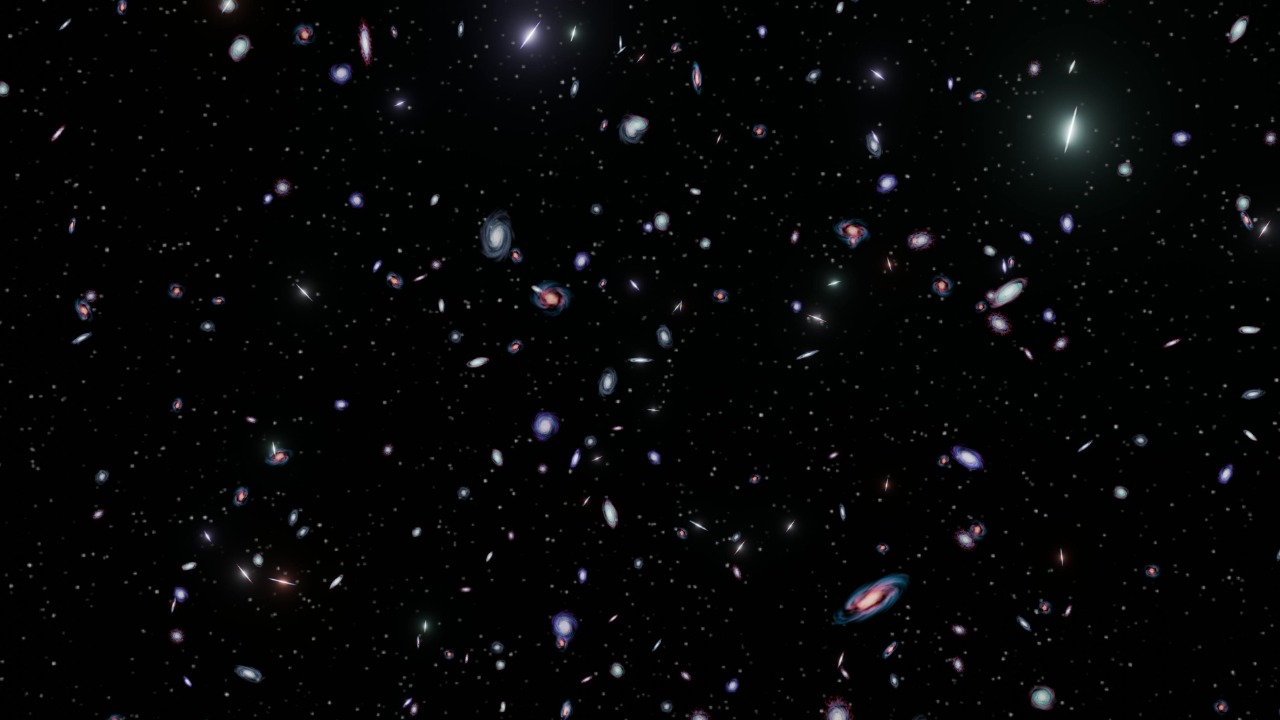

I’ve always found space to be a vast, mysterious expanse, full of phenomena that defy explanation. Despite the advances in technology and science, there are still cosmic enigmas that leave even the brightest minds puzzled. Here are six intriguing things found in space that continue to baffle scientists.
Dark Matter
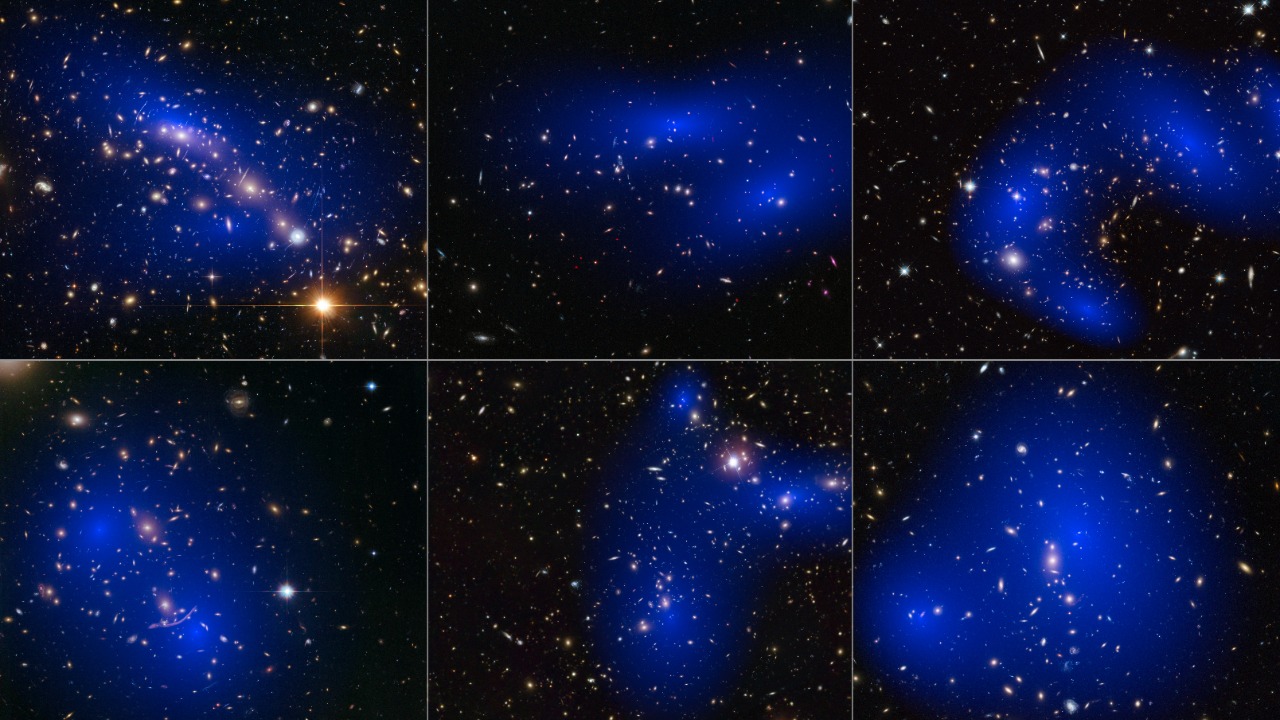

