In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, innovations continuously push the boundaries of what’s possible. However, some advancements raise ethical, legal, and environmental concerns, prompting discussions about potential bans or regulations. Here, I explore eight innovations that might face legal challenges in the near future.
Facial Recognition Technology

Facial recognition technology has become a ubiquitous tool in security and surveillance. It aids in identifying individuals quickly and accurately. However, concerns about privacy and misuse have led to calls for its regulation. Critics argue that it can be used for racial profiling and unauthorized surveillance, infringing on civil liberties. Some cities and countries have already enacted bans or restrictions, and this trend could grow as the debate over privacy versus security intensifies.
Deepfake Software

Deepfake technology has advanced to the point where it can create incredibly realistic yet entirely fake videos. While it offers exciting possibilities for entertainment and media, it also poses significant risks. The potential for misuse in spreading misinformation or manipulating public opinion is a major concern. As deepfake software becomes more accessible, governments may move to regulate or ban the technology to prevent its use in malicious activities.
Cryptocurrency Mining Operations

Cryptocurrency mining operations have exploded in popularity, driving up demand for computing power and electricity. However, the environmental impact of these operations is staggering, with some studies suggesting they consume more energy than entire countries. As concerns about climate change grow, some governments are considering imposing restrictions or outright bans on mining activities to curb their environmental footprint. The future of crypto mining could hinge on finding more sustainable practices.
Autonomous Drones
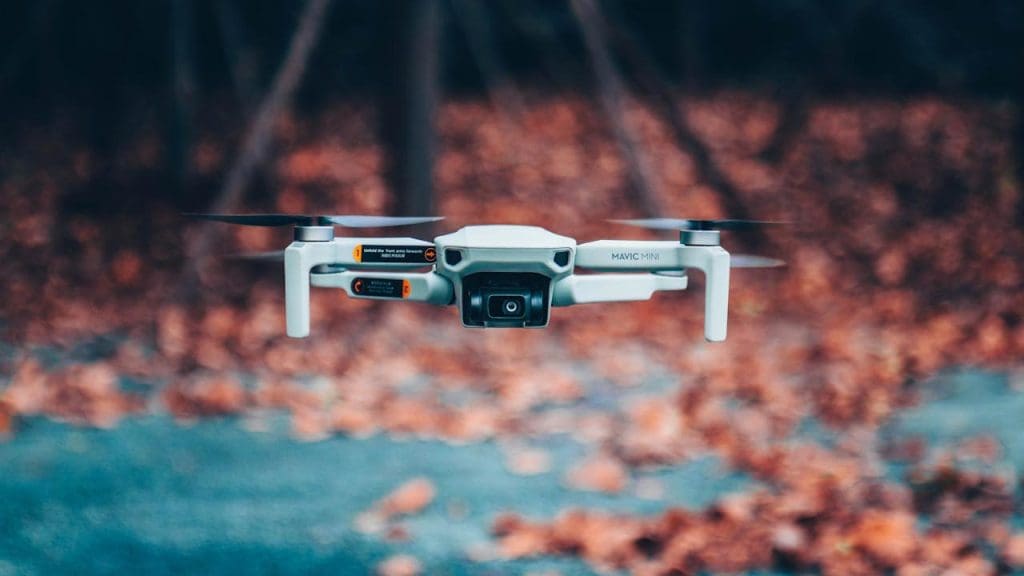

Autonomous drones are revolutionizing industries from delivery to agriculture. However, their rapid deployment raises issues of safety, privacy, and airspace regulation. There are fears about drones being used for surveillance or even weaponization. As incidents involving drones increase, governments may introduce tighter controls or outright bans to ensure public safety and protect personal privacy.
Gene Editing Tools
Gene editing tools like CRISPR have the potential to eradicate genetic diseases and enhance human capabilities. However, the ethical implications of modifying human DNA are profound. Concerns about “designer babies” and unforeseen genetic consequences have sparked debates about the responsible use of this technology. Some countries may choose to ban or heavily regulate gene editing to prevent misuse and protect human genetic integrity.
Encrypted Messaging Apps

