China’s rocket factories are taking a page from the automotive industry’s playbook, adopting a car-style mass production approach. This strategy is aimed at surpassing the pace set by SpaceX in the space industry.
China’s adoption of a car-style mass production approach is reflective of the country’s broader ambitions in the space industry. The country has been investing heavily in space exploration and satellite technology, with the aim of becoming a major player in the global space industry. This mass production strategy is a key part of China’s plan to achieve this goal, as it allows for a faster and more cost-effective production of rockets. source
Moreover, this strategy also aligns with China’s broader economic and industrial policies. The country has long been known for its mass production capabilities in various industries, from electronics to automobiles. By applying this approach to rocket production, China is leveraging its existing strengths to gain a competitive edge in the space industry.
China’s Approach to Rocket Production
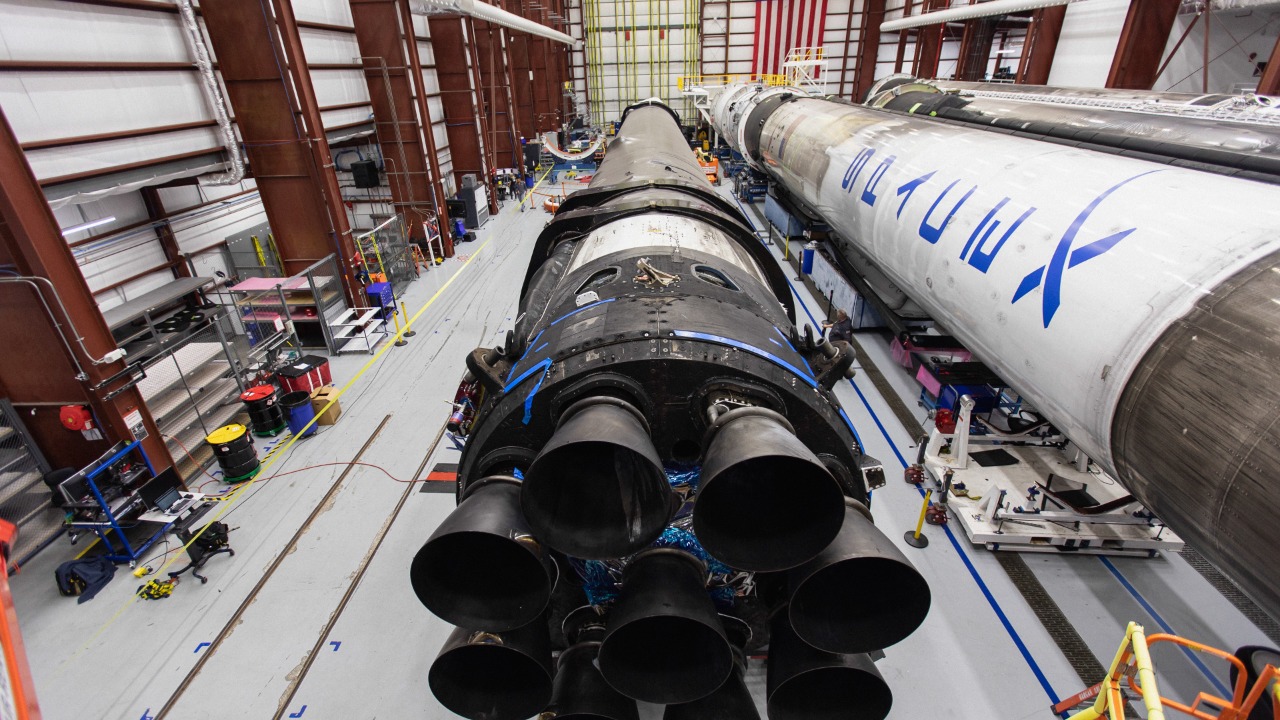

China’s rocket factories are implementing a strategy reminiscent of the automotive industry, where mass production is key. This approach is designed to increase the pace of rocket production, with the ultimate goal of surpassing SpaceX’s current rate. The strategy is not just about quantity, but also about efficiency and cost-effectiveness, as mass production can lead to economies of scale and reduced costs per unit. source
This car-style mass production approach is a significant shift in the space industry, which traditionally has been characterized by bespoke, handcrafted rockets. By adopting this strategy, China is aiming to gain a competitive edge against SpaceX and other players in the space industry. The goal is to produce more rockets, faster, and at a lower cost, thereby increasing China’s presence and influence in space.
China’s mass production approach is being implemented across its rocket factories, with the aim of standardizing production processes and reducing costs. This involves the use of assembly lines and automated machinery, similar to those used in car factories. The rockets are designed to be modular, with interchangeable parts that can be produced in large quantities. This allows for a more streamlined and efficient production process, which can lead to a higher production rate. source
Furthermore, China’s mass production approach also involves a focus on continuous improvement and innovation. Just like in the automotive industry, the goal is not just to produce more rockets, but also to constantly improve the design and performance of these rockets. This is achieved through a process of testing, feedback, and iterative design, which allows for continuous improvements in efficiency, reliability, and performance.
