NASA’s Curiosity rover recently made a significant geological discovery on Mars by accidentally breaking open a rock. This serendipitous event revealed unexpected mineral compositions, offering new insights into the planet’s history and geochemical processes. The revelation of sulfur and other elements inside the rock is shaping new theories about Mars’s past, potentially rewriting our understanding of the Red Planet’s geological narrative.
The Discovery of the Martian Rock

The Curiosity rover has been a pivotal part of Mars exploration since its landing in 2012. Equipped with advanced scientific instruments, the rover’s mission is to study the planet’s climate and geology, assess whether conditions were ever favorable for microbial life, and prepare for future human exploration. Recently, during its routine exploration, Curiosity inadvertently rolled over a rock, breaking it open in the process. This unexpected incident triggered excitement among scientists, as the rover’s cameras and sensors immediately documented the contents of the fractured rock.
The circumstances leading to the rock’s fracture were quite unplanned. As Curiosity maneuvered across the rocky terrain of Mars, its wheels exerted pressure on a particularly fragile rock. The resulting breakage revealed an interior previously hidden from view, sparking a flurry of scientific inquiry. Initial observations made by Curiosity’s onboard instruments were transmitted back to Earth, where scientists were surprised by the unexpected mineralogical composition within the rock, which included a notable presence of sulfur.
What Was Inside the Rock

The interior of the rock turned out to be a treasure trove of mineral compositions that were previously unobserved in such abundance. Among the elements discovered, sulfur stood out as particularly intriguing, suggesting complex chemical reactions that may have occurred in Mars’s past. The presence of sulfur, along with other minerals, provides valuable clues about the geological processes that shaped the planet’s surface.
This discovery contrasts with previous findings on Mars, where surface rocks primarily consisted of basaltic compositions. The newfound minerals, including sulfates, hint at a more varied geological history than previously thought. The presence of sulfur suggests the possibility of water-related processes, as sulfates often form in the presence of water. This aligns with other research that suggests Mars once harbored liquid water, further supporting theories of a potentially habitable environment in the planet’s distant past.
Implications for Martian Geology
This unexpected find provides a fresh perspective on the geological history of Mars. The presence of sulfur and other minerals within the rock suggests that Mars may have experienced periods of volcanic activity that contributed to its diverse geological landscape. The interaction of volcanic materials with water could have led to the formation of these mineral deposits, offering a glimpse into the planet’s dynamic past.
Understanding the role of water in forming these mineral compositions is crucial for reconstructing Mars’s climatic history. The implications extend to theories regarding the planet’s ancient climate and environmental conditions. If water played a significant role in shaping these minerals, it could indicate that Mars once had conditions suitable for sustaining life. This discovery enriches our understanding of the Red Planet’s geological narrative, potentially guiding future research and exploration efforts.
Technological Advances in Rover Exploration
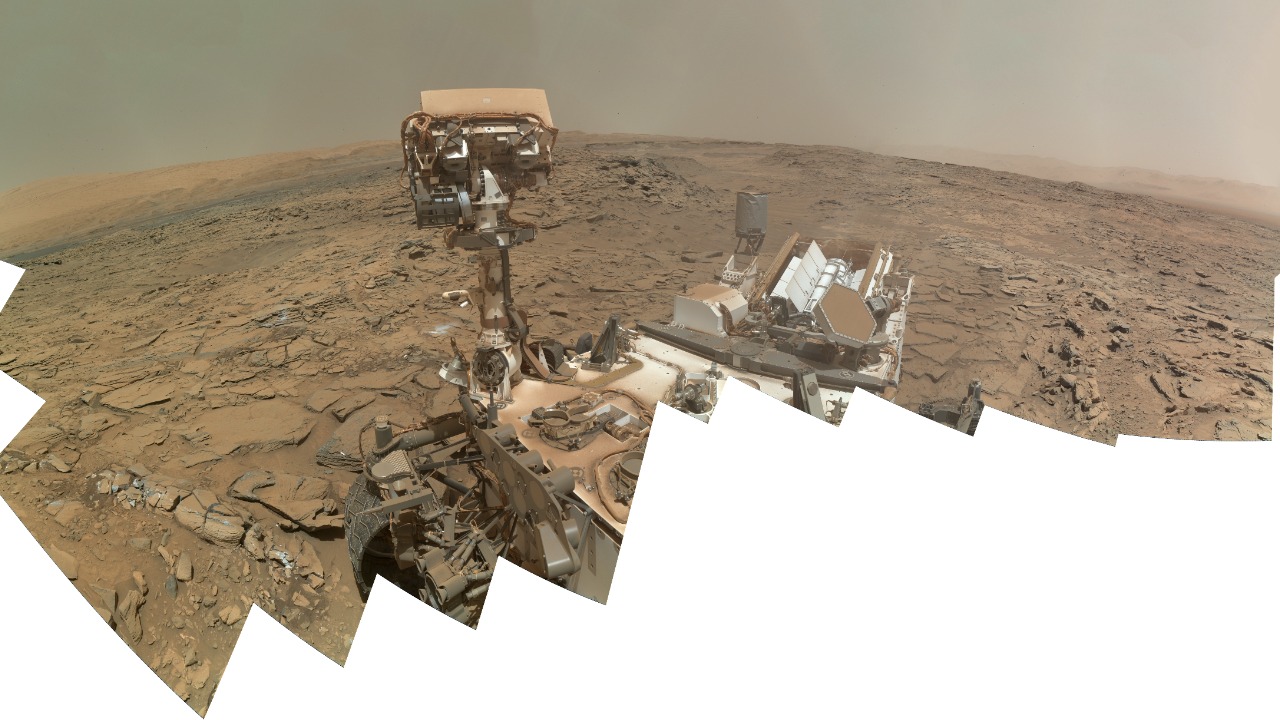
The Curiosity rover’s ability to analyze rocks and transmit data back to Earth is a testament to technological advancements in space exploration. Equipped with sophisticated instruments such as the Chemistry and Camera (ChemCam) and the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI), Curiosity can conduct detailed analyses of rock and soil samples. These tools allow scientists to study the mineral composition and texture of Martian rocks, providing valuable insights into the planet’s geological past.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning play a significant role in enhancing the rover’s capabilities. These technologies enable Curiosity to make autonomous decisions, such as selecting which rocks to analyze and optimizing its exploration path. As space exploration technology continues to evolve, future missions may benefit from these advancements, paving the way for more efficient and effective exploration of Mars and beyond. According to an IEEE research paper, integrating AI into planetary exploration can significantly enhance data collection and analysis processes.
The Broader Impact on Mars Research
The accidental discovery made by the Curiosity rover has broader implications for Mars research, particularly in the search for past life on the planet. The presence of sulfur and other minerals suggests that Mars may have once had a more complex environment than previously thought, potentially capable of supporting microbial life. This finding fuels ongoing research efforts aimed at understanding the planet’s habitability and the likelihood of life beyond Earth.
Serendipitous discoveries like this one highlight the unpredictable nature of space exploration and its potential to yield groundbreaking insights. Such findings underscore the importance of ongoing missions to Mars, as each mission contributes to a growing body of knowledge that informs future exploration endeavors. As we look to the future, the insights gained from this discovery could play a crucial role in planning for manned missions to Mars, ultimately moving us closer to the possibility of human colonization.