Delving into the depths of the human mind, researchers are using advanced forms of brain imaging to uncover hidden memories in comatose patients. These findings not only challenge our previous understanding of cognitive abilities during comas but also open up new possibilities for communication and patient care in the medical field.
Uncovering Memories in the Unconscious Brain
Scientists are making significant strides in understanding the cognitive abilities of coma patients. Using advanced brain scans, these researchers are detecting memory activity in individuals who are otherwise unresponsive. This is a substantial breakthrough, challenging the long-held belief that coma patients exist in a state devoid of cognitive processes.
The first inklings of this possibility arose from studies conducted on patients in vegetative states. These studies suggested that despite the lack of external signs of awareness, some patients showed neural activity reminiscent of memory formation. This hinted at the possibility of retained cognitive function, even in a comatose state.
Brain Scans as a Window into Consciousness
Brain scans have become an invaluable tool in this research. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) specifically, is being used to detect memory traces in the brain. By tracking changes in blood flow, fMRI allows scientists to identify areas of the brain that are active during memory formation.
Advanced neuroimaging techniques are also being employed to explore the neural correlations of consciousness. These techniques provide a detailed look at the structure and function of the brain, shedding light on the areas involved in memory retention and consciousness. They are pivotal in understanding how memories might persist in an otherwise unconscious brain.
Real Life Implications: How these Findings Could Change Patient Care
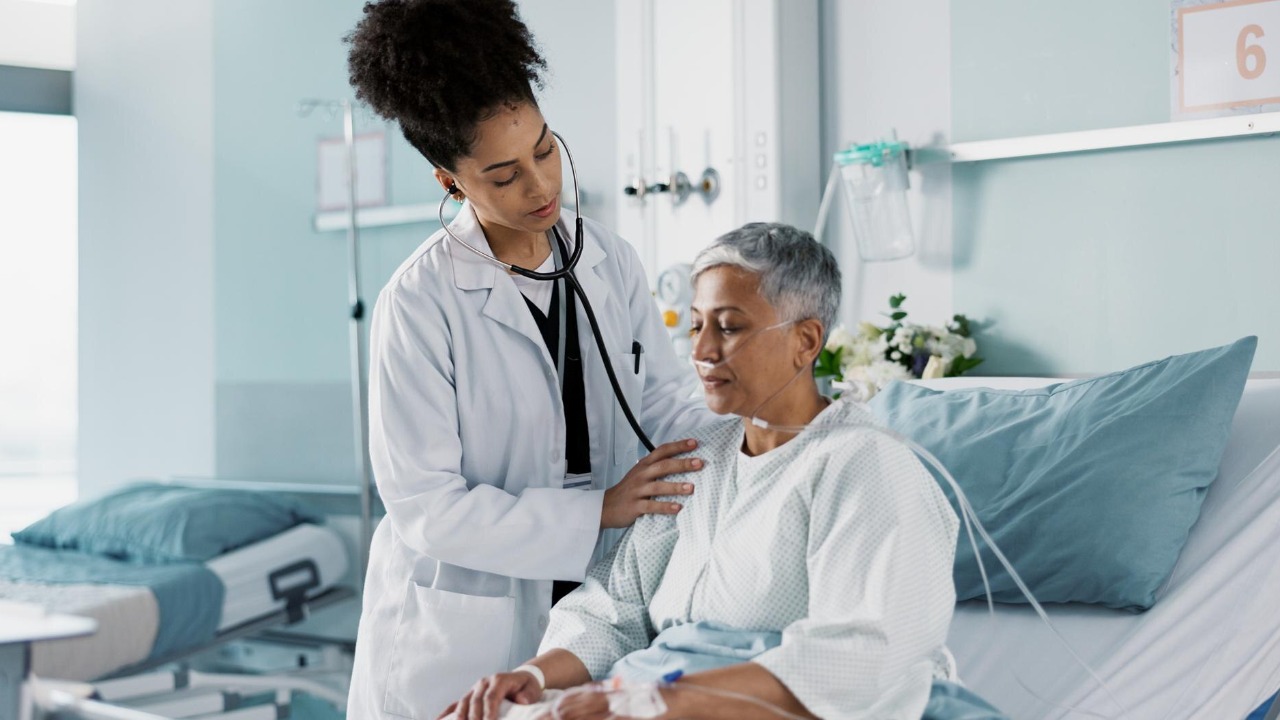