Dark matter makes up about 27% of the universe, yet it remains one of the most elusive components of space. It doesn’t emit, absorb, or reflect light, making it invisible and detectable only through its gravitational effects on visible matter. Scientists believe that dark matter holds galaxies together, but understanding its true nature is still a major challenge.
Despite various theories, including possible connections to black holes, the exact composition of dark matter remains unknown. Researchers worldwide continue to develop sophisticated experiments aimed at revealing its secrets, but it remains one of the universe’s biggest mysteries.
Fast Radio Bursts
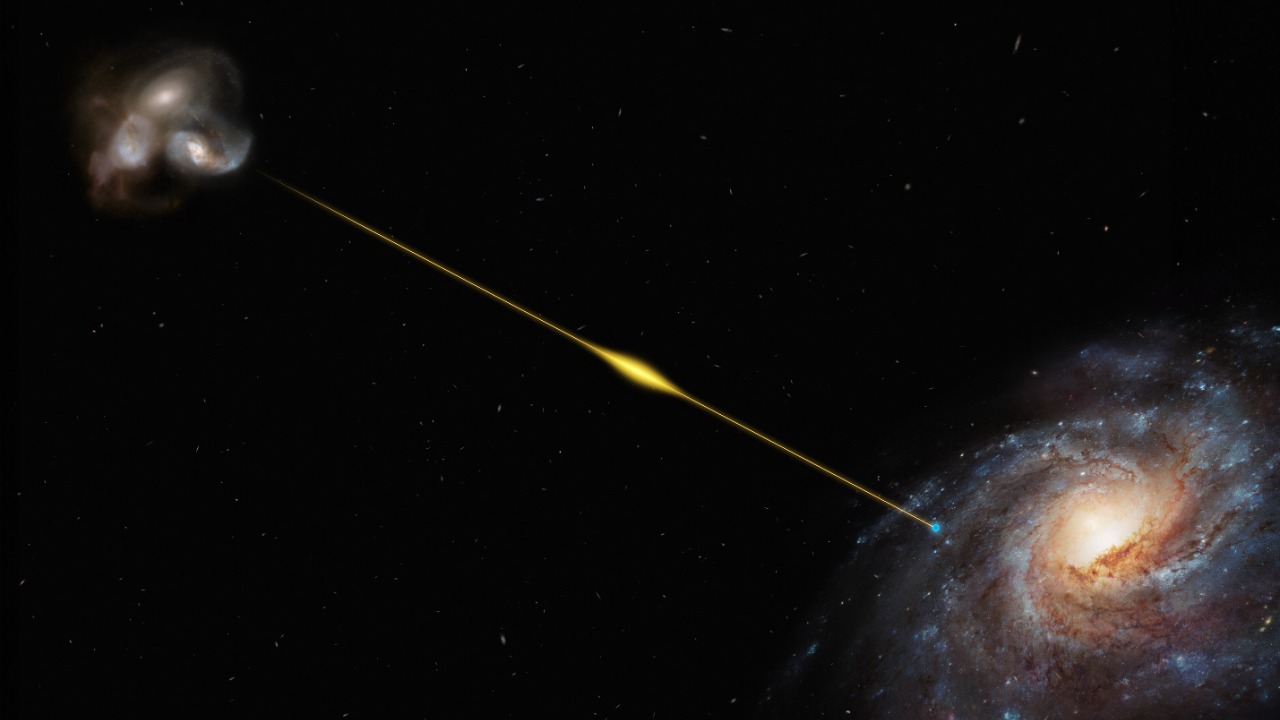

Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) are intense bursts of radio waves that last only milliseconds, yet they release as much energy as the sun does in a year. First discovered in 2007, these bursts are challenging to study due to their brief duration and unpredictable occurrence.
While some FRBs have been traced to distant galaxies, their origin remains a matter of speculation. Theories range from magnetars to alien technology, but no definitive explanation has been found. Researchers continue to search for patterns and hope that future observations will unlock the mystery of these cosmic signals.
The Great Attractor

