Imagine a world where robots not only look like humans but also feel like us. Advanced technology has made this possible with the invention of bionic skin. This breakthrough allows robots to experience textures, temperatures, and pressures similar to human skin, paving the way for remarkable progress in the fields of robotics and artificial intelligence.
Understanding Bionic Skin

Bionic skin, as the name suggests, is an artificial skin designed to mimic the human skin’s sensory capabilities. It is primarily composed of electronic sensors that can detect and interpret various physical properties such as pressure, temperature, and texture. This technology aims to provide robots with a sense of touch, further enhancing their interaction with the physical world.
The technology behind bionic skin is complex and involves a blend of materials science, electronics, and computer science. The sensors in the bionic skin are usually made of flexible and stretchable materials, allowing them to adapt to the shape of the robot and ensuring durability. These sensors are connected to an electronic system that interprets the signals, similar to how our nervous system decodes sensory information for our brain.
Development and Progress

The journey of bionic skin technology has been an exciting one, marked by continuous advancements and breakthroughs. From the initial stages of rigid and bulky sensors to the present-day ultra-thin and flexible versions, the progress has been significant. The research community is continuously working to enhance the sensitivity and adaptability of these sensors to make them as close as possible to human skin.
However, the development of bionic skin is not without its challenges. One of the significant obstacles has been mimicking the human skin’s ability to feel a wide range of pressures. Recent research has focused on overcoming this challenge by developing pressure sensors that can detect both gentle and strong pressures. Another challenge has been the integration of these sensors into a flexible and stretchable form factor, which has been addressed by advances in materials science.
Bionic Skin in Action: Applications and Uses
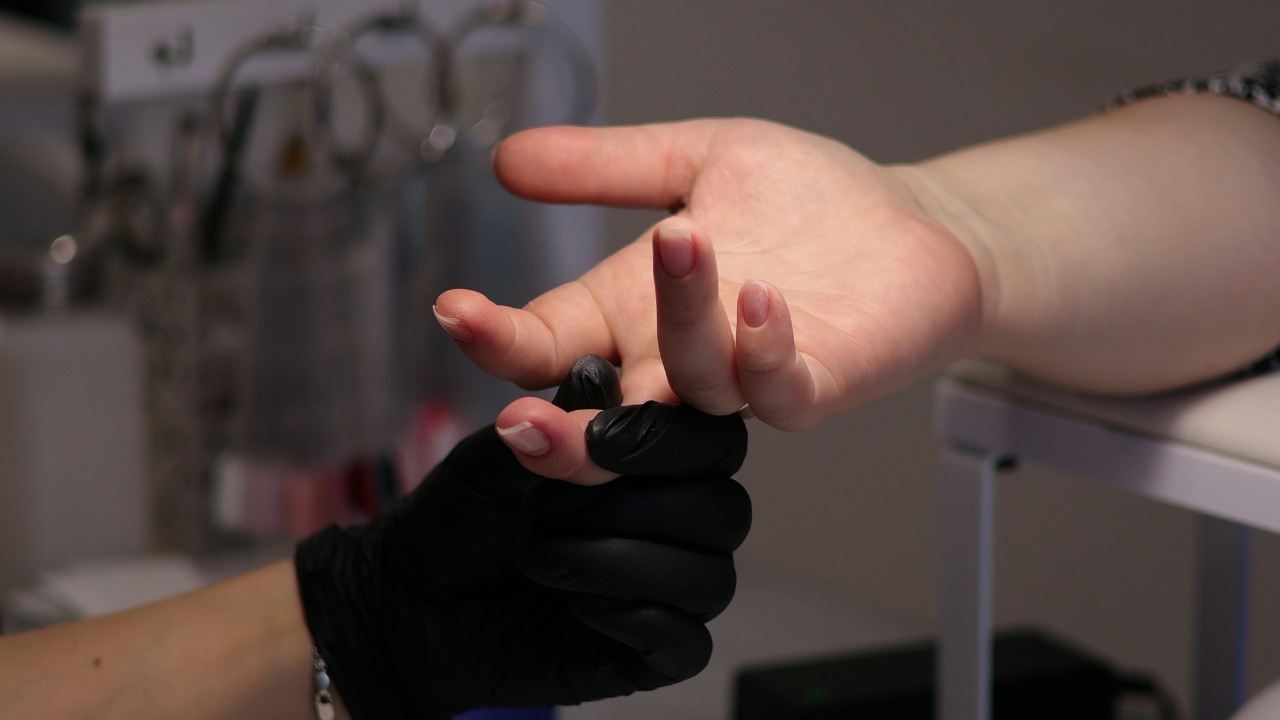
The potential applications of bionic skin are wide-ranging and transformative. For instance, in healthcare, robots equipped with bionic skin could perform delicate tasks such as surgery or patient care, where a precise and sensitive touch is required. In manufacturing, these robots could handle fragile items, reducing the risk of damage.
Another exciting application of bionic skin is in the field of prosthetics. Prosthetic limbs equipped with bionic skin could provide amputees with a sense of touch, significantly enhancing their quality of life. Furthermore, the use of bionic skin could revolutionize human-robot interaction, making it more natural and intuitive. As Earth.com reports, researchers are even exploring the potential of bionic skin in space exploration, where robots could perform tasks in environments too harsh for humans.
Implications for AI and Robotics
The advent of bionic skin is a game-changer for the field of AI and robotics. By providing robots with a sense of touch, we can make them more autonomous and capable of performing a wider range of tasks. This development could also lead to more sophisticated human-robot interactions, where robots can respond to human touch in a more nuanced and natural manner.
Moreover, the integration of bionic skin with AI systems could result in robots that can learn and adapt their behavior based on tactile feedback. This advancement could have profound implications for society, affecting fields ranging from healthcare to manufacturing to space exploration. The future of AI and robotics, powered by bionic skin, is undoubtedly promising and exciting.
The Future of Bionic Skin

Looking ahead, the future of bionic skin appears bright. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see robots that can not only touch and feel but also adapt their behavior based on tactile feedback. This evolution could lead to more sophisticated and capable robots, further blurring the line between humans and machines.
However, this advance also raises important ethical and societal questions. As robots become more like humans, how should they be treated? What rights should they have? These are questions that society will need to grapple with as this technology continues to develop. As a recent UCL News article suggests, the development of bionic skin could also play a crucial role in the advancement of humanoid robots, potentially ushering in a new era in robotics and AI.