As technology advances, so does the ability of automakers to monitor drivers. While these innovations can enhance safety and convenience, they also raise questions about privacy. From data collection to third-party sharing, here’s a closer look at how automakers are keeping tabs on us.
Data Collection Through In-Car Connectivity Systems
The rise of in-car connectivity systems has made it easier than ever for automakers to collect data from drivers. These systems gather information on driving habits, vehicle performance, and even entertainment preferences. While this data helps improve vehicle features, it also means that every trip is potentially being monitored and recorded.
Cars equipped with modern connectivity systems are like smartphones on wheels, constantly communicating with manufacturers’ servers. This data collection allows automakers to offer personalized services and updates, but it also means a considerable amount of personal information is being stored and possibly shared.
GPS Tracking and Location Monitoring
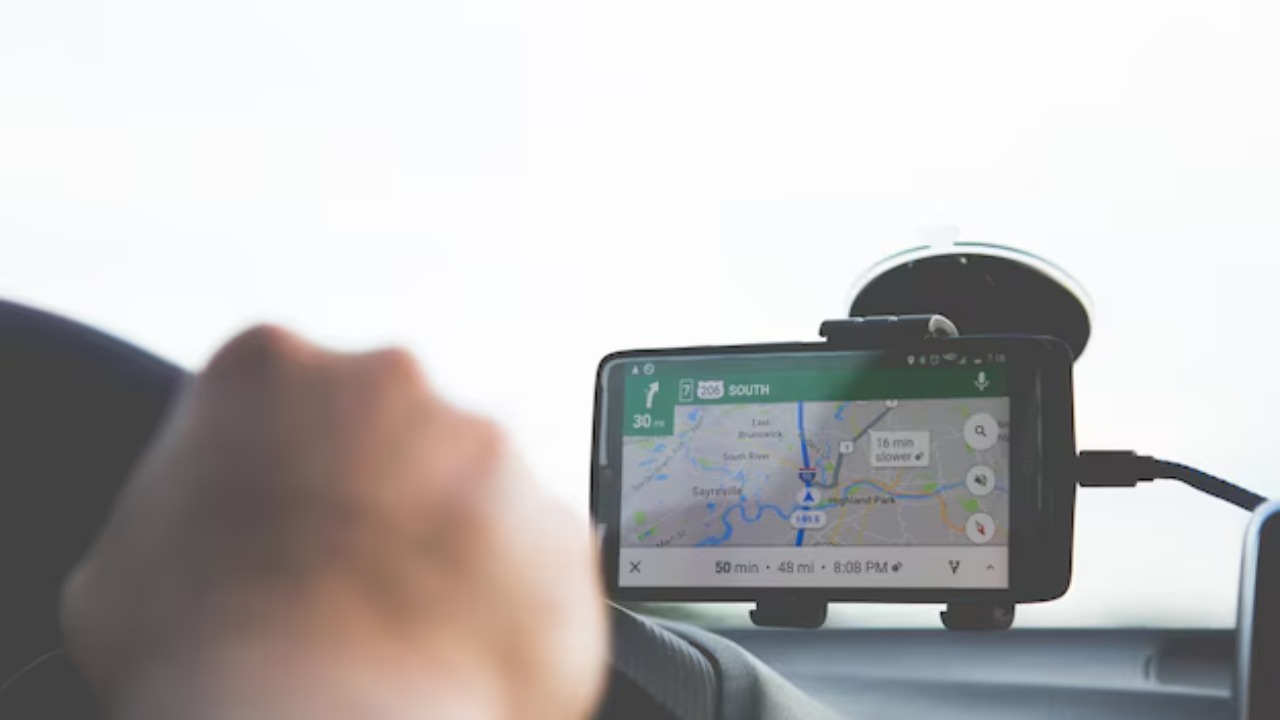
GPS technology is a staple in most vehicles today, offering navigation and location-based services. However, this feature also enables automakers to track a vehicle’s every movement. The constant GPS tracking allows for precise monitoring of your location, which can be used for various purposes, including targeted advertising and service adjustments.
While GPS can greatly enhance the driving experience, it also raises privacy concerns. Drivers might not be aware of the extent to which their location data is stored and possibly shared with third-party entities without explicit consent.
Event Data Recorders and Black Boxes

Event Data Recorders (EDRs), commonly known as black boxes, are installed in many vehicles to record data related to road incidents. This includes speed, braking patterns, and seatbelt usage. While these devices are primarily for accident analysis, they also capture a wealth of information that could potentially be accessed by automakers and other stakeholders.
The presence of EDRs in vehicles is often unknown to drivers, raising questions about transparency and consent. Understanding their role and how the data is used can help drivers be more informed about the extent of surveillance in their vehicles.
Voice Recognition and Cabin Surveillance

Voice recognition systems are designed to enhance convenience by allowing drivers to control various features hands-free. However, these systems often listen continuously for voice commands, potentially capturing conversations within the cabin. Cabin surveillance technologies, including cameras, may also be present in some models.
While these features aim to assist drivers, they also present privacy challenges. The data collected through voice and video may be stored by automakers, raising questions about who has access to this information and how it might be used.
Smartphone Integration and App Data Sharing

Smartphone integration through systems like Apple CarPlay and Android Auto offers seamless connectivity, but it also opens the door to data sharing between your phone and your car. Automakers can access contact lists, messages, and app usage data, potentially sharing this information with third parties.
This integration offers convenience but also requires drivers to be mindful of permissions and data sharing policies. Understanding how apps interact with your vehicle can help you manage what personal information is accessible through your car.
Usage-Based Insurance and Telematics

Usage-based insurance programs use telematics devices to monitor driving behavior, offering potential discounts for safe driving. However, this also means insurers have access to detailed data about your driving habits, including speed, braking, and distance traveled.
While these programs can provide financial benefits, they also represent another layer of surveillance. Drivers should weigh the potential savings against the privacy implications of sharing detailed driving data with insurance companies.
Third-Party Partnerships and Data Sharing Agreements

Automakers frequently engage in partnerships with third-party companies, sharing collected data for various purposes. These partnerships may include tech companies, advertisers, or service providers, allowing them access to valuable consumer data.
While these collaborations can lead to enhanced services and innovations, they also complicate the privacy landscape. Drivers should be aware of automakers’ data sharing agreements and consider the potential implications of their personal information being distributed to multiple entities.