The Great Attractor is a gravitational anomaly located in the Laniakea Supercluster, pulling galaxies, including our own Milky Way, towards it. Despite its significant influence, the exact nature of the Great Attractor is shrouded in mystery due to its location behind the “Zone of Avoidance,” an area obscured by the Milky Way’s dense galactic plane.
Some scientists speculate that the Great Attractor could be a massive concentration of dark matter, while others suggest it might be a supercluster of galaxies. Ongoing studies aim to better understand this powerful force that seems to hold sway over a large part of the universe.
Cosmic Microwave Background Cold Spot
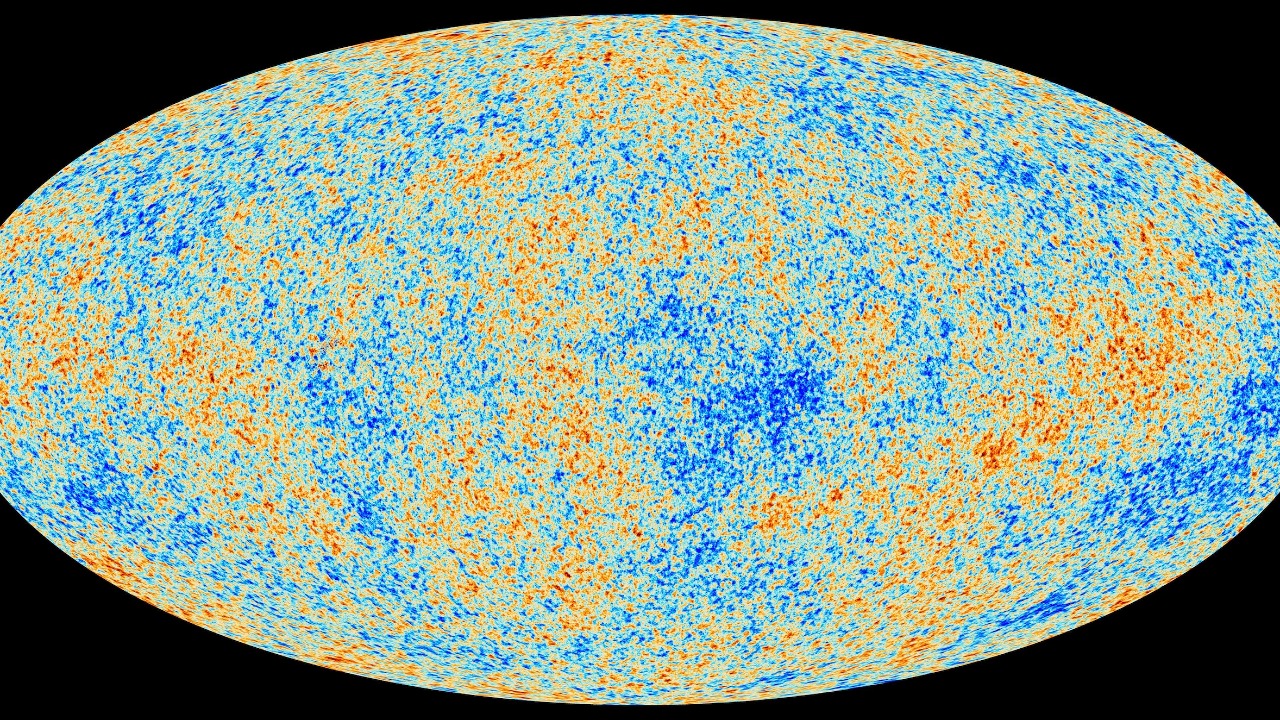
The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) Cold Spot is an unusually large and cold region in the CMB, the afterglow radiation of the Big Bang. Detected by the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe, this area challenges the standard model of cosmology, suggesting the presence of something beyond current understanding.
Some theories propose that the Cold Spot could be the result of a supervoid or a collision with another universe. However, no hypothesis has been confirmed, leaving the Cold Spot one of the most perplexing features in the universe.
Oumuamua’s Anomalous Trajectory

In 2017, Oumuamua became the first known interstellar object to pass through our solar system. Its elongated shape and strange trajectory sparked debates over its origin. Unlike any comet or asteroid observed before, Oumuamua’s path suggested it was propelled by some unknown force.
Some scientists speculated it might be a piece of advanced alien technology, while others believed it was a natural object with unusual properties. Despite its brief visit, Oumuamua left a lasting impression, challenging our understanding of what lies beyond our solar system.
Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays
Ultra-high-energy cosmic rays are particles traveling through space at nearly the speed of light, carrying energies millions of times greater than those produced by human-made accelerators. Their origin remains one of the biggest mysteries in astrophysics, as they are extremely rare and difficult to trace back to their sources.
Potential sources include supernovae, gamma-ray bursts, and active galactic nuclei, but none have been definitively identified. The study of these cosmic rays continues to be a frontier in understanding the universe, as scientists hope to uncover the mechanisms behind their immense energy.