It’s an exciting time in the world of civil engineering and construction. The advent of 3D printing technology has now made it possible to construct bridges that can withstand earthquakes as powerful as a 9.0 magnitude. This groundbreaking development promises to change the face of infrastructure projects, paving the way for safer, more resilient structures around the world.
The Technology Behind 3D-Printed Bridges
3D printing technology has been making waves in various sectors, and construction is no exception. The application of 3D printing in the construction of bridges involves layering materials in a specific manner to create a durable, sturdy structure. The materials used for these projects are typically a combination of concrete and a special type of plastic that provides additional strength and flexibility. The Polytechnic University of Turin has conducted extensive research on this subject.
The design elements in a 3D-printed bridge are meticulously crafted to enhance earthquake resistance. For instance, the structure incorporates specific geometries and reinforcements that distribute the seismic forces, thus minimizing the risk of collapse. These design adaptations are a significant departure from traditional bridge construction and underscore the innovative nature of 3D printing technology.
The Process of Constructing a 3D-Printed Bridge
The construction of a 3D-printed bridge begins with a detailed design, which is then translated into a 3D model. The 3D printer uses this model as a blueprint, building the structure layer by layer. The process is not without challenges; for instance, maintaining the precision and accuracy required for such a complex structure can be demanding. However, the advantages, such as reduced construction time and minimized waste, are substantial.
A notable example of a successful 3D-printed bridge project is the house designed by a company that survived a simulated 9.0 magnitude earthquake. This project demonstrated the potential of 3D printing technology in creating structures capable of withstanding extreme seismic activity.
Testing the Durability of 3D-Printed Bridges
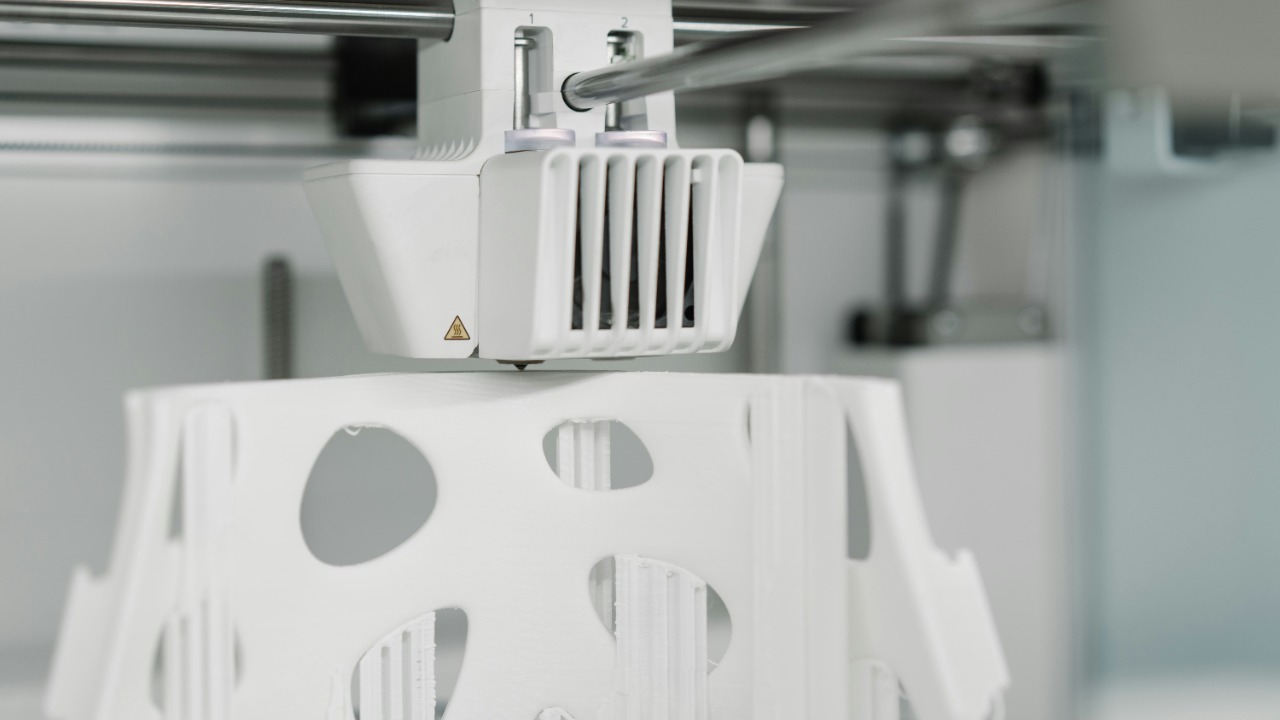

Ensuring the durability of 3D-printed bridges involves rigorous testing processes. These include both computer simulations and physical tests, where the structure is subjected to forces similar to those experienced during an earthquake. The world’s first earthquake test on a 3D-printed home is a prime example of these testing processes in action.
