New findings suggest that massive volcanoes played a pivotal role in shaping the early Martian landscape. We are about to explore the scientific evidence that supports this hypothesis and the implications it carries for our understanding of Mars’s geological history.
Geological Evidence of Massive Volcanoes on Mars
Physical evidence of ancient volcanoes has been found on Mars, most notably Olympus Mons, recognized as the largest known volcano in our solar system. This colossal shield volcano stands at a staggering height of 13.6 miles, nearly three times the height of Mount Everest, Earth’s tallest peak. Its vast size and unique geological features provide valuable insight into the volcanic activity that once occurred on Mars.
Research published in Science Direct and Wiley Online Library delves deeper into the geological characteristics and age of these Martian features. The study suggests that these massive volcanic eruptions significantly impacted the Martian landscape, leading to the formation of unique geological formations that we observe on Mars today.
Volcanic Activity and Water Presence on Mars
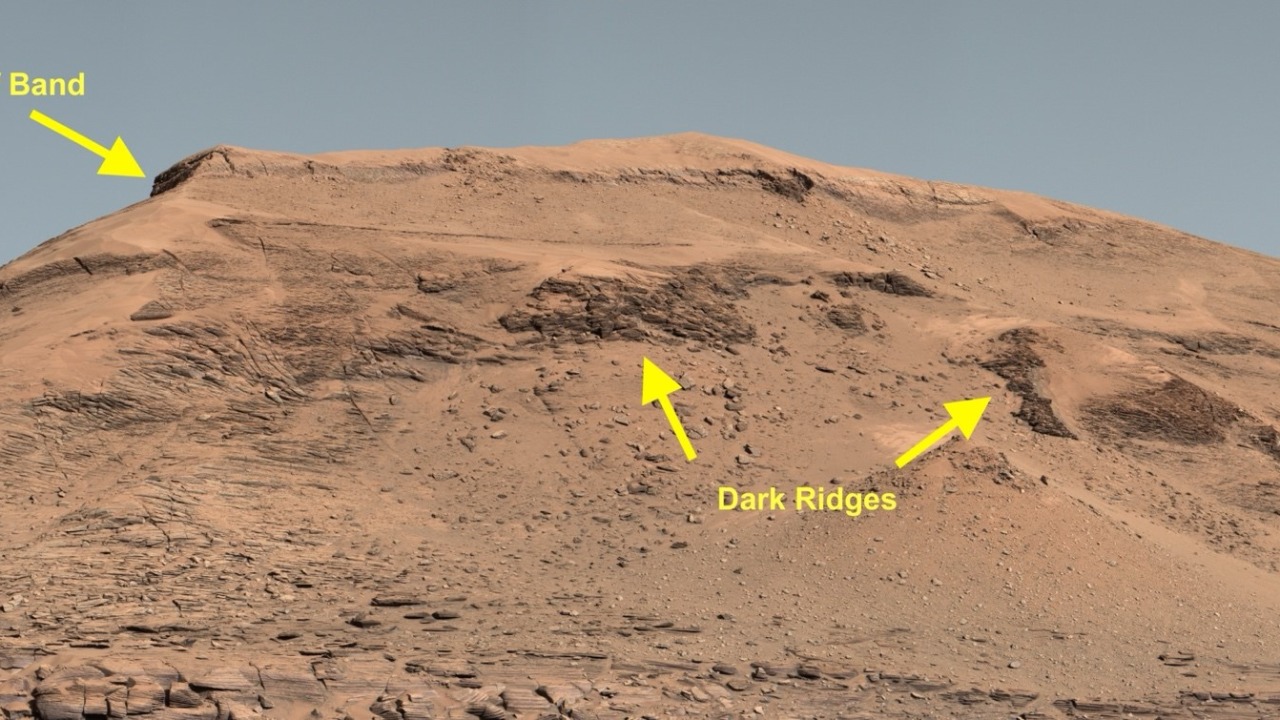

New findings from the Chinese Rover have suggested a potential relationship between volcanic activity and the presence of water on Mars. The rover detected evidence of ancient water bodies, further supporting the hypothesis that Mars was once a wet planet. This discovery has sparked excitement and curiosity among the scientific community.
Supporting this evidence, Discover Magazine reports the discovery of ancient beaches on Mars, suggesting the presence of large, ice-free oceans. The article theorizes that volcanic activity may have contributed to the creation of these water bodies, possibly through the release of water vapor during eruptions.
