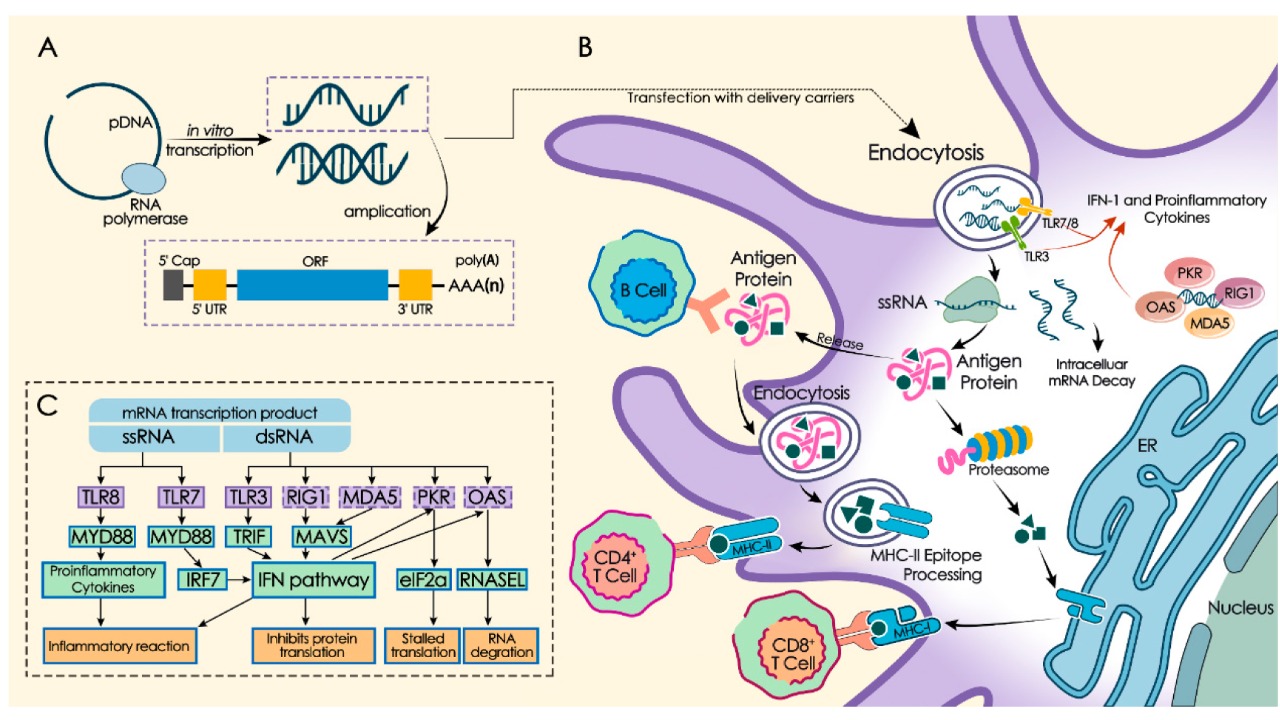
mRNA plays a crucial role in medical research, serving as a key component in the development of vaccines and treatments for a wide range of diseases. By simulating mRNA patterns, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of how these molecules function within the body, paving the way for more precise and effective medical interventions. The ability to accurately model mRNA structures can significantly accelerate drug discovery, reducing the time and cost associated with bringing new therapies to market.
The simulation of the longest mRNA pattern represents a significant breakthrough in our understanding of complex biological processes. This achievement could lead to advancements in vaccine development, enabling researchers to design more targeted and effective vaccines against emerging pathogens. Moreover, the insights gained from these simulations could have far-reaching implications for the development of new therapeutics, offering hope for the treatment of diseases that have long eluded conventional medical approaches.
Challenges and Future Directions

Despite the promise of quantum computing, the simulation of extensive mRNA patterns presents significant technical challenges. The current limitations of quantum computing technology, such as qubit coherence time and error rates, pose obstacles to achieving accurate and reliable simulations. Researchers must continuously work to enhance the stability and scalability of quantum systems to fully realize their potential in simulating complex biological structures.
Looking ahead, ongoing research and development in quantum computing are essential to overcoming these challenges. As the technology matures, we can expect expanded applications not only in healthcare but also in a wide range of fields. The potential to revolutionize areas such as personalized medicine, genomics, and drug discovery is immense, promising a future where quantum computing plays an integral role in tackling some of the most pressing challenges in science and medicine.
The collaboration between IBM and Moderna is a testament to the transformative power of quantum computing in advancing medical research. By simulating the longest mRNA pattern without AI, they have demonstrated the potential of quantum technology to unlock new frontiers in our understanding of biology. As research continues to evolve, the possibilities for quantum computing in healthcare and beyond are truly boundless.