There are also real-world examples where 3D-printed bridges have proven their mettle. These cases offer invaluable data that supports the reliability and durability of 3D printing technology in bridge construction. The data collected from these tests and real-world scenarios is instrumental in the continuous improvement of this innovative technology.
Implications for Future Infrastructure Projects
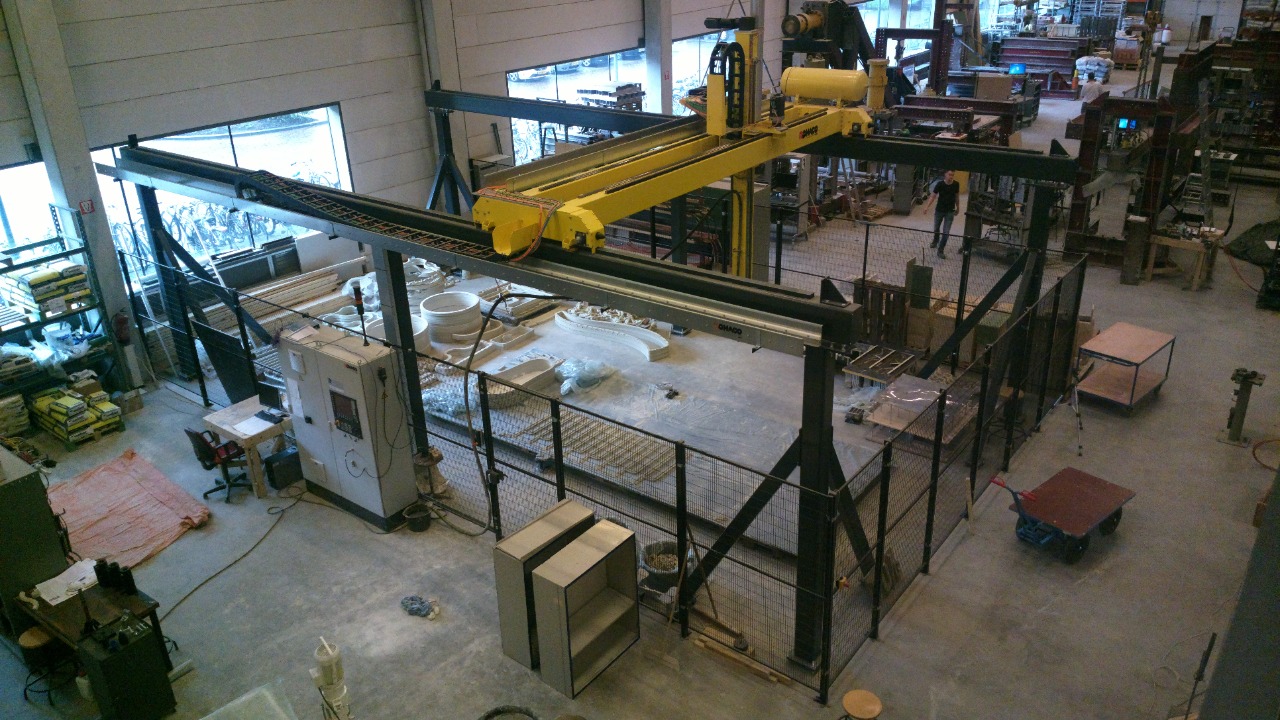

The use of 3D printing technology in construction could revolutionize the industry. Not only does this method offer the potential for quicker and more cost-effective infrastructure development, but it also has significant environmental benefits. For instance, the precision of 3D printing reduces waste, and the materials often used are more sustainable than traditional construction materials.