Volcanoes and Mars’s Atmosphere
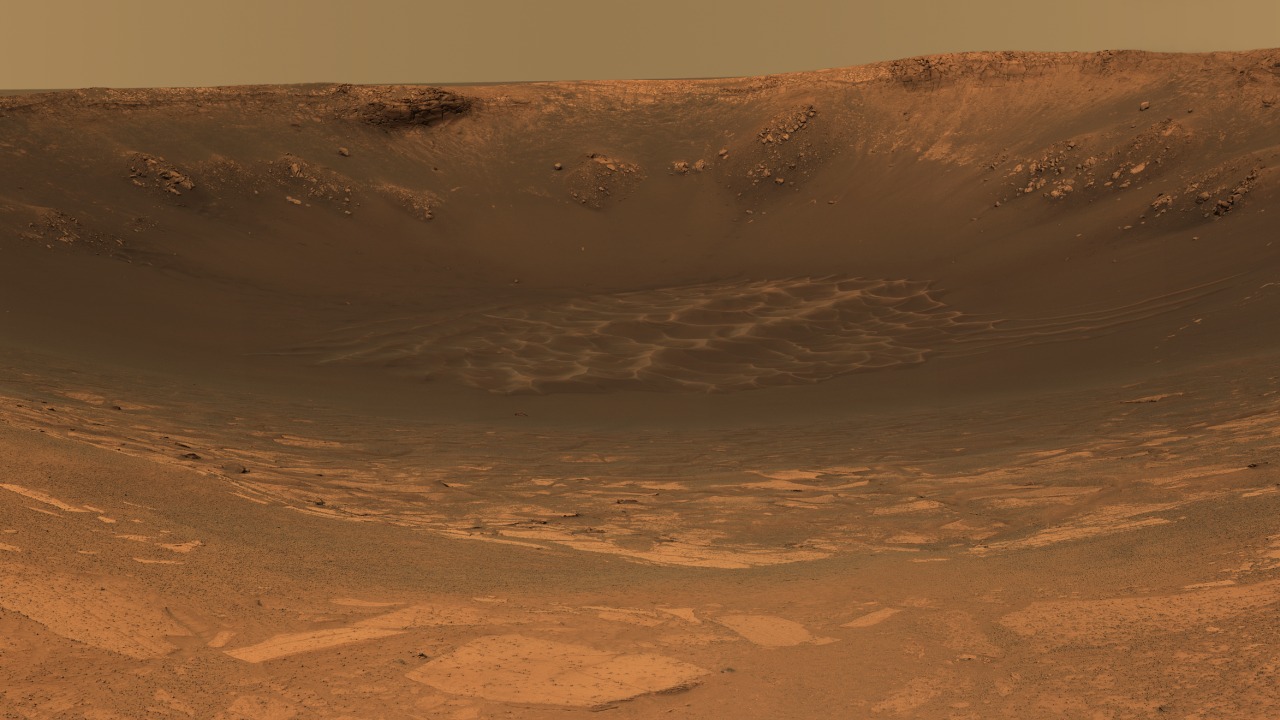

Massive volcanic eruptions could have drastically altered Mars’s early atmosphere. The intense heat and force of these eruptions would have released an immense quantity of gases into the atmosphere. These gases, including carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide, could have contributed to the creation of a thicker, warmer atmosphere.
An article published in Nature discusses evidence suggesting that volcanic activity may have played a significant role in the atmospheric evolution of Mars. The release of large amounts of gas during volcanic eruptions could have led to the formation of a dense, warm atmosphere, conducive to the presence of liquid water on the planet’s surface.
Implications for Life on Mars
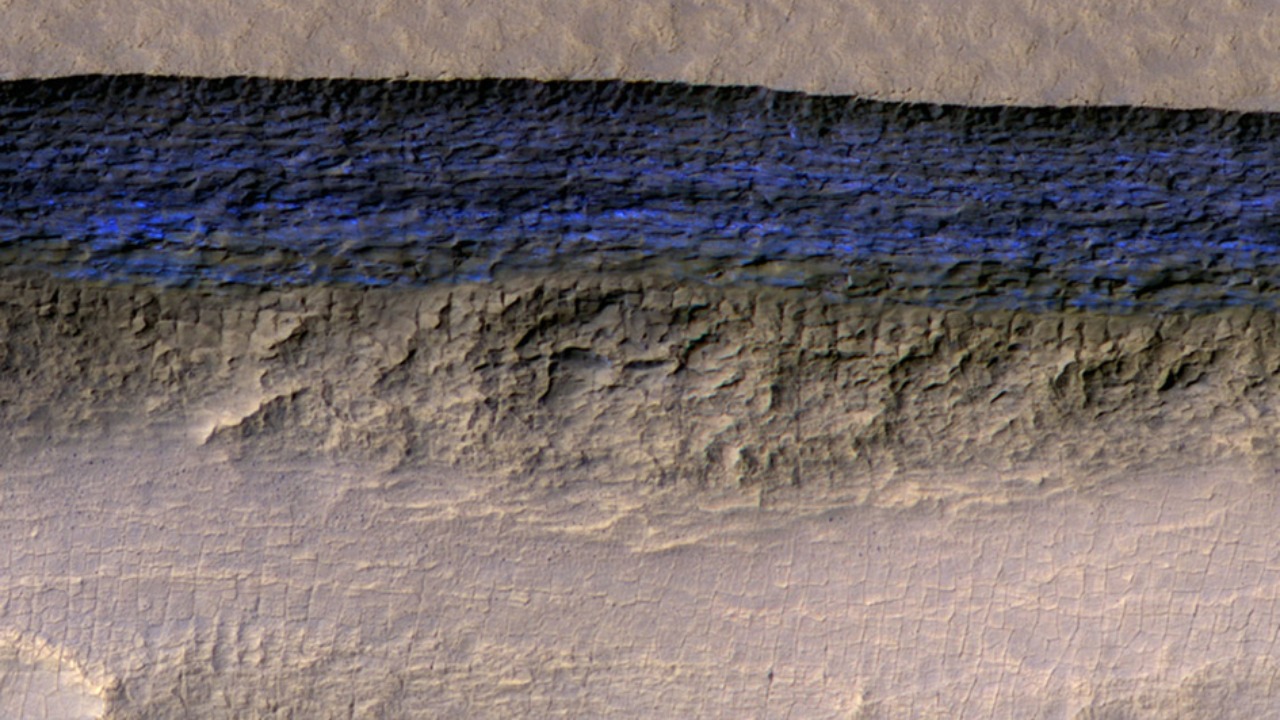

The possibility that these volcanic activities and subsequent environmental changes might have made conditions suitable for life on Mars is a topic of ongoing research. The presence of water and a potentially thicker atmosphere could have created an environment conducive to primitive life forms. These findings fuel the ongoing search for signs of ancient life on Mars and provide new avenues for future research.
