When it comes to power and efficiency, diesel engines often outperform their gasoline counterparts. There are several key reasons why diesel engines create more torque, a measure of rotational force, than gasoline engines. Let’s take a closer look at these factors.
Higher Compression Ratio of Diesel Engines
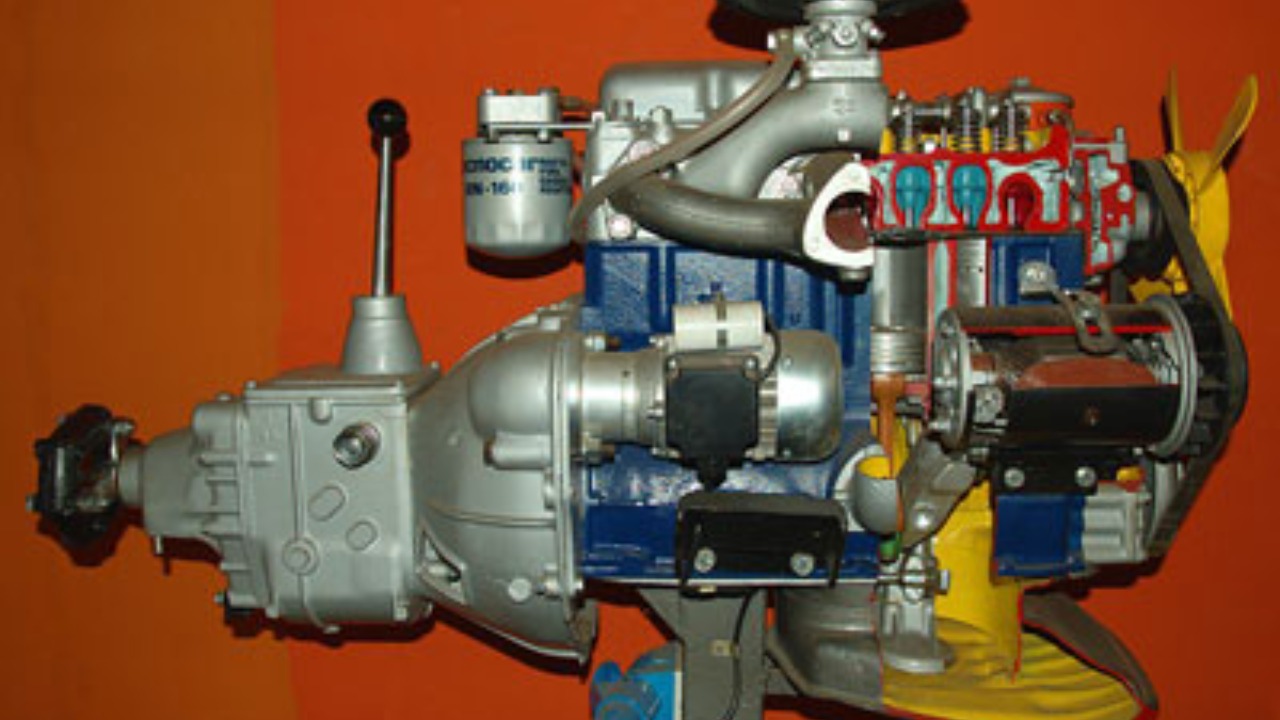

The first reason lies in the higher compression ratio found in diesel engines. Unlike gasoline engines, diesel engines compress the air before fuel is injected, which results in a higher compression ratio. This higher compression ratio leads to more torque because it allows the engine to extract more energy from each drop of fuel.
Moreover, the higher compression ratio also makes diesel engines more efficient. They create more power from less fuel, leading to better fuel economy and lower emissions.
Superior Energy Density of Diesel Fuel

Diesel fuel has a higher energy density than gasoline, which means it contains more potential energy per unit of volume. This superior energy density allows diesel engines to create more torque and power. It’s one reason why monster trucks often use diesel engines – the extra torque helps the trucks perform their signature jumps and stunts.
Furthermore, the high energy density of diesel fuel contributes to the overall efficiency of diesel engines. They can go farther on a tank of fuel compared to gasoline engines.
