In a groundbreaking achievement for aerospace technology, the first-ever 3D printed rocket successfully launched, marking a new era in space exploration. This innovative approach not only promises to revolutionize the manufacturing process but also significantly reduce the costs associated with launching rockets. As industries and researchers continue to explore the potential of 3D printing, the successful launch serves as a testament to the technology’s viability and future possibilities.
The Technology Behind 3D Printed Rockets
The fundamentals of 3D printing technology in rocketry lie in its ability to create complex structures with precision and efficiency. This process, known as additive manufacturing, involves building objects layer by layer from digital models, allowing for intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. In the context of rocketry, this means creating lightweight components that are both strong and resilient.
The materials used in 3D printed rockets are crucial to their success. Typically, aerospace-grade alloys and high-performance polymers are employed to ensure durability and reliability under the extreme conditions of space travel. The development of these components involves overcoming significant engineering challenges, such as ensuring the structural integrity of the printed parts and optimizing the printing process to avoid defects. Engineers have innovated solutions such as advanced simulation software and real-time monitoring systems to address these challenges, paving the way for successful launches.
Significance of the Launch
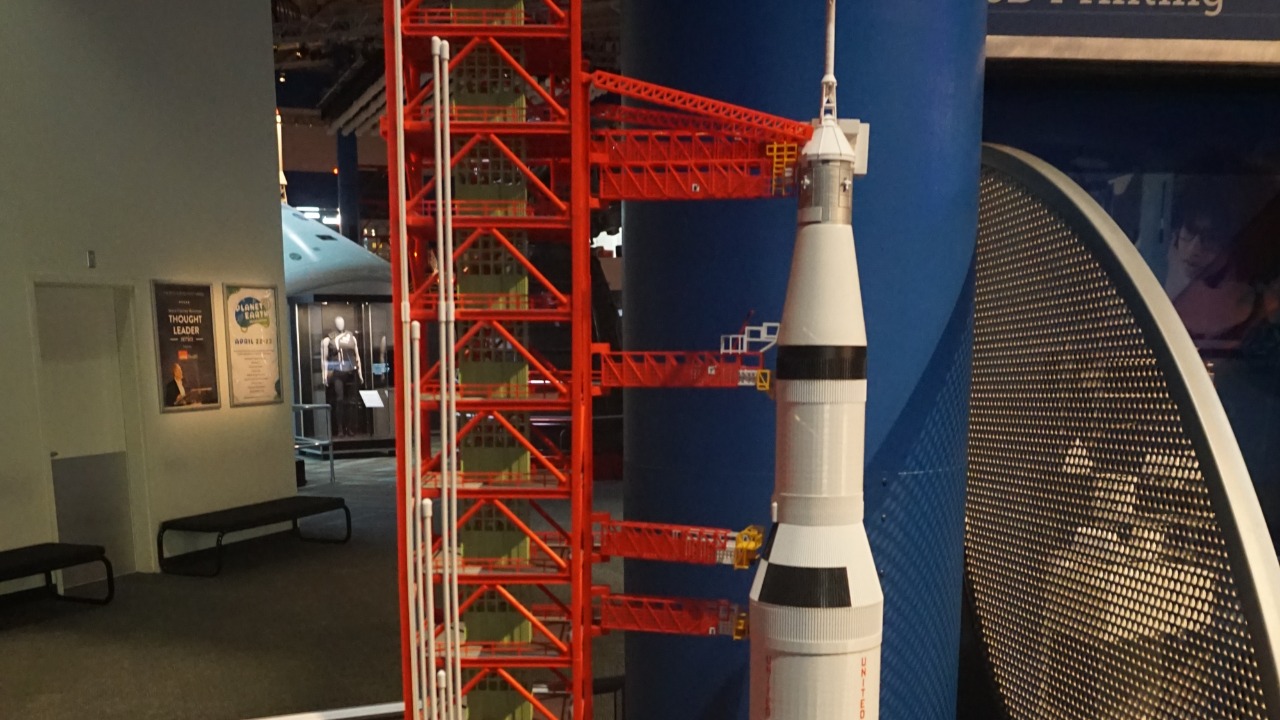

The launch of the first 3D printed rocket is a historic milestone in the space industry. It signifies a shift towards more sustainable and cost-effective methods of exploring space. By reducing the time and resources needed to manufacture rocket parts, this launch demonstrates the potential for rapid iteration and innovation in spacecraft design, paving the way for more frequent and affordable space missions.
The economic and environmental benefits of 3D printed rockets are also noteworthy. Traditional rocket manufacturing involves a significant amount of material waste and energy consumption. In contrast, additive manufacturing minimizes waste by using only the necessary material to construct each part. This efficiency not only reduces costs but also lessens the environmental impact, making space exploration more sustainable in the long run.
Key Players in the Development
Relativity Space, the company behind the world’s first 3D printed rocket, has been at the forefront of integrating 3D printing technology into aerospace. Their mission is to revolutionize how rockets are built and launched, with the ultimate goal of making space more accessible to everyone. The company has achieved this by harnessing the talents of engineers, scientists, and stakeholders who have worked tirelessly to bring this project to life.
Collaboration with educational institutions and the influence of academic research have played a critical role in advancing 3D printing applications in rocketry. By partnering with universities and research centers, Relativity Space has tapped into a wealth of knowledge and innovation, ensuring the continuous improvement of their technology and practices.
Implications for the Future of Aerospace

The advent of 3D printing technology in aerospace has the potential to transform spacecraft manufacturing and design. By enabling the creation of complex geometries and lightweight structures, it opens new avenues for innovation in propulsion systems and materials. This technology allows for the customization of spacecraft components to meet specific mission requirements, enhancing performance and efficiency.
Future missions and projects stand to benefit significantly from 3D printing. As the technology matures, we can expect advancements in propulsion systems that leverage the unique capabilities of additive manufacturing. This could lead to the development of more advanced spacecraft, capable of reaching new frontiers in space exploration. The potential for on-demand manufacturing of replacement parts during missions also promises to enhance the longevity and success of space endeavors.
Challenges and Considerations

Despite its promising potential, the development and launch of 3D printed rockets are not without challenges. Ensuring the reliability and safety of printed components is paramount, as any failure could have catastrophic consequences. Regulatory and safety considerations must be thoroughly addressed, requiring rigorous testing and certification processes.
The scalability of 3D printing technology in aerospace is another consideration. While it offers significant advantages, integrating this technology into existing aerospace infrastructures involves logistical and technical hurdles. As the industry continues to adapt, it will be essential to overcome these challenges to fully realize the benefits of 3D printed rockets and their role in the future of space exploration.