Digging beneath the ocean’s surface requires specialized machinery designed to withstand intense underwater conditions. These machines are pivotal for various applications such as laying cables, constructing tunnels, and mining resources. Let’s delve into some of the remarkable machines that make underwater digging possible.
Tunnel Boring Machines (TBMs)

Tunnel Boring Machines, or TBMs, are engineering marvels used to excavate tunnels through rock and soil. They are essential for constructing underwater tunnels, such as those found in subways or roadways connecting landmasses. These machines are designed to operate under extreme pressure and varying geological conditions beneath the sea floor. One of the most impressive TBMs was employed for the Jinan-Huanggang Road Yellow River Crossing Tunnel, showcasing their capability to handle complex and large-scale projects.
TBMs work by using a rotating cutting wheel at the front to bore through the earth, while a conveyor system moves the excavated material away. The machine simultaneously installs precast concrete segments to form the tunnel lining, ensuring stability. With advancements in technology, TBMs have become more efficient and environmentally friendly, making them a preferred choice for underwater construction.
Subsea Trenchers
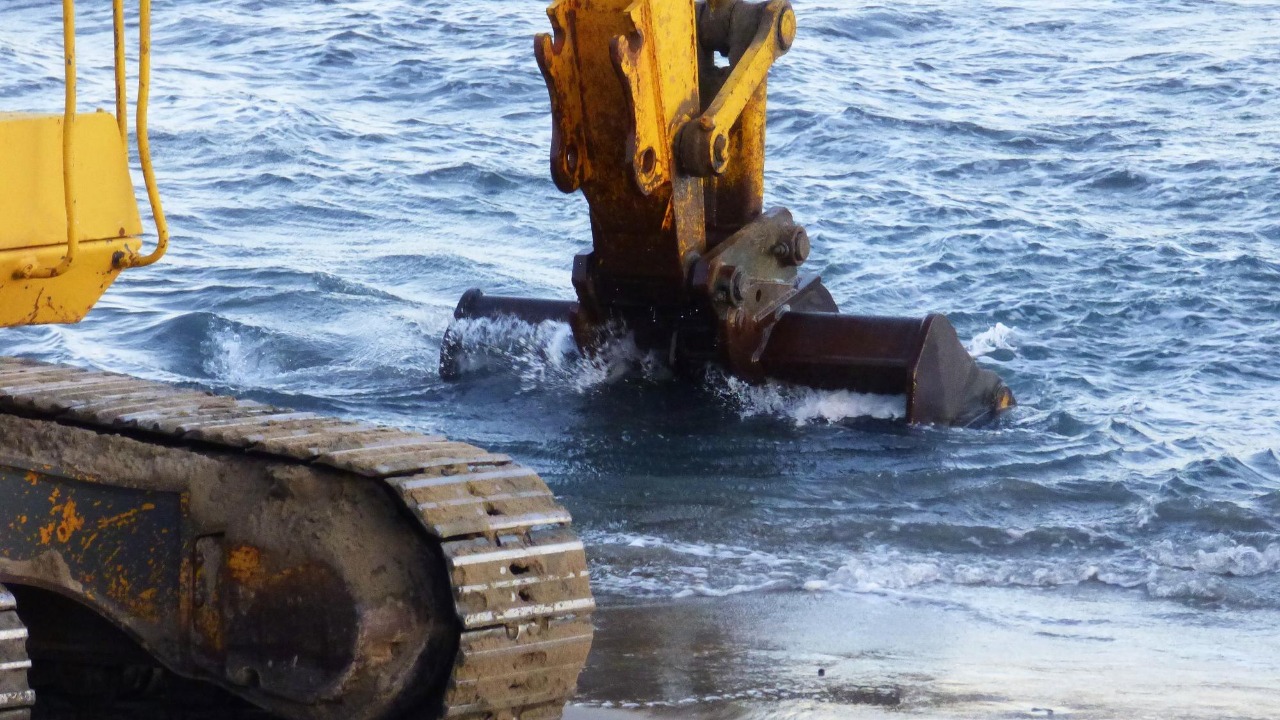

Subsea trenchers are vital for creating trenches on the ocean floor to lay pipelines and cables. These machines are often equipped with powerful jets or mechanical tools that cut through sediment and rock. Their ability to precisely control the trench depth and width makes them indispensable for undersea construction projects.