The discovery of memory activity in comatose patients holds profound implications for their care. Medical professionals have started considering these findings when deciding treatment plans. They offer a new way of understanding and communicating with patients who were previously thought to be entirely unconscious.
Moreover, these findings raise significant ethical questions. If a comatose patient retains memory and some degree of consciousness, decisions regarding life support and end-of-life care become even more complex. Research suggests that these findings could lead to new methods for assessing consciousness in comatose patients, potentially changing the criteria on which these decisions are based.
AI and Advanced Technologies in Consciousness Detection

Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in detecting signs of consciousness in comatose patients. Machine learning algorithms are being trained to interpret brain scan data, identifying patterns that might indicate the presence of memories or consciousness.
These AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data more quickly and accurately than humans, potentially improving both the prognosis and treatment plans for patients. For example, AI has already been used to identify signs of consciousness in patients who were clinically diagnosed as being in a vegetative state.
Future of Coma Research: What’s on the Horizon?
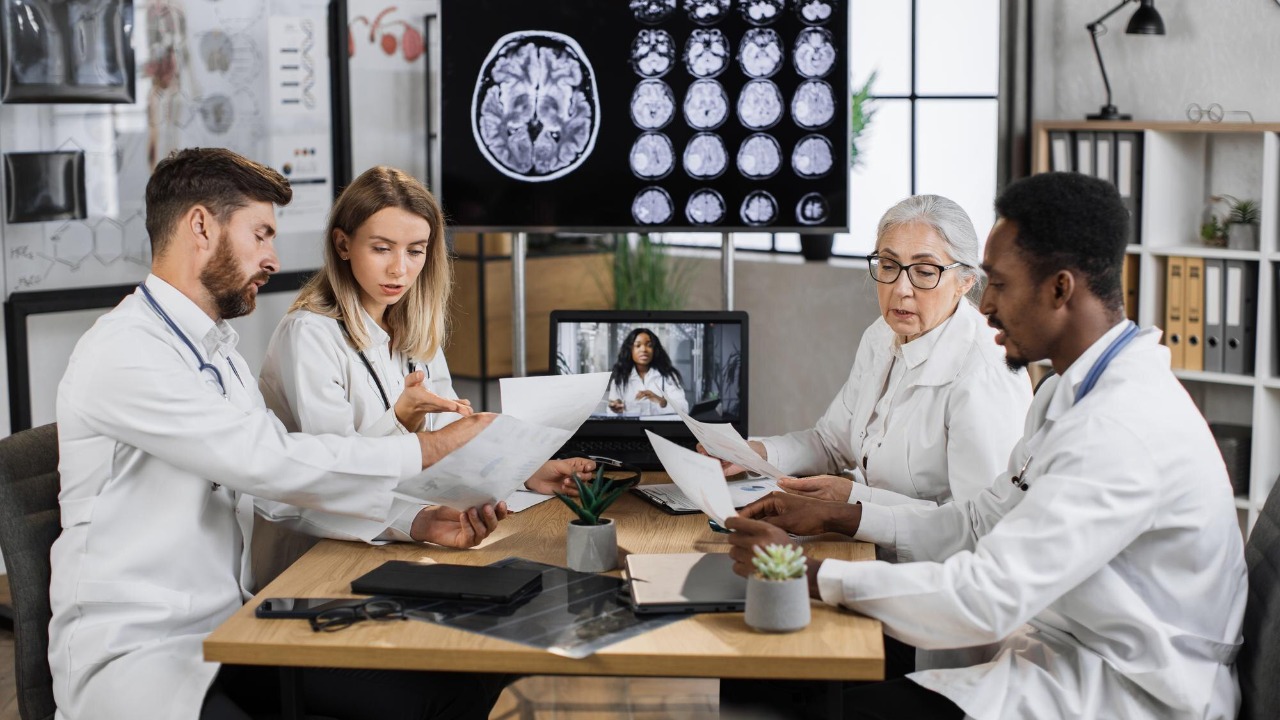

The field of coma research is rapidly evolving, with ongoing research aimed at deepening our understanding of consciousness and cognitive function in comatose patients. Scientists hope to refine the techniques currently used and develop new methods for detecting consciousness and memories.
Furthermore, these advancements could have far-reaching implications beyond the realm of coma research. They may influence broader fields such as neuroscience and cognitive science, changing the way we think about consciousness and memory. There is also the potential for these findings to influence legal and societal views on comas and consciousness, prompting a reevaluation of the rights and care of comatose patients. Recent studies are already sparking important discussions on these topics.