A recent study has sparked a wave of speculation by suggesting that hostile alien civilizations might be hiding in our galaxy. This research, which challenges traditional astrobiology assumptions, posits that extraterrestrial intelligence may deliberately avoid detection. The findings hint at the possibility of widespread hidden life across the cosmos, urging a reevaluation of search strategies for alien civilizations.
The Study’s Core Claim
The study, published in 2022, centers on the provocative idea that hostile alien civilizations might be hiding in our galaxy right now. This assertion is derived from models of interstellar behavior and survival strategies. The timing of the study is particularly notable in the context of ongoing Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) efforts.
The research offers a fresh perspective on why advanced civilizations might choose to remain concealed. The study implies that avoidance of conflict or resource competition could be motivating factors for such behavior. These implications urge us to reconsider our understanding of extraterrestrial life and its potential strategies for survival.
Furthermore, the study suggests that these hidden civilizations might not only be advanced but also potentially superior in terms of technology and resources. This could explain their ability to remain undetected despite our increasingly sophisticated search methods. The study also raises the question of whether these civilizations might have observed us without our knowledge, further challenging our assumptions about our place in the cosmos.
Additionally, the study’s core claim prompts us to consider the potential consequences of contact with these civilizations. If they are indeed hostile and technologically superior, such encounters could pose significant risks. This underscores the importance of developing strategies not only for detection but also for potential interaction with extraterrestrial intelligence.
Evidence from Galactic Models

The study employs theoretical models to predict the presence of hidden alien civilizations in the Milky Way. These models focus on simulations of civilization expansion and the risks associated with detection. The specificity of the claim to “our galaxy right now” suggests that current observational data from telescopes like Hubble or James Webb might be overlooking these hidden societies.
Examples of galactic zones where hiding could be feasible due to natural cosmic phenomena are also explored. Dense star clusters, for instance, could provide ideal conditions for concealment, further complicating our efforts to detect advanced civilizations.
Moreover, the study’s models suggest that the distribution of these hidden civilizations might not be uniform across the galaxy. Certain regions, such as the galactic center or the outer rim, might be more conducive to concealment. This could have significant implications for our search strategies, prompting us to focus our efforts on these potentially high-yield areas.
The study also highlights the role of cosmic events, such as supernovae or gamma-ray bursts, in shaping the distribution of hidden civilizations. These events could create ‘safe zones’ where civilizations can hide, or ‘danger zones’ that they would likely avoid. Understanding these dynamics could further refine our search for extraterrestrial life.
Implications for Distant Galaxies

The study’s findings on potential hiding places in the Milky Way could extend to distant galaxies, like Andromeda or those in the Virgo Cluster. In these galaxies, signals from alien civilizations might be even harder to detect. The research provides metrics, such as estimated civilization densities, which could be scaled to intergalactic distances.
Observational challenges, including light travel times and redshift effects, could further mask alien activity in far-off galaxies. These factors underscore the complexity of the search for extraterrestrial intelligence and the need for innovative detection strategies.
Furthermore, the study’s findings could have profound implications for our understanding of the universe’s large-scale structure. If hidden civilizations are common in our galaxy, they might also be common in other galaxies, potentially even in galaxy clusters or superclusters. This could significantly expand the scope of our search for extraterrestrial intelligence.
The study also suggests that the presence of hidden civilizations could influence the evolution of galaxies. For instance, advanced civilizations might harness the energy of their host galaxies in ways that could leave detectable signatures. Identifying these ‘galactic technosignatures’ could be a promising avenue for future research.
Hostility and Survival Strategies

The study delves into the “hostile” aspect of the alien civilizations it describes. It examines evolutionary pressures that might lead to aggressive or defensive behaviors. The claim that “Hostile Alien Civilizations Might Be Hiding In Our Galaxy Right Now” is rooted in theories such as game theory or dark forest hypotheses.
The study’s conceptual framework provides examples of potential strategies that these civilizations might employ. Technological stealth or signal jamming, for instance, could be used to evade detection by other advanced societies.
Moreover, the study explores the potential motivations behind the hostility of these hidden civilizations. It suggests that these civilizations might perceive any form of contact as a threat, prompting them to adopt a ‘shoot first, ask questions later’ strategy. This could explain their apparent hostility and their efforts to remain hidden.
The study also discusses the potential implications of these survival strategies for our own civilization. It warns that our current efforts to broadcast our presence might be perceived as a threat, potentially provoking a hostile response. This raises important ethical and strategic questions about our approach to the search for extraterrestrial intelligence.
Connections to SETI Research
The 2022 study has significant implications for ongoing SETI programs. These programs are currently scanning for technosignatures in both nearby and distant galactic regions. The timing of the study’s release coincides with breakthroughs in radio astronomy, adding another layer of relevance to its findings.
The study also suggests that search protocols may need to be revised to account for hidden or evasive civilizations. This could involve a shift from passive listening to active signaling, or the development of new detection technologies.
Moreover, the study’s findings could inform the design of future SETI experiments. For instance, they could guide the development of new search algorithms that are better suited to detect hidden or evasive civilizations. They could also inspire novel experimental approaches, such as the use of machine learning or artificial intelligence to analyze complex astronomical data.
The study also highlights the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in SETI research. It suggests that insights from fields such as evolutionary biology, game theory, or computer science could enhance our understanding of extraterrestrial intelligence and its potential behaviors. This underscores the need for a holistic approach to the search for alien life.
Scientific Skepticism and Debate

