In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial manufacturing, lasers have emerged as a transformative force, revolutionizing various facets of factory operations. From enhancing precision to bolstering safety, lasers are at the forefront of modernizing production lines. Here are five key ways lasers are reshaping factories today.
Enhanced Precision in Manufacturing
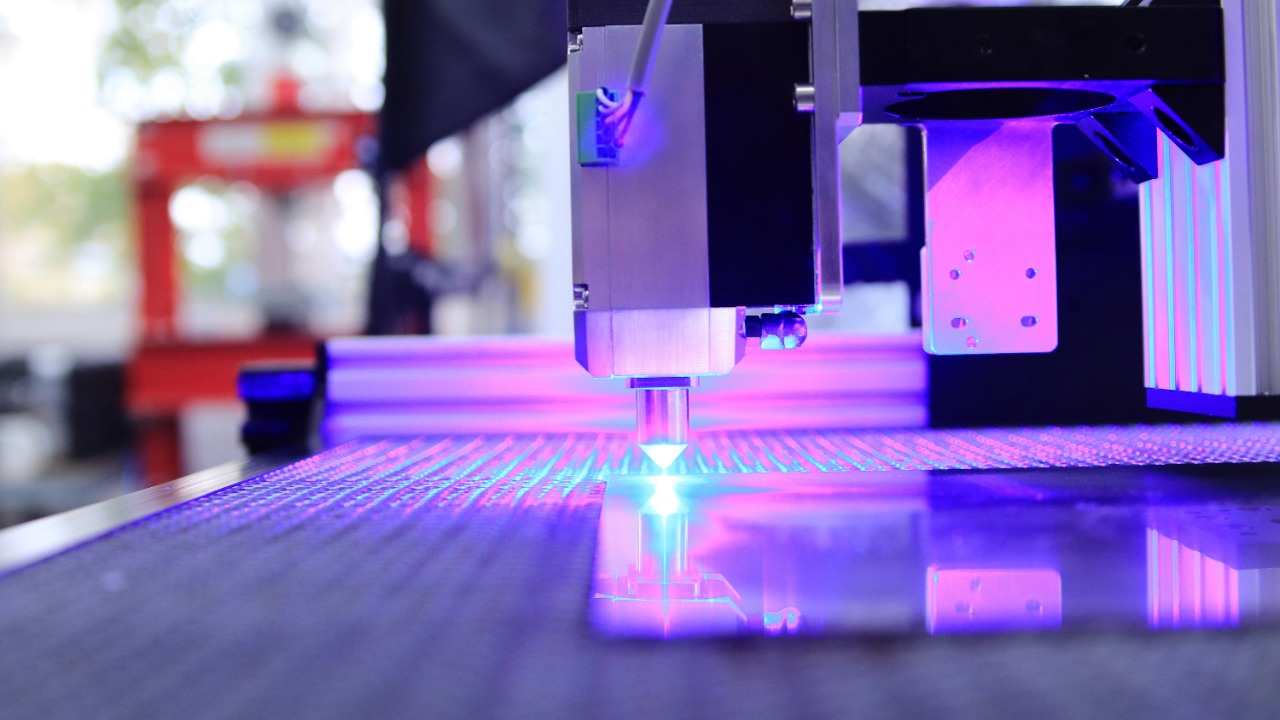
Lasers have set a new benchmark for precision in manufacturing. Unlike traditional cutting tools, lasers offer unparalleled accuracy, making them ideal for intricate designs and complex geometries. By focusing a concentrated beam of light, lasers can slice through materials with minimal waste and error, resulting in cleaner cuts and higher quality products.
This level of precision is particularly beneficial in industries where detail is paramount, such as aerospace and electronics. The use of lasers minimizes the need for manual intervention, reducing the potential for human error. As a result, manufacturers can achieve tighter tolerances and produce components that meet exact specifications, enhancing the overall quality and reliability of their products.
