In the realm of theoretical physics, certain concepts ignite the imagination by challenging our understanding of natural laws. From the elusive perpetual motion machines to the enigmatic dark matter harvesters, these power sources captivate scientists and dreamers alike. Let’s delve into these fascinating ideas that defy conventional physics.
Perpetual Motion Machines
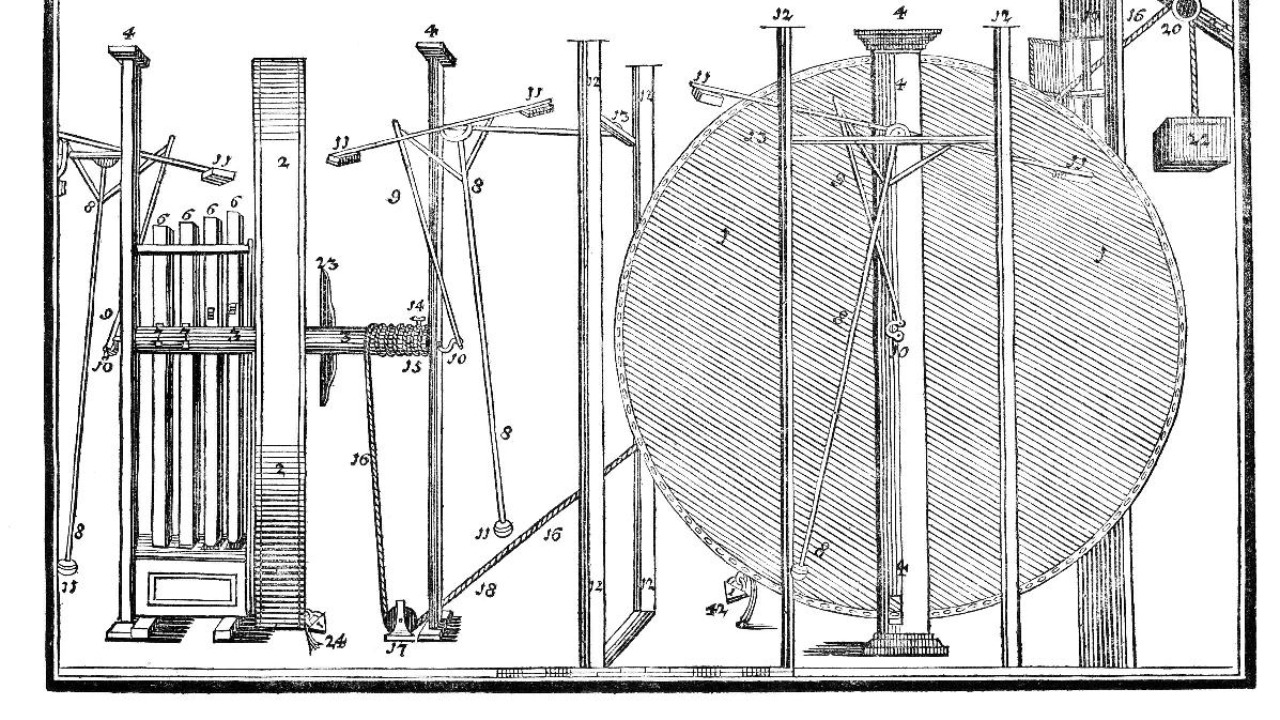
Perpetual motion machines have long been the holy grail for inventors and scientists who dream of creating a device that can operate indefinitely without an external energy source. These machines are theoretically impossible because they violate the laws of thermodynamics. Specifically, they contradict the first and second laws, which state that energy cannot be created or destroyed and that entropy, or disorder, tends to increase over time.
Despite the theoretical impossibility, perpetual motion machines occasionally resurface in scientific discussions and popular culture. While they remain a fascinating concept, they serve as a reminder of the fundamental principles governing energy and motion. The pursuit of such machines often leads to innovative thinking, even if the ultimate goal remains unreachable.