Diesel’s Direct Injection System
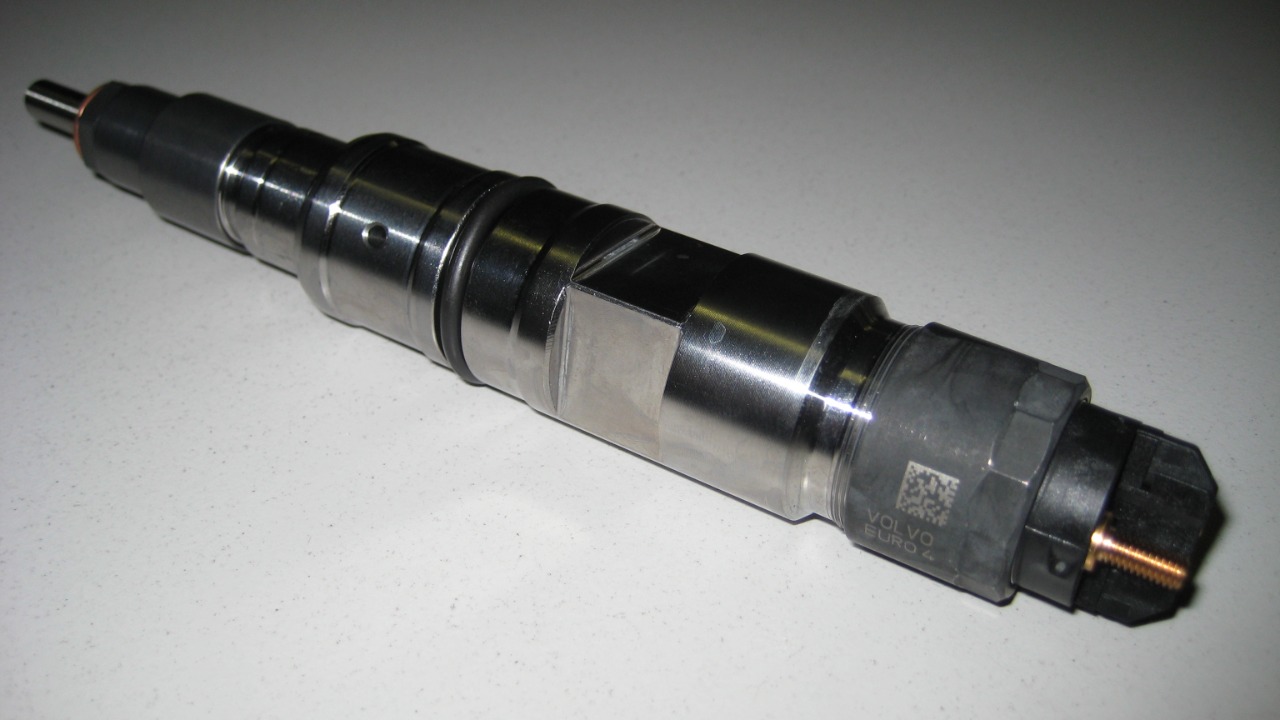

Unlike gasoline engines which mix air and fuel before they enter the combustion chamber, diesel engines use a direct injection system. This system injects fuel directly into the combustion chamber, resulting in a more efficient burn and consequently, more torque.
The direct injection system also allows for better control of the combustion process, leading to improved engine performance and efficiency. It’s a key reason why companies like Cummins have started to incorporate diesel technology into their gasoline engines.
Longer Stroke Length in Diesel Engines
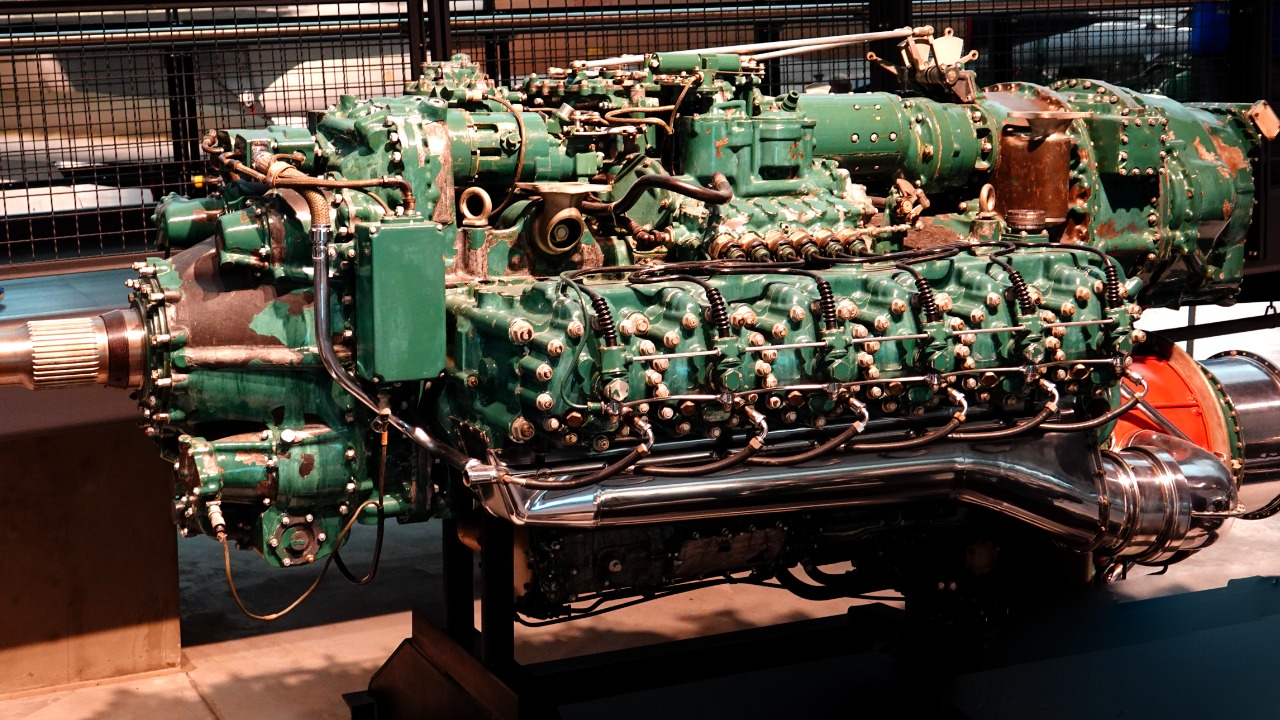
The stroke length, or the distance the piston travels in the cylinder, is generally longer in diesel engines than in gasoline engines. This longer stroke length allows the engine to generate more torque. Essentially, the longer the stroke, the greater the leverage the piston has on the crankshaft, and the more torque the engine can produce.
