Recent discoveries by NASA’s Curiosity Rover have sparked excitement and speculation in the scientific community about the possibility of past life on Mars. Key deposits found on the Martian surface suggest that conditions may have once been favorable for alien lifeforms. These findings have profound implications for our understanding of the Red Planet’s history, and they inspire further exploration in the quest to uncover the mysteries of extraterrestrial life.
The Discovery of Martian Deposits
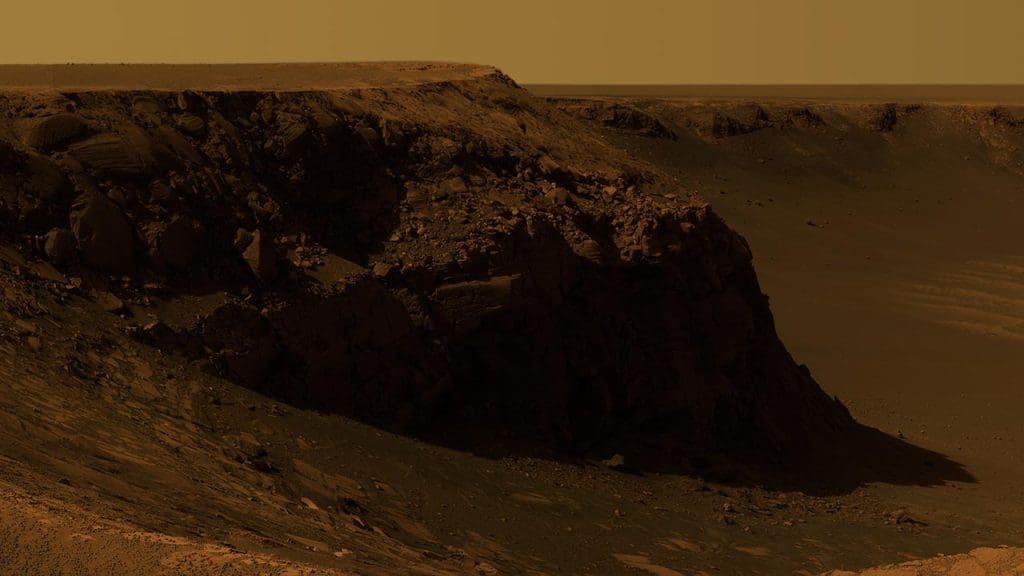

NASA’s Curiosity Rover has been at the forefront of uncovering new evidence on Mars, revealing deposits that hint at the planet’s potentially life-supporting past. These discoveries include mineral formations and sedimentary structures that are similar to those found in habitable environments on Earth. The types of deposits found play a crucial role in understanding the Red Planet’s past climate and geological activity.
Comparatively, the Martian deposits bear a striking resemblance to Earth’s geological formations that are known to support life, such as clay minerals and sulfates. These similarities suggest that Mars might have once possessed conditions suitable for microbial life. However, differences in the chemical makeup and distribution of these deposits raise intriguing questions about the possibility of life on Mars and how it might differ from life on Earth.
Scientific Evidence and Theories

The chemical composition of these Martian deposits provides valuable insights into the planet’s history. Detailed analyses have identified minerals like hematite and phyllosilicates, which are indicative of past water activity. Such elements could have created an environment favorable for microbial life, much like certain regions on Earth. As scientists continue to investigate these compounds, new theories about Mars’s wet past and potential habitability are emerging.
Several hypotheses have been proposed regarding the history of water on Mars and its role in supporting life. These range from the existence of ancient lakes and rivers to the possibility of subsurface water reservoirs. The potential scenarios of how life could have existed in such an environment are vast, from simple microbial organisms to more complex life forms that may have thrived in Mars’s once water-rich environment.
Technology and Methodology Behind the Discoveries
The role of advanced technology cannot be overstated in uncovering the secrets of Mars. The Curiosity Rover, equipped with sophisticated instruments, has been instrumental in detecting signs of life. Its powerful cameras, spectrometers, and drilling tools allow for detailed analysis of the Martian surface. These technological advancements have revolutionized our understanding of the planet and continue to provide valuable data that could indicate past life.
Methodologically, scientists employ a variety of techniques to study Martian geology. From analyzing soil and rock samples to interpreting remote sensing data, the challenges of studying a planet millions of miles away are significant. Despite these challenges, ongoing efforts to interpret this data are crucial for piecing together Mars’s geological history and assessing its potential for past life.
Implications for Future Mars Missions
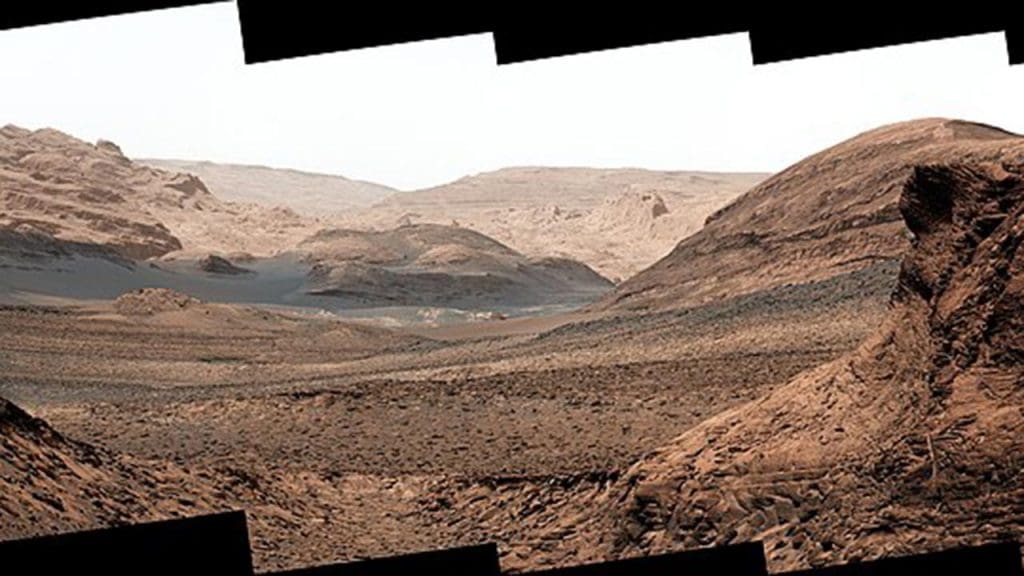