Zero-Point Energy Devices
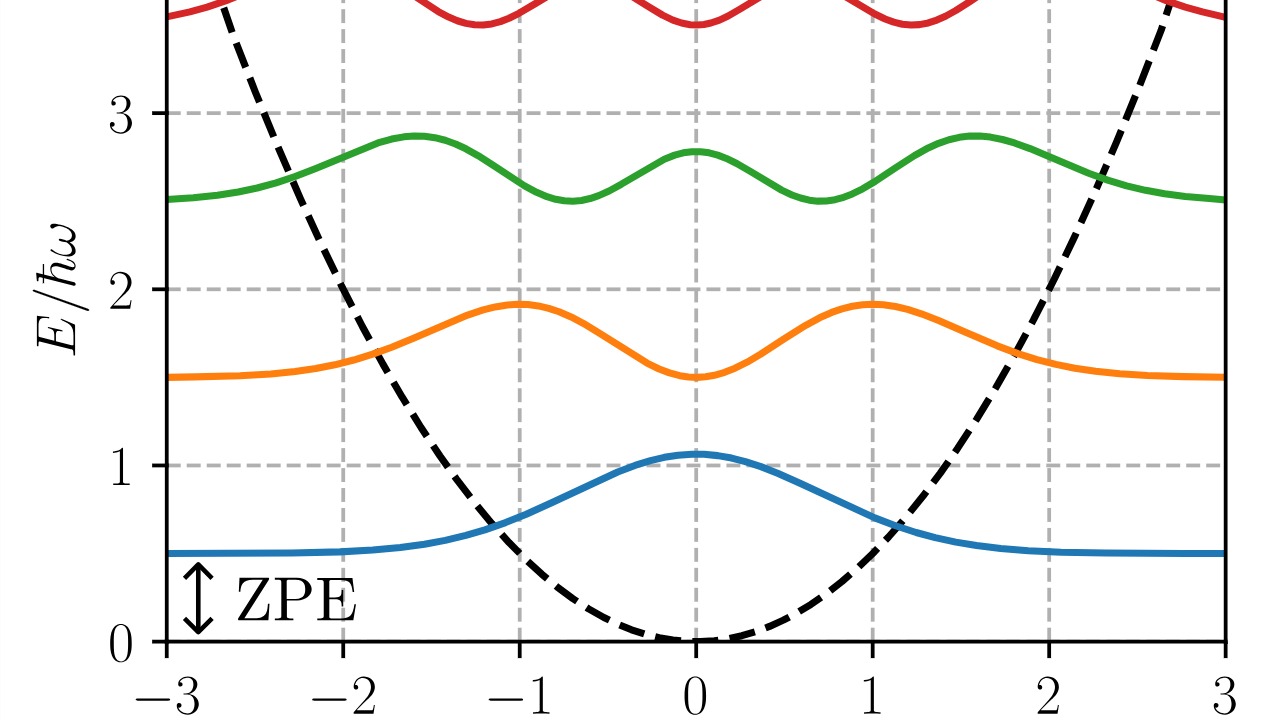
Zero-point energy devices propose to harness the energy present in a vacuum, where quantum fluctuations occur even at absolute zero temperature. This concept stems from quantum mechanics, where it’s believed that vacuum energy pervades all of space. Theoretically, if this energy could be tapped into, it could provide an almost limitless power source.
However, zero-point energy devices face significant challenges. Firstly, the amount of energy available at the quantum level is exceedingly small, and extracting it without violating energy conservation laws is problematic. Secondly, our current understanding of quantum mechanics suggests that such energy extraction could have unpredictable consequences. Thus, while tantalizing, zero-point energy remains on the fringe of scientific exploration.