Streamlined Quality Control Processes
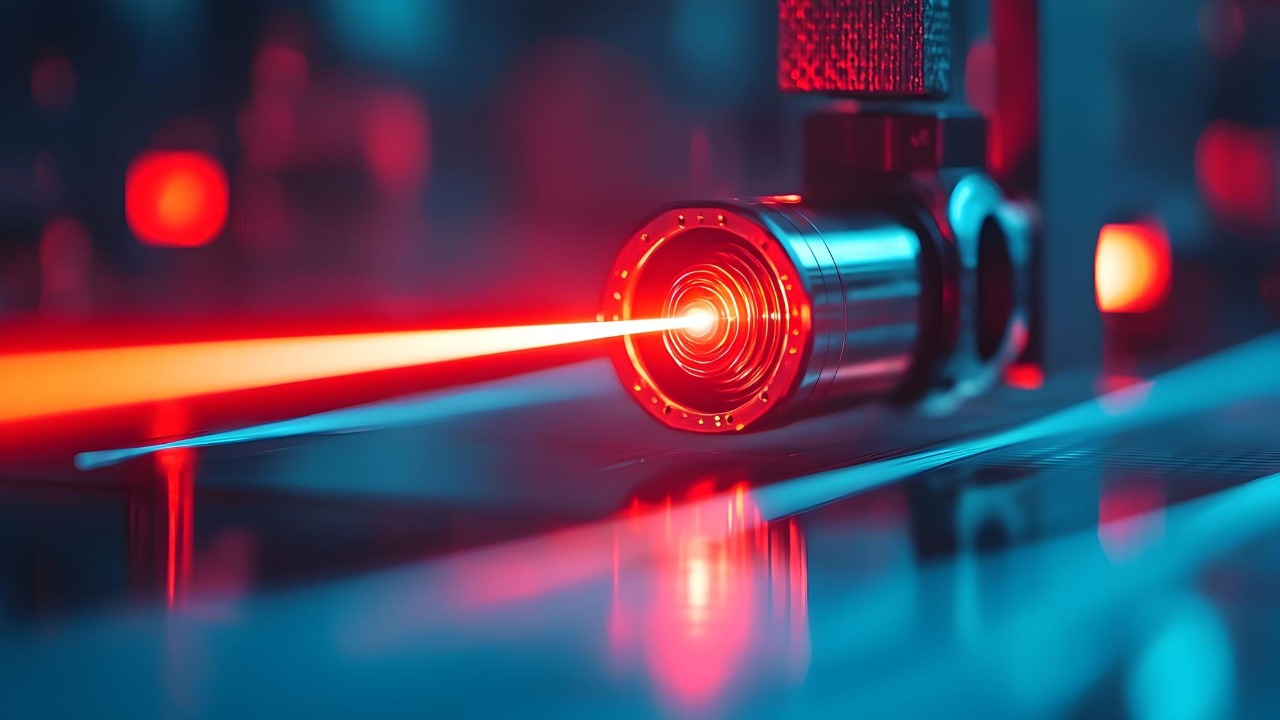
Quality control is an essential component of manufacturing, and lasers are playing a pivotal role in streamlining these processes. With laser-based inspection systems, factories can quickly and accurately assess the quality of their products. These systems use laser technology to scan items for defects, ensuring that only products that meet stringent standards make it to market.
The adoption of laser technology in quality control not only boosts accuracy but also reduces waste by identifying issues early in the production cycle. This proactive approach allows manufacturers to address problems before they escalate, leading to cost savings and increased customer satisfaction.
Increased Automation and Efficiency

Automation is the future of manufacturing, and lasers are at the heart of this transformation. By integrating lasers into production lines, factories can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers for more complex and creative endeavors. This shift not only enhances efficiency but also reduces the likelihood of repetitive strain injuries among workers.