Typically, subsea trenchers are deployed from ships and operated remotely to ensure precision and safety. They are essential in the deep-sea mining industry, where they prepare the seabed for resource extraction. By creating stable pathways, they help protect cables and pipelines from environmental hazards and human interference, ensuring the longevity and reliability of underwater infrastructure.
Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs)
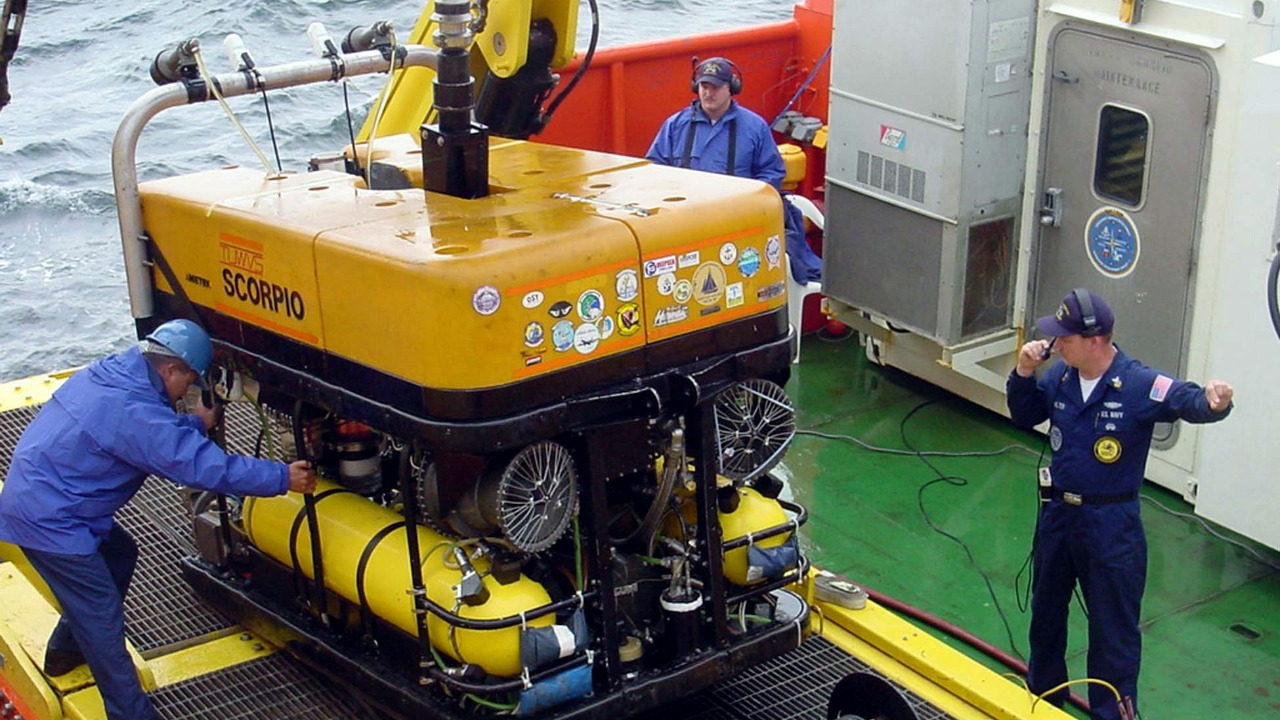

Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs) are crucial for underwater exploration and excavation. Controlled from the surface, these robotic machines are equipped with cameras and various tools to perform tasks ranging from inspection to excavation. They are particularly useful in environments that are too dangerous or inaccessible for human divers.