The discovery of past volcanic activity and its potential impact on Mars’s environment opens up exciting possibilities for astrobiology. The search for signs of ancient life on Mars, whether microbial or more complex, is a significant focus of current Mars missions, including NASA’s Perseverance rover and the upcoming European-Russian ExoMars mission.
Understanding Mars’s Geological History
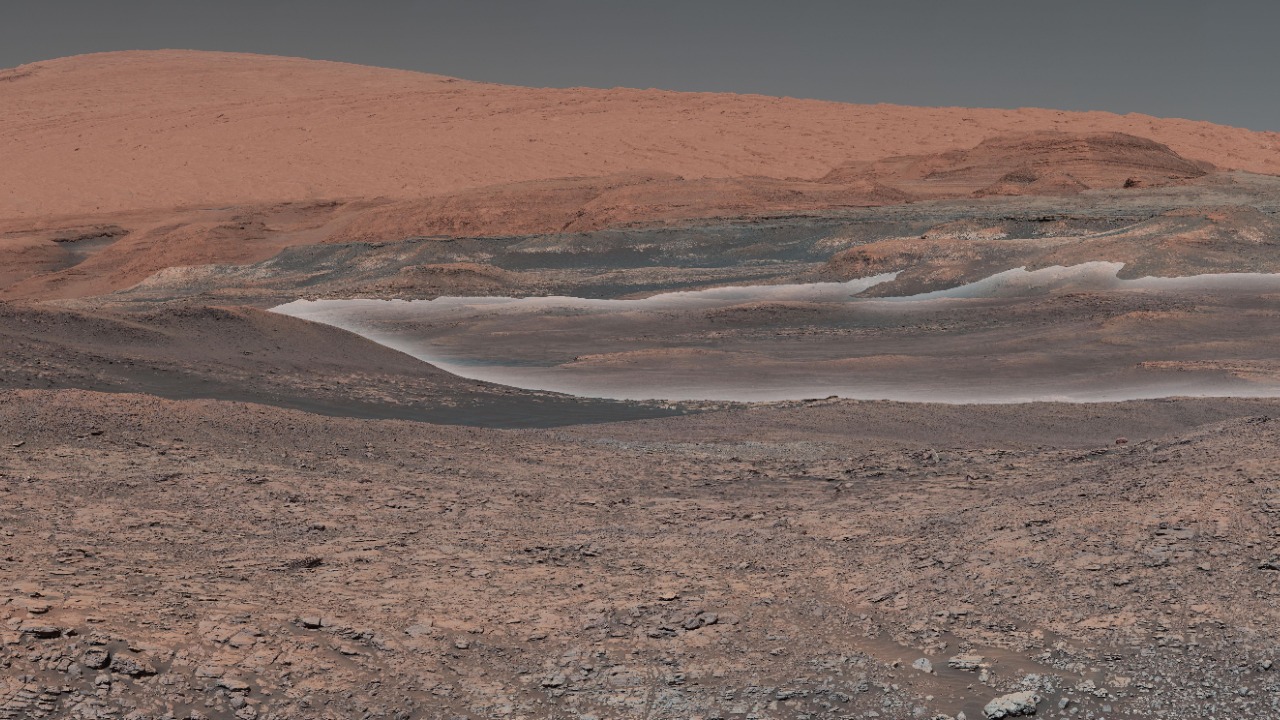

These findings provide valuable insights into the geological evolution of Mars. The discovery of massive ancient volcanoes and the evidence of their impact on the Martian landscape help us piece together the planet’s volcanic history.
When compared to Earth, Mars’s volcanic history presents both striking similarities and intriguing differences. Both planets have experienced substantial volcanic activity, but the scale and impact of this activity differ due to their varied geological conditions. This knowledge can significantly inform future missions to Mars, particularly those aimed at exploring the planet’s geological history and potential for life.