Lasers contribute to increased efficiency by accelerating production times and reducing downtime. With the ability to operate continuously, laser systems ensure that factories can meet demanding production schedules without compromising on quality. As a result, manufacturers can increase output while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Advanced Material Processing
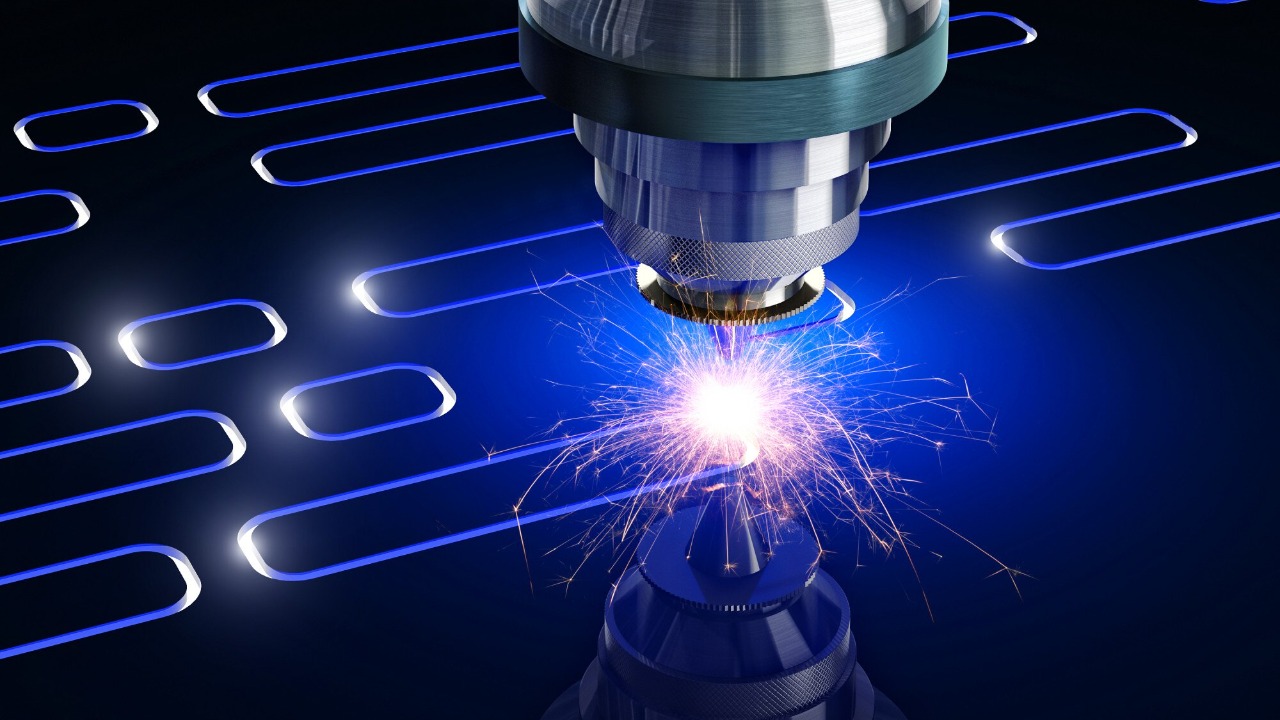
The versatility of lasers extends to their ability to process a wide range of materials, from metals to plastics. This capability opens up new possibilities for manufacturers, allowing them to experiment with innovative designs and materials that were previously difficult to work with. Lasers can efficiently cut, engrave, and weld diverse materials, enabling greater flexibility in product development.
Advanced material processing with lasers also supports the development of lightweight and durable components, which are crucial in industries such as automotive and aerospace. By leveraging the unique properties of lasers, manufacturers can enhance the performance and sustainability of their products, meeting the growing demand for eco-friendly solutions.
Improved Safety Measures

Safety is a top priority in manufacturing environments, and lasers are helping to create safer workplaces. Traditional cutting tools can pose significant risks to workers, but lasers minimize these hazards through non-contact processing. This means that there is less risk of injury from sharp blades or heavy machinery.
Furthermore, the precision of lasers reduces the need for manual handling of materials, decreasing the likelihood of accidents. As factories continue to adopt robotics and automation, laser technology is proving to be an invaluable asset in maintaining a safe and productive work environment. By prioritizing safety, manufacturers can protect their workforce while optimizing production processes.