Google has once again claimed the prestigious milestone of quantum supremacy, asserting that its latest quantum computer has outperformed classical counterparts in specific computational tasks. This achievement, however, has sparked a heated debate within the scientific community, with some experts raising skepticism about the validity and implications of Google’s claims.
Understanding Quantum Supremacy
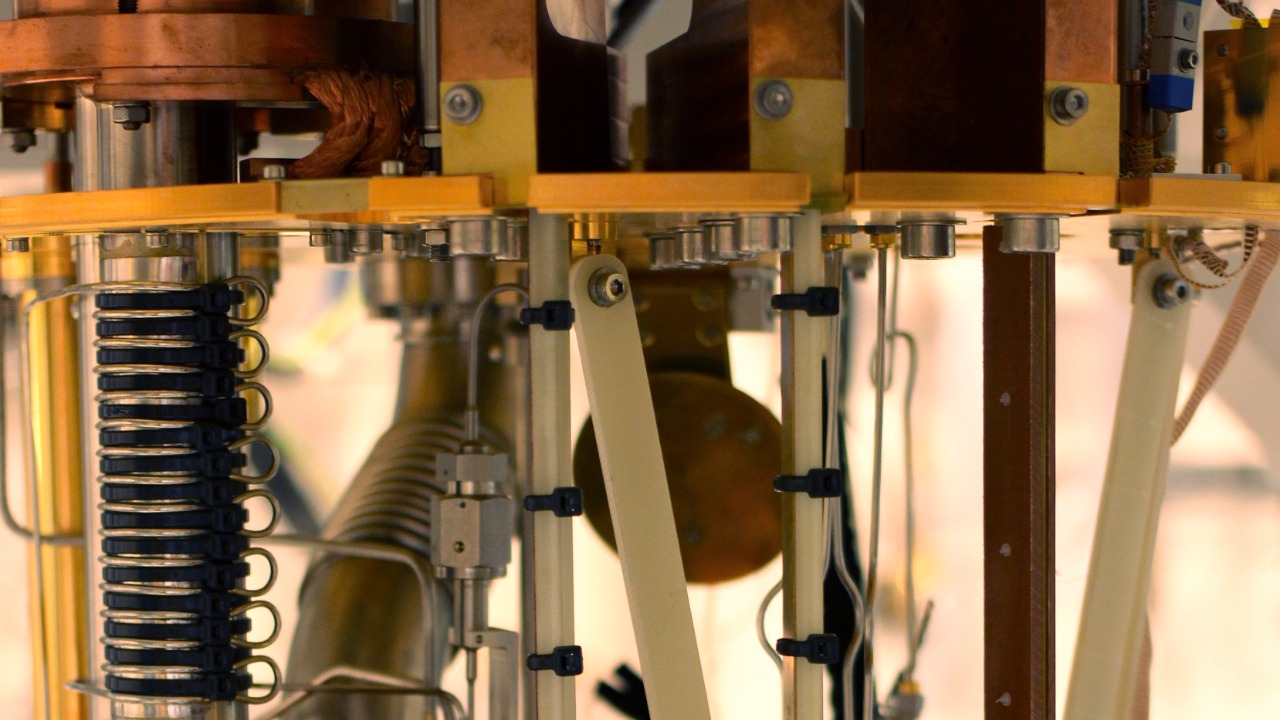