Cold Fusion Reactors
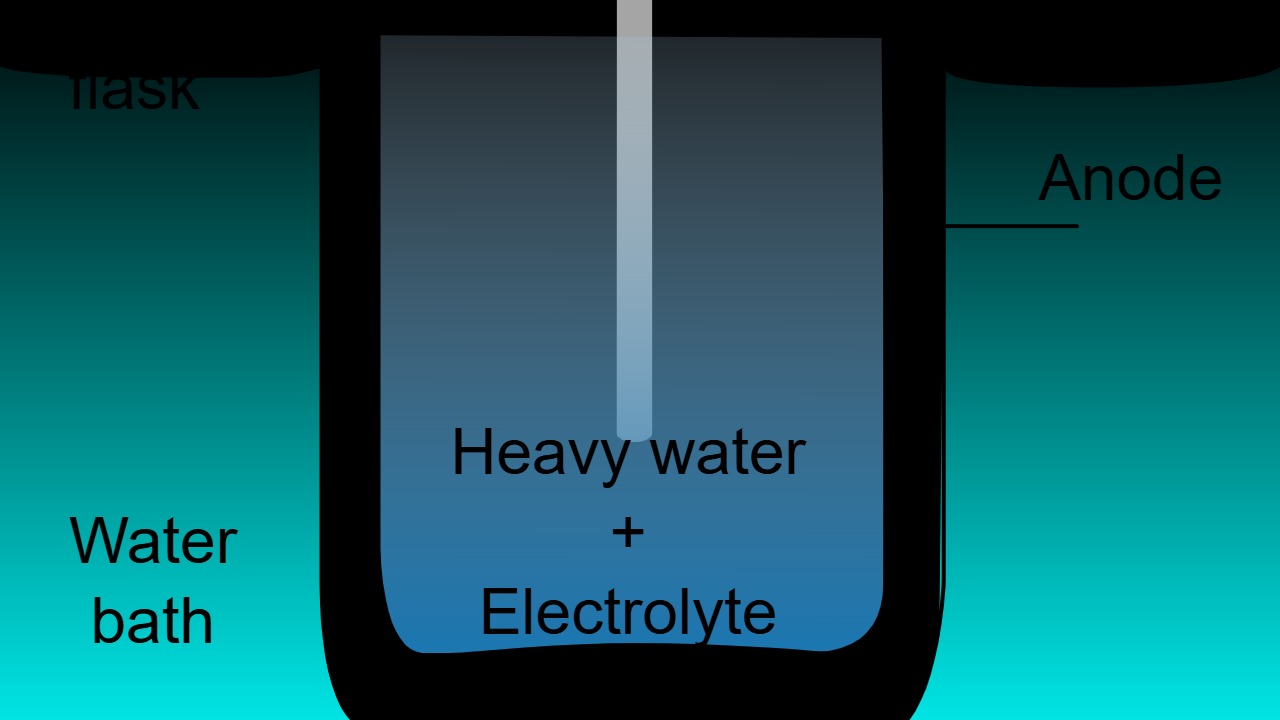
Cold fusion reactors aim to achieve nuclear fusion at or near room temperature, offering a clean and virtually limitless energy source. Unlike traditional fusion reactors that require extremely high temperatures, cold fusion suggests a more accessible approach. The idea gained popularity in the late 20th century but soon fell into disrepute due to experimental inconsistencies and lack of reproducibility.
Despite the skepticism, research into cold fusion continues, albeit under different terminologies such as “low-energy nuclear reactions.” While mainstream science remains cautious, the potential benefits keep the field alive. If validated, cold fusion could revolutionize how we produce and consume energy, making it a topic of enduring interest and debate.
Anti-Gravity Generators
The concept of anti-gravity generators captivates the imagination by suggesting the possibility of negating or reversing gravitational forces. Such technology, if feasible, could revolutionize transportation, space travel, and energy consumption. However, it currently defies our understanding of gravity as an inherent force tied to mass and space-time curvature.
While theories in quantum mechanics and general relativity occasionally broach the idea of manipulating gravity, practical applications remain elusive. The pursuit of anti-gravity technology often leads to speculative science fiction rather than concrete breakthroughs. Nonetheless, the allure of overcoming gravity ensures this concept remains a staple of futuristic thought.
Dark Matter Harvesters

Dark matter, an unseen component of the universe, constitutes about 27% of its mass-energy content. Although it doesn’t interact with electromagnetic forces, its gravitational effects are observable in cosmic phenomena. Theoretical dark matter harvesters propose capturing and utilizing this elusive substance as a power source.
However, the nature of dark matter remains one of the biggest mysteries in astrophysics. As scientists continue to explore its properties, the idea of harvesting it for energy is purely speculative. Despite the challenges, any progress in understanding dark matter could have profound implications for energy science, making the pursuit a tantalizing prospect for future generations.