This leverage, combined with the high compression ratio and superior energy density of diesel fuel, creates a powerful engine that’s capable of producing significant torque.
The Role of Turbochargers in Diesel Engines
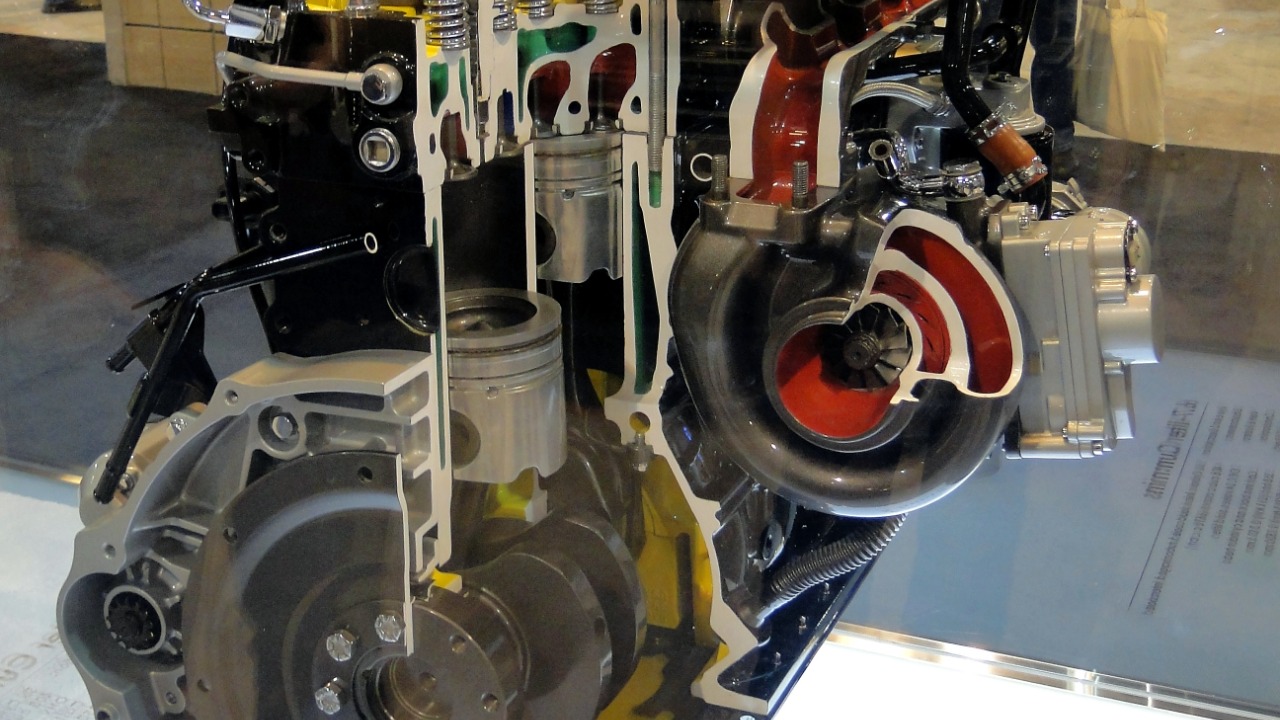
Finally, diesel engines often come equipped with turbochargers. These devices use the engine’s exhaust gases to spin a turbine, which then forces more air into the combustion chamber. The result? More fuel can be burnt, and more torque can be produced.
It’s one of the reasons why you might want to build a turbo diesel pickup. The extra torque provided by the turbocharger can give the truck an impressive amount of pulling power, making it ideal for heavy-duty tasks and off-road adventures.