For earthquake-prone regions, the emergence of 3D-printed bridges could be a game-changer. These structures offer the potential for safer, more resilient infrastructure that can better withstand the damaging impacts of seismic activity. The promising results of current 3D-printed bridge projects provide a hopeful glimpse into the future of construction in these regions.
The Future of 3D-Printed Bridges
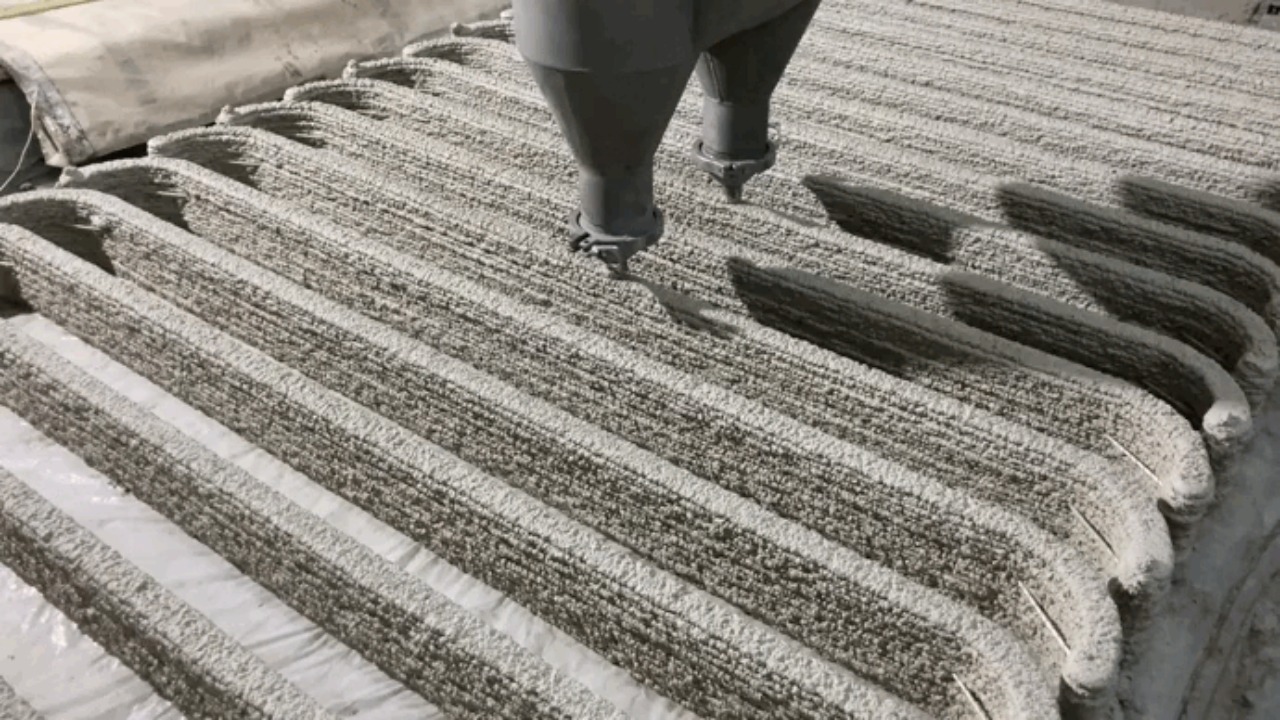

Looking ahead, the development of 3D-printed bridges is set to continue evolving. With ongoing advancements in 3D printing technology, the durability and resilience of these structures are likely to improve further. A YouTube video provides a visual demonstration of the potential future of 3D-printed bridges.
3D-printed bridges have already marked their place in the realm of civil engineering. Their ability to withstand high-magnitude earthquakes is a testament to the remarkable potential of 3D printing technology. However, this is just the beginning. With continued research and development, 3D-printed bridges could reshape the landscapes of cities worldwide, making them safer and more resilient in the face of natural disasters.