ROVs have been instrumental in numerous marine research and industrial projects. Their adaptability allows them to perform complex tasks, such as cable installation and maintenance, with precision. The versatility of ROVs makes them a staple in oceanographic studies and subsea construction, providing invaluable support to scientists and engineers alike.
Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs)
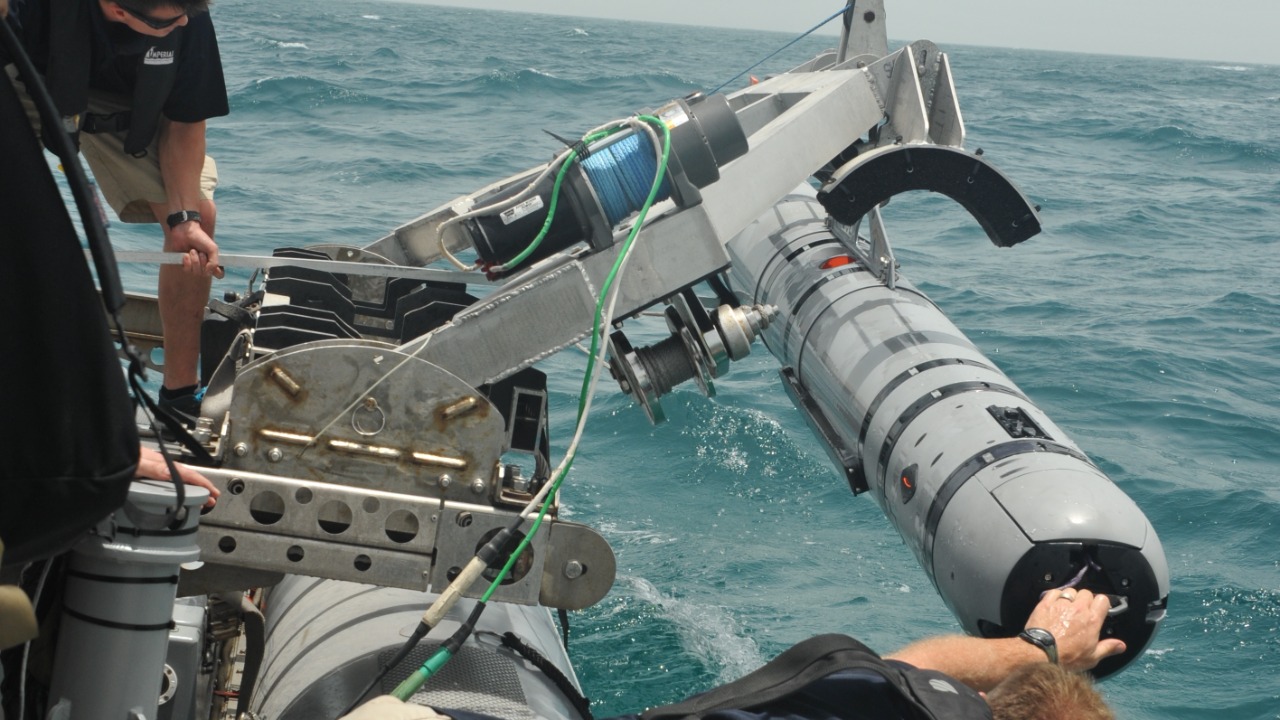
Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) are self-guided machines used for mapping and surveying the ocean floor. Unlike ROVs, AUVs operate independently without direct human control, making them ideal for long-duration missions. They are equipped with advanced sensors and cameras to collect data and navigate autonomously.
AUVs play a significant role in underwater research and exploration, providing detailed maps of the seabed and identifying potential resources. Their ability to operate in harsh environments makes them valuable tools for scientific studies and commercial applications, such as oil and gas exploration or environmental monitoring.