The recent findings have significant implications for future Mars missions. These discoveries will heavily influence the strategies of upcoming explorations, particularly in the selection of landing sites and scientific objectives. Areas with promising deposits are likely to be prioritized, as they hold the key to unlocking Mars’s past and assessing its habitability.
International collaboration is becoming increasingly important in Mars exploration. Countries and organizations around the world are pooling resources and expertise to unravel the mysteries of the Red Planet. Joint missions and shared technologies not only enhance scientific understanding but also pave the way for a broader exploration of the solar system in the search for life.
The Broader Impact on Astrobiology
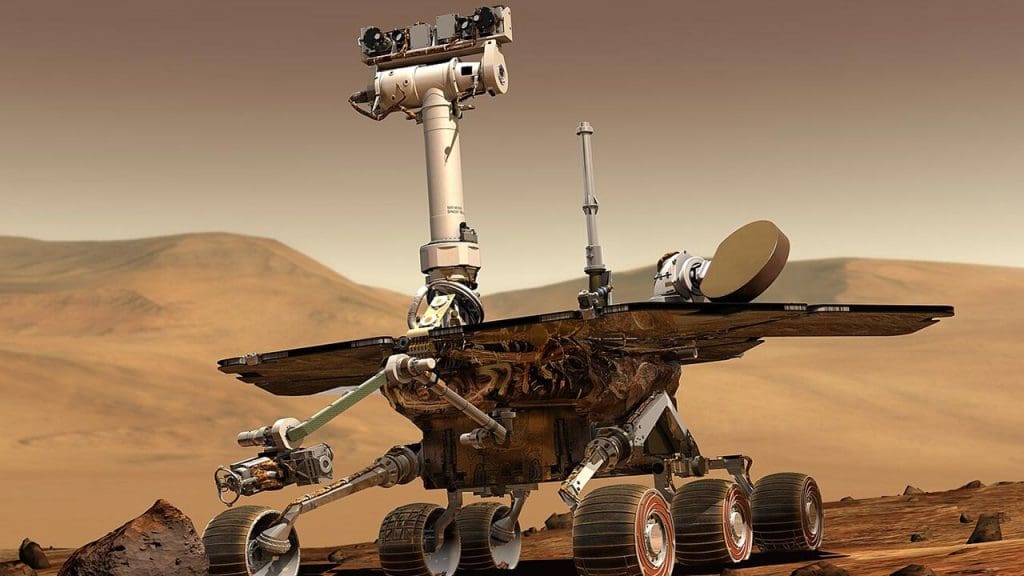

The discoveries on Mars significantly influence our understanding of life beyond Earth. Mars serves as a crucial model for studying extraterrestrial life forms, offering insights into how life might evolve in different environments. The implications extend beyond Mars, guiding the search for life on other planets and moons within our solar system.
Public interest in the discovery of potential life on Mars is immense, shaping perceptions of space exploration and inspiring a new generation of scientists and explorers. The possibility of life on another planet raises profound philosophical and existential questions, challenging us to reconsider our place in the universe and the diversity of life forms that might exist beyond our world.