While the study’s claim is intriguing, it has also sparked debate. Critics point to the lack of direct evidence for hostile aliens in our galaxy or distant ones. The assertion that “hostile alien civilizations might be hiding” is weighed against solutions to the Fermi Paradox, which questions the apparent contradiction between high estimates of extraterrestrial life and the lack of contact or evidence for such civilizations.
Expert opinions and related studies offer a range of perspectives, with some supporting the idea of widespread cosmic concealment and others challenging it. This ongoing debate underscores the complexity and uncertainty of the search for extraterrestrial intelligence.
Moreover, the study’s claim has sparked discussions about the role of speculation in scientific research. While some argue that speculative hypotheses can stimulate innovative thinking and drive progress, others caution against the risk of unfounded conjecture. This debate reflects the broader tension between imagination and rigor in the scientific process.
The study also serves as a reminder of the inherent uncertainty in our search for extraterrestrial intelligence. Despite our best efforts, we might never find definitive proof of alien life, let alone hostile hidden civilizations. This humbling prospect underscores the importance of maintaining an open mind and a critical perspective in our cosmic quest.
Future Directions in Exploration
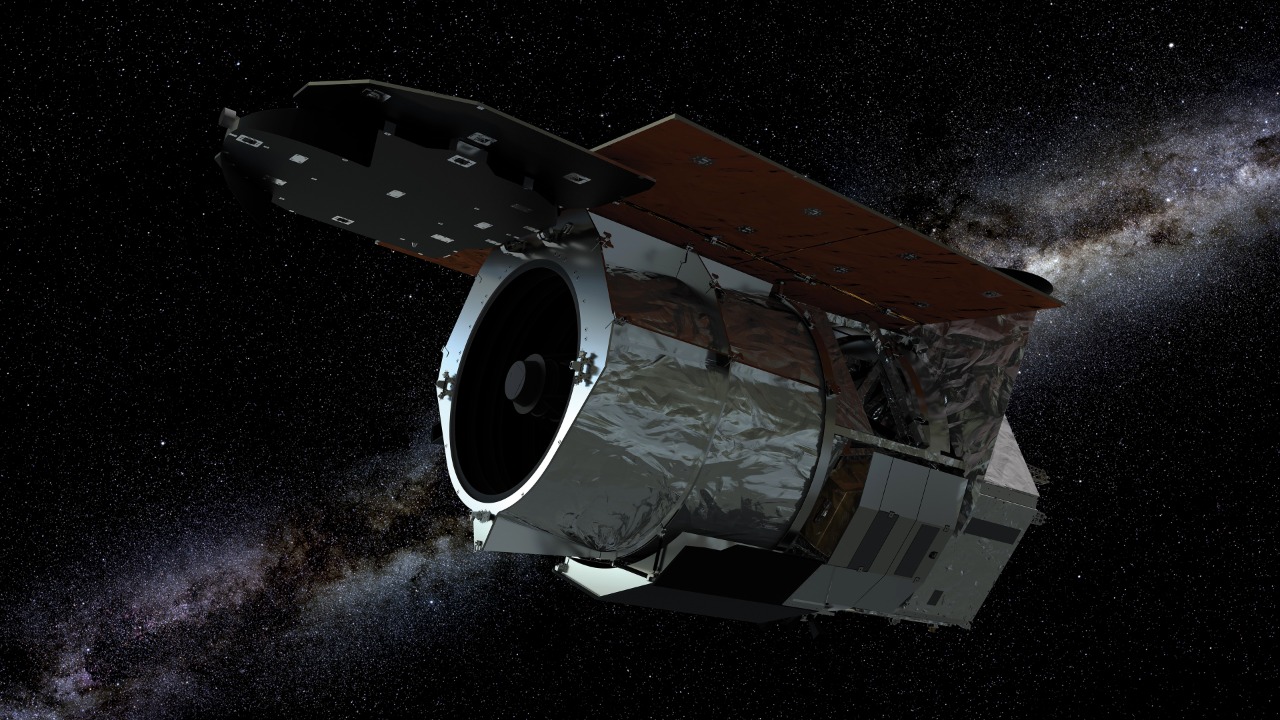

Inspired by the study, future exploration efforts might involve enhanced surveys of distant galaxies. Upcoming missions like the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope could play a crucial role in these endeavors. The study’s core finding, published in 2022, serves as a catalyst for interdisciplinary research in astrobiology and cosmology.
The study also has implications for public engagement. While it’s important to avoid overhyping unverified possibilities, claims like these can fuel interest in the search for alien life and inspire a new generation of scientists and explorers.
Moreover, the study’s findings could inspire new technological developments. For instance, they could drive the design of advanced telescopes or sensors capable of detecting subtle signs of hidden civilizations. They could also stimulate research into novel communication technologies that could facilitate contact with these civilizations.
The study also underscores the importance of international cooperation in the search for extraterrestrial intelligence. Given the global implications of potential contact with alien life, it is crucial that this endeavor is pursued as a collective human effort. This could involve sharing data and resources, coordinating search strategies, and developing joint protocols for potential contact scenarios.
Source: BGR