Encrypted messaging apps provide users with privacy and security in their communications. However, they also pose challenges for law enforcement agencies trying to combat crime and terrorism. The debate over privacy versus security could lead to legal battles over whether these apps should be regulated or banned. A balance must be struck between protecting individual privacy and ensuring national security.
Smart Home Surveillance Devices
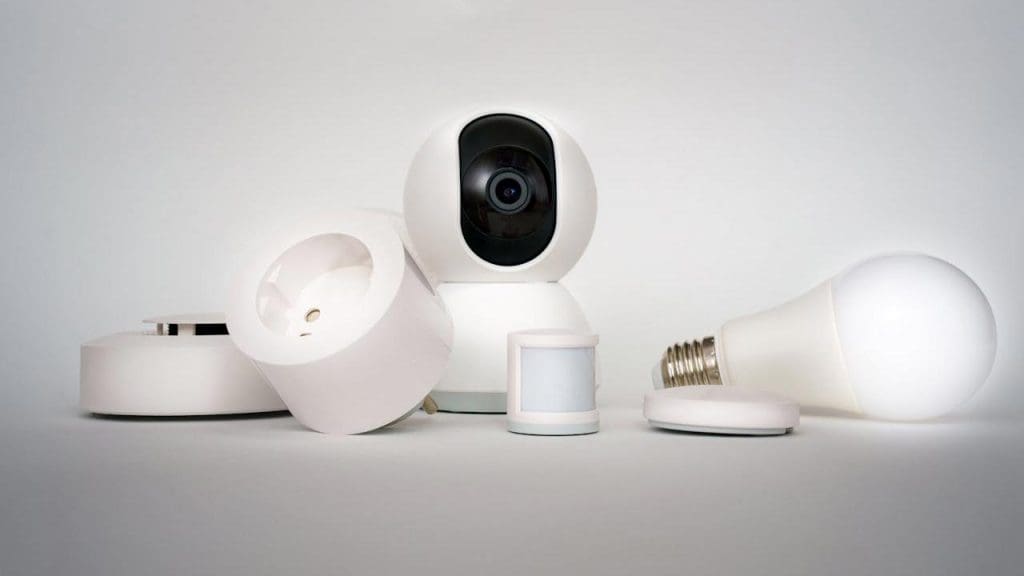

Smart home surveillance devices offer convenience and enhanced security for homeowners. However, they also raise concerns about privacy invasion and data security. The potential for these devices to be hacked or misused for unauthorized surveillance has led to calls for stricter regulations. As the smart home market grows, we may see increased scrutiny and potential bans on certain surveillance technologies to protect consumer privacy.
Synthetic Meat Production
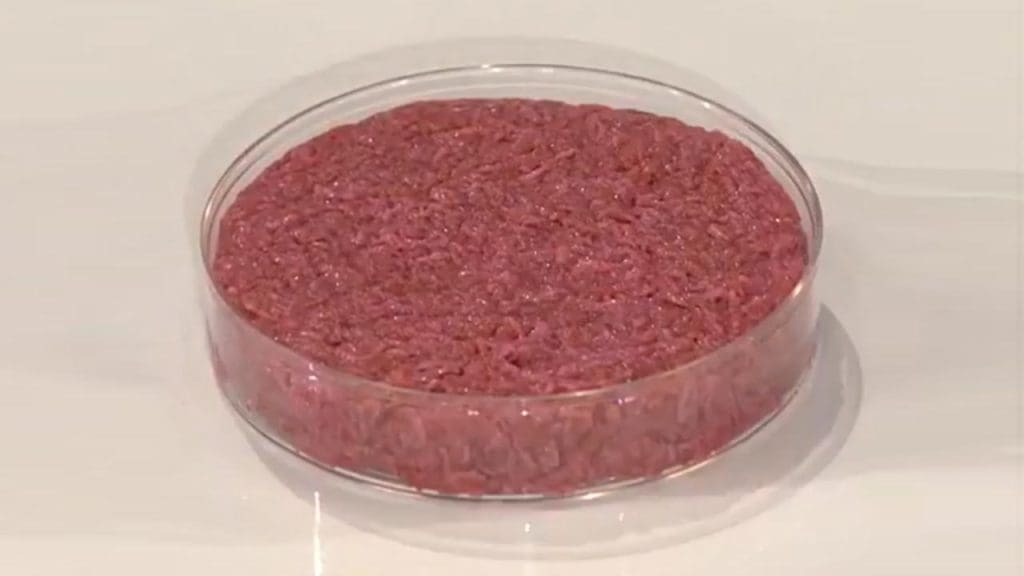

Synthetic meat production promises to revolutionize the food industry by reducing the environmental impact of traditional meat farming. However, the technology behind lab-grown meat is still in its infancy, and concerns about health, safety, and labeling have emerged. Some countries might impose bans or stringent regulations on synthetic meat production until these issues are resolved. The future of food could be shaped by how these concerns are addressed.