A groundbreaking case has emerged in the medical field where a single dose of an experimental cell therapy led to the rapid reduction of a woman’s aggressive brain tumor, nearly vanishing within just five days. This remarkable development offers a glimpse of hope for future treatments of deadly brain cancers, particularly glioblastomas, which have long posed a challenge to oncologists due to their aggressive nature.
The Promise of Experimental Cell Therapies
The experimental cell therapy in question is a promising advancement in the field of oncology, particularly for its potential to treat aggressive brain tumors like glioblastomas. This therapy differs from traditional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation, as it uses genetically modified cells to target and destroy cancer cells more precisely. Unlike conventional methods, which can harm healthy tissue, experimental cell therapies are designed to hone in on tumor-specific antigens, minimizing collateral damage and enhancing treatment efficacy.
At the cellular level, this therapy employs a mechanism that involves reprogramming the patient’s immune cells, often T-cells, to recognize and attack cancer cells. By altering these cells outside the body and reintroducing them, the therapy acts like a guided missile, targeting the tumor with increased accuracy. Previous applications have shown promise, with several case studies indicating significant tumor shrinkage in patients who had exhausted other treatment options. These successes have fueled optimism in the medical community about the potential of cell therapy to revolutionize cancer treatment.
The Case Study: A Closer Look
The patient in this remarkable case is a 56-year-old woman diagnosed with a particularly aggressive form of glioblastoma, a brain tumor known for its rapid growth and poor prognosis. Her medical history included several failed attempts with standard treatments, leaving her with limited options and a dire outlook. Upon administration of the experimental therapy, however, her condition took an unprecedented turn.
The timeline of her treatment was astonishingly brief. Within just five days of receiving the therapy, medical imaging revealed a dramatic reduction in the size of the tumor. Medical professionals documented this rapid response with detailed imaging and clinical observations, noting the extent of tumor shrinkage and the patient’s improved neurological function. This case has been meticulously documented, with findings shared widely in the scientific community to encourage further exploration of this approach.
Implications for Glioblastoma Treatment
Treating glioblastoma has historically been fraught with challenges, largely due to the tumor’s ability to infiltrate surrounding brain tissue and its resistance to conventional treatments. Current therapies, including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, often fail to completely eradicate the tumor, leading to recurrence. Additionally, the blood-brain barrier poses a significant obstacle, preventing many drugs from reaching the tumor site effectively.
This breakthrough in cell therapy could potentially transform the landscape of glioblastoma treatment. By overcoming some of the key limitations of existing therapies, such as non-specific targeting and the inability to cross the blood-brain barrier, this approach offers a new avenue for treatment. Experts believe that, with further research, cell therapy could be integrated into standard treatment protocols, providing hope for patients who previously had few options. Oncologists and researchers, such as those cited in a recent report, are optimistic about the future applications of this therapy in clinical settings.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations

For any experimental therapy to transition from the lab to the clinic, it must undergo a rigorous approval process. This involves multiple phases of clinical trials to assess safety, efficacy, and potential side effects. Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA, play a crucial role in this process, ensuring that new treatments meet stringent standards before becoming widely available.
However, the use of experimental therapies also raises ethical considerations. Patients must provide informed consent, fully understanding the potential risks and benefits of the treatment. This can be challenging, as the novelty of such therapies means that long-term outcomes are often unknown. Balancing optimism with caution is essential, as highlighted by experts who emphasize the need for comprehensive testing to ensure patient safety. These ethical dilemmas are further explored in discussions about the future of medical innovation.
Future Directions and Research
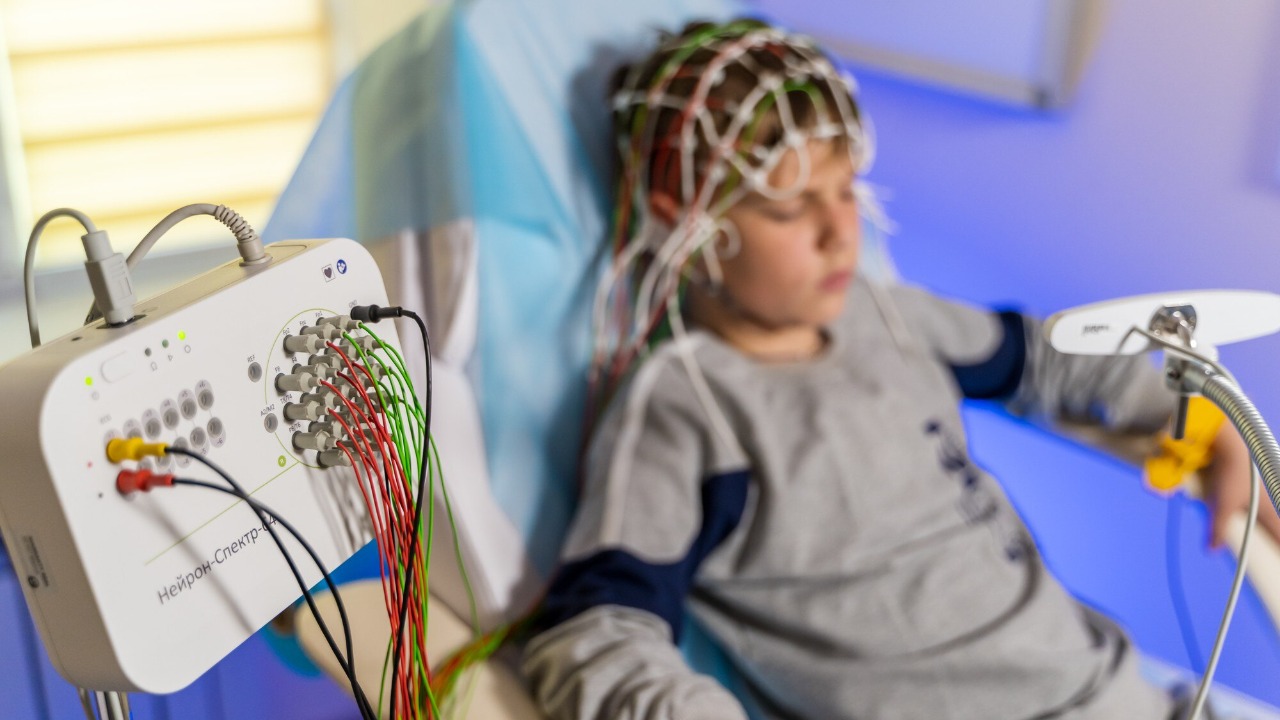

The promising results of this case study have spurred ongoing research and clinical trials aimed at refining and expanding the use of cell therapy for brain tumors. Scientists are exploring various modifications to enhance the specificity and potency of these treatments, with several trials currently underway. These efforts are crucial in determining the optimal conditions for therapy administration and identifying which patient populations may benefit most.
Moreover, this advancement underscores the potential of personalized medicine in cancer treatment. By tailoring therapies to the individual genetic and molecular profiles of patients, healthcare providers can increase the likelihood of success. Such personalized approaches are gaining traction, as they promise to improve outcomes and reduce side effects. The broader implications for cancer treatment are significant, with potential applications extending beyond brain tumors to other challenging cancers. Researchers and clinicians remain hopeful that the insights gained from this therapy will inspire similar advances, as discussed in a detailed analysis.