Comparison with SpaceX’s Production
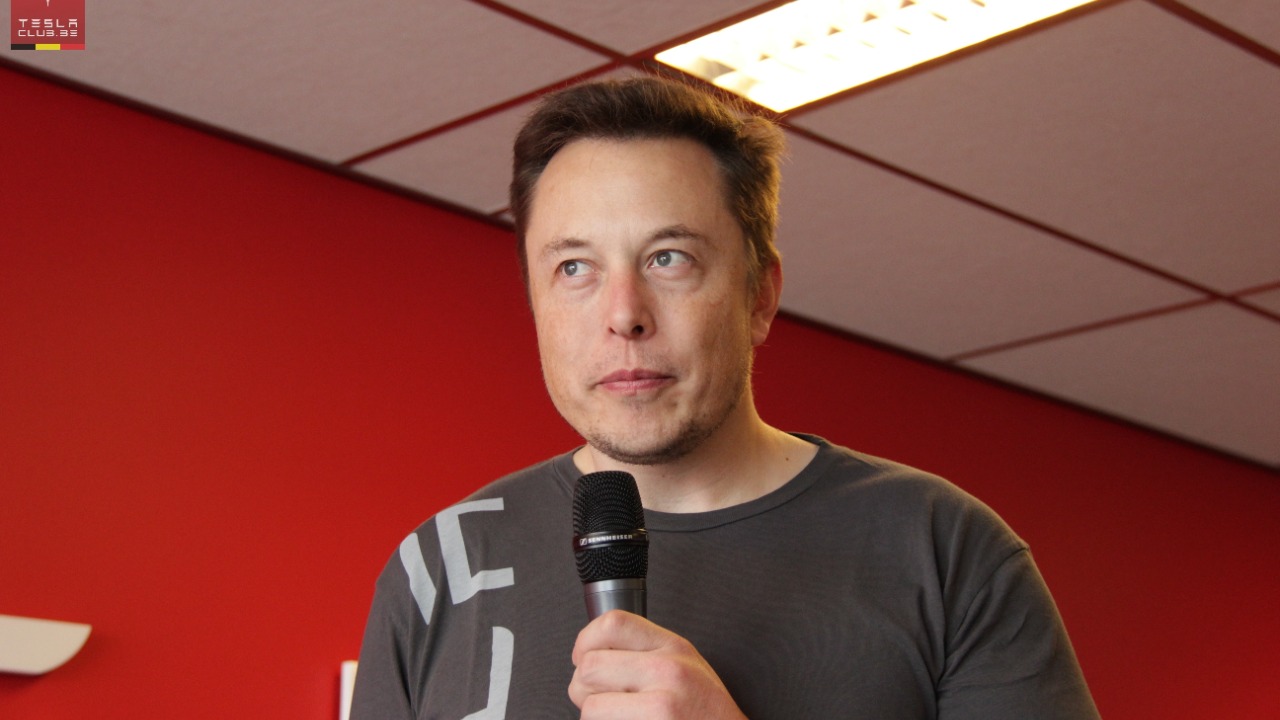

SpaceX, under the leadership of Elon Musk, has been a trailblazer in the space industry, setting a high bar for pace and innovation. The company’s production model has been focused on rapid iteration and improvement, with a strong emphasis on reusability to reduce costs. However, China’s new approach of car-style mass production presents a different strategy that could potentially challenge SpaceX’s dominance. source
While SpaceX has been successful with its approach, the mass production strategy adopted by China could potentially lead to a higher production rate. This could allow China to launch more missions and achieve more objectives in space in a shorter time frame. However, it remains to be seen how this approach will compare in terms of quality, reliability, and overall success rate of the missions.
SpaceX’s approach to rocket production, while different, has also been highly successful. The company’s focus on reusability and rapid iteration has allowed it to achieve significant advancements in rocket technology. However, China’s mass production approach presents a different set of advantages. By producing rockets on a larger scale, China could potentially achieve a higher launch frequency, allowing it to carry out more missions and achieve more objectives in space. source
It’s also worth noting that SpaceX and China’s rocket factories are operating in different contexts. SpaceX, as a private company, operates under a different set of constraints and incentives compared to China’s state-backed rocket factories. This could potentially influence the effectiveness and outcomes of their respective strategies.
Potential Implications for the Global Space Industry
China’s mass production approach to rocket manufacturing could have significant implications for the global space industry. If successful, this strategy could potentially reshape the industry, setting a new standard for pace and cost-effectiveness. This could lead to increased competition, pushing other players in the industry to innovate and adapt to keep up. source
However, this strategy also presents challenges. Mass production could potentially lead to quality control issues, and the increased pace could put pressure on safety standards. Furthermore, the increased number of launches could contribute to the growing problem of space debris. Despite these challenges, China’s car-style mass production approach represents a bold and ambitious move in the space industry, and its impact will be closely watched by industry observers and competitors alike.
The success of China’s mass production approach could potentially have far-reaching implications for the global space industry. If China is able to significantly increase its pace of rocket production and launch frequency, it could potentially challenge the dominance of established players like SpaceX. This could lead to a shift in the balance of power in the global space industry, with China becoming a more influential player. source
Furthermore, the adoption of a mass production approach could potentially influence the strategies and practices of other players in the industry. If China’s approach proves successful, it could encourage other countries and companies to adopt similar strategies, leading to a broader shift towards mass production in the space industry. However, this could also lead to increased competition and pressure on safety and quality standards, presenting new challenges for the industry.