Cable Plows

Cable plows are specialized machines designed to install cables beneath the ocean floor. These devices are towed by ships and use a blade to create a trench in which the cable is laid. The trench is then backfilled, securing the cable in place and protecting it from external damage.
The use of cable plows is essential for the deployment of undersea communication and power cables. They ensure that the cables are buried at the correct depth to prevent damage from marine traffic or natural oceanic movements. By safeguarding these vital connections, cable plows contribute significantly to global communication and energy transmission networks.
Suction Dredgers
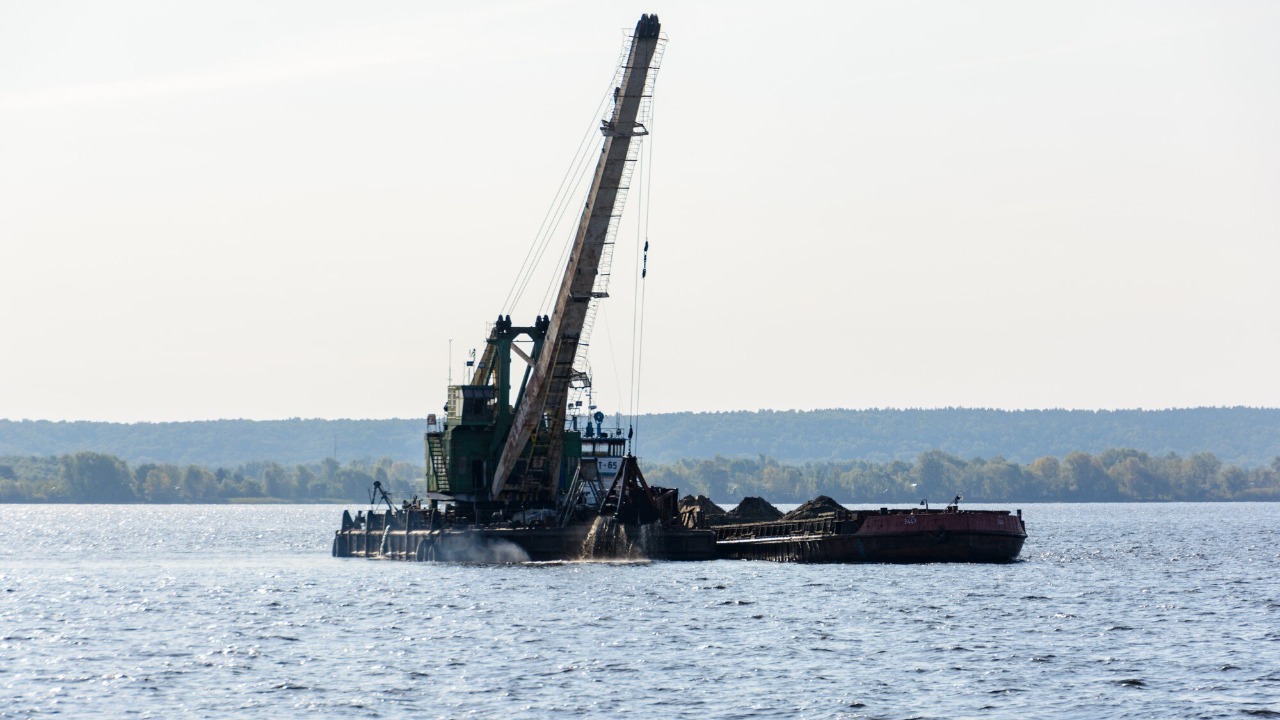

Suction dredgers are machines used to remove sediment from the ocean floor, making them vital for maintaining navigable waterways and preparing sites for construction. These dredgers use powerful pumps to suck up sediment and transport it through a pipeline to a designated disposal area. In addition to clearing shipping channels, suction dredgers are used in land reclamation projects and underwater mining. They are particularly effective in areas with loose sediment, where precision and efficiency are required. The versatility and capability of suction dredgers make them indispensable in managing and modifying marine environments for various purposes.