Definition and Historical Context
Quantum supremacy is a term used to describe the moment when a quantum computer can perform a calculation that is impossible or infeasible for a classical computer. This milestone is significant as it marks a pivotal point in the field of quantum computing, indicating that quantum machines have reached a new level of capability. Google’s previous claim of quantum supremacy in 2019, using its Sycamore processor, stirred the tech industry by asserting that it had completed a task in 200 seconds that would take the world’s most powerful supercomputer 10,000 years.
Google’s initial claim catalyzed a surge in quantum computing research and investment, pushing other companies to accelerate their quantum efforts. Although their 2019 claim faced criticism and skepticism, it undeniably highlighted the potential of quantum technology and set the stage for further developments in the field.
Criteria for Quantum Supremacy
Determining quantum supremacy involves benchmarks that compare the performance of quantum and classical computers on particular tasks. These tasks are often carefully selected to highlight the strengths of quantum systems, which can sometimes lead to criticism. A major challenge is ensuring these tasks have real-world relevance, as critics argue that some chosen benchmarks do not translate into practical applications.
The criteria for quantum supremacy have been a topic of controversy, with some experts questioning their fairness and applicability. The scientific community continues to debate the best standards for evaluating quantum advancements, emphasizing the need for transparent and reproducible results.
Google’s Latest Quantum Breakthrough
The Willow Quantum Computer
Google’s new quantum computer, named Willow, represents a significant leap over previous systems. With advanced technical specifications, Willow is designed to handle more complex computations and a higher number of qubits, which are the fundamental units of quantum information. This machine is seen as a testament to Google’s commitment to advancing quantum technology.
Willow showcases critical improvements in error rates and coherence times, addressing some of the limitations that have plagued earlier quantum systems. These advancements make Willow a powerful tool for exploring the potential of quantum computing in solving problems that are currently intractable for classical computers.
Performance and Achievements
One of the notable achievements of the Willow quantum computer is its ability to solve a complex optimization problem significantly faster than classical computers. This task, which involves intricate calculations, highlights Willow’s potential to surpass traditional computing methods. Google’s claim of quantum supremacy relies on these kinds of benchmarks to demonstrate the quantum computer’s superiority.
The specific tasks Willow has accomplished have reignited discussions about the benchmarks used to claim quantum supremacy. While Google’s achievement is undeniably impressive, it also underscores the ongoing debate about the criteria for determining such breakthroughs in the quantum realm.
Industry Skepticism and Criticism

Reactions from Competitors
The announcement of Google’s latest achievement has not gone unnoticed by its competitors in the quantum computing arena. Companies like D-Wave have expressed skepticism about Google’s claims. D-Wave, for instance, has been vocal about its own advancements, as seen in their recent assertion of achieving quantum supremacy before others, a claim that has sparked its own debates.
Competing claims of quantum supremacy, such as those from IBM and D-Wave, highlight the fiercely competitive nature of the industry. Each company employs different approaches and technologies, contributing to a diverse landscape of strategies and innovations.
Scientific Community’s Response
The scientific community has responded to Google’s announcement with a mix of intrigue and skepticism. Some researchers question the validity of Google’s results, pointing out potential issues with reproducibility and the practicality of the tasks used to demonstrate supremacy. For instance, a recent article challenges the robustness of Google’s claims, emphasizing the need for careful scrutiny.
Concerns about the real-world applicability of Google’s achievements are prevalent among experts. While the tasks completed by Willow are impressive, critics argue that they do not necessarily translate into practical applications, leaving the door open for further debate on the true impact of quantum supremacy claims.
Implications for the Future of Quantum Computing

Potential Applications
The advancements made by Google’s Willow quantum computer could have transformative effects on various industries. Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize fields like cryptography, where it could break current encryption methods, and drug discovery, where it might accelerate the development of new medications. These potential applications underscore the importance of continued research and development in quantum technologies.
As quantum computing progresses, its impact may extend to areas such as logistics optimization, financial modeling, and artificial intelligence. The ability to solve complex problems more efficiently could lead to significant breakthroughs across these domains, making quantum computing a critical area of focus for future technological advancements.
The Road Ahead
Despite Google’s impressive achievements, significant challenges remain in the development of quantum computing. Issues such as error correction, scalability, and the development of practical applications continue to pose hurdles for researchers. Addressing these challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of quantum technology.
Looking forward, the quest for quantum supremacy will likely involve a combination of technological advancements and collaborative efforts. The future of quantum computing promises exciting possibilities, but it also demands careful consideration of the ethical and practical implications of these powerful technologies.
The Competitive Landscape of Quantum Computing

Key Players and Strategies
The quantum computing industry is characterized by a diverse set of players, each pursuing unique strategies to achieve breakthroughs. Major companies like Google, IBM, and D-Wave are at the forefront of this technological race. Google’s approach, focusing on developing more powerful quantum processors, contrasts with D-Wave’s emphasis on annealing-based quantum systems.
Each of these companies employs different technologies and methodologies, contributing to a vibrant and competitive landscape. These differences highlight the multifaceted nature of quantum computing and the various paths to achieving quantum supremacy.
Innovations and Collaborations
Recent innovations in quantum computing have been driven by both individual company efforts and collaborative initiatives. Companies are increasingly engaging in partnerships with academic institutions and government agencies to accelerate research and development. These collaborations are crucial for pooling resources and expertise, fostering an environment of shared knowledge and rapid progress.
As the field continues to evolve, the role of collaborations will likely become even more significant. By working together, organizations can overcome the challenges inherent in quantum computing and pave the way for groundbreaking advancements. For instance, Google’s recent developments have been a topic of discussion, as seen in a detailed analysis of Willow’s impact on the industry.