In what can only be described as an astonishing breakthrough, astronomers have pinpointed a world of unimaginable heat, where the atmospheric conditions could theoretically conjure storms of diamonds. Let’s take a deep dive into this discovery, and explore what it means for our comprehension of extreme planetary environments.
The Discovery of the Diamond Planet
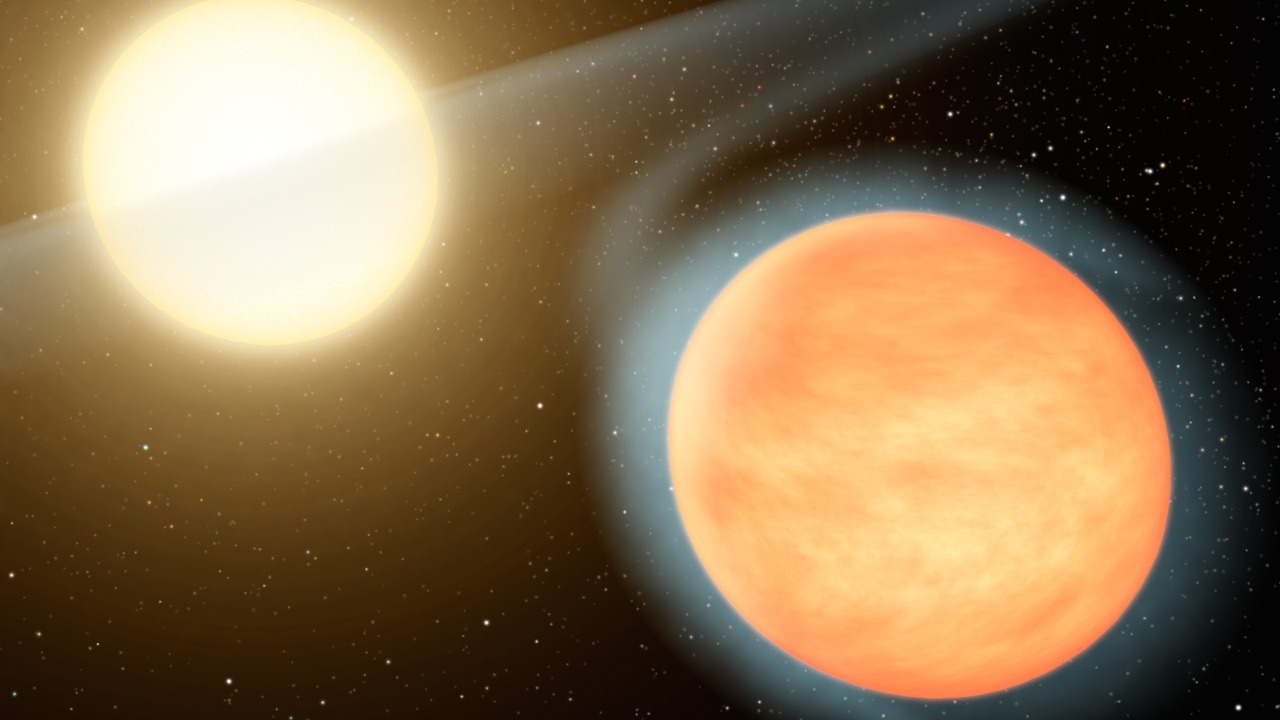
The team behind this extraordinary discovery is a group of international astronomers, who, equipped with cutting-edge telescopes and advanced observational techniques, identified this incredible planet. Utilizing infrared measurements and spectroscopic analyses, they were able to verify the planet’s unique atmospheric characteristics, suggesting the potential for diamond precipitation. Their findings were published in a series of academic papers.
The planet, situated in a distant star system, is considerably larger than Earth. Its location and size were determined through careful astronomical observation and measurement, giving us a glimpse of this exotic world from afar.
Understanding the Atmospheric Conditions

The planet’s conditions are nothing short of extreme. With temperatures reaching tens of thousands of degrees, and pressures far beyond anything we experience on Earth, this world is a testament to the diversity of environments in the cosmos. Its atmosphere, rich in carbon and hydrogen, under such extreme heat and pressure, can potentially lead to the formation of diamonds.
This is no ordinary rain, but a torrent of diamonds that forms deep within the planet’s atmosphere. As carbon and hydrogen atoms bond under extreme heat and pressure, they form diamond particles which then fall towards the planet’s core. This entire process is explained in this educational video.
The Physics Behind Diamond Rain

Let’s delve a little deeper into the fascinating science behind diamond rain. When carbon and hydrogen atoms in the atmosphere combine under extreme heat and pressure, they form diamond structures. These diamond particles are then heavy enough to fall as ‘rain’ towards the planet’s core, a phenomenon known as diamond precipitation.
Interestingly, while the concept of diamond rain may seem alien to us, we do have similar phenomena in our own solar system. The methane rains on Titan, Saturn’s moon, provide a perfect example.
Implications for Space Research

This discovery certainly broadens our understanding of planetary atmospheres and climates. The potential for such extreme environments to exist challenges our conventional notions of planetary science. Furthermore, while it may not be hospitable to life as we know it, the existence of such a planet demonstrates the incredible diversity of worlds out there.
Moreover, the discovery of this diamond planet could also influence the search for other exotic planets. As our astronomical observation techniques and tools improve, we are becoming increasingly capable of detecting and studying such extreme environments.
Future Prospects for Exploration

Exploring such a planet poses both challenges and opportunities. The extreme conditions would require advanced technology and innovative approaches. However, the potential scientific rewards are enormous – from expanding our understanding of planetary science to potentially discovering new materials and phenomena.
Looking ahead, this discovery may pave the way for future space missions and research projects. Technological advancements will play a crucial role in exploring such extreme planetary environments. As we continue our journey into the cosmos, who knows what other remarkable discoveries await us?