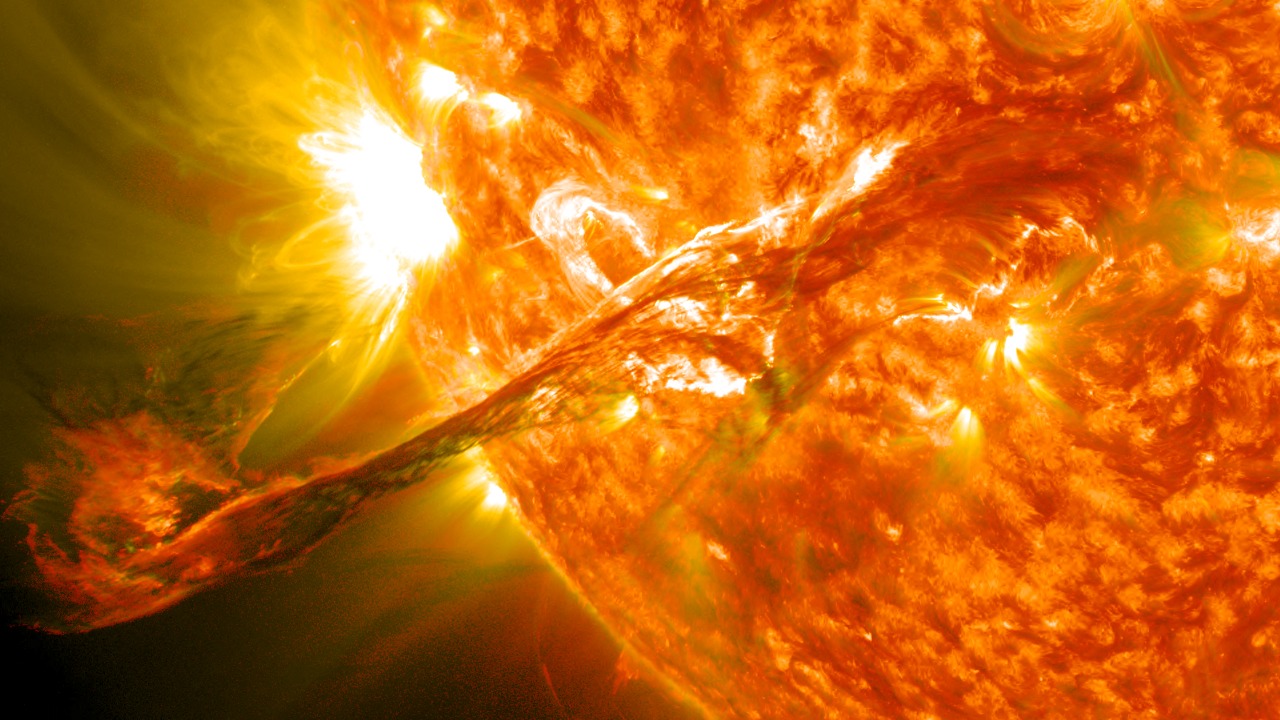

The concept of our Sun exploding is both fascinating and terrifying, often depicted in science fiction as an apocalyptic event. While the Sun is not expected to explode anytime soon, understanding the potential consequences of such an event can provide insight into the life cycle of stars and the fate of our solar system.
Exploring the science behind a hypothetical solar explosion, its impact on Earth, and what it could mean for the universe reveals a world of intricate cosmic processes and possibilities.
The Life Cycle of the Sun

The Sun, our nearest star, is currently in a stable phase known as the main sequence. As a middle-aged star, it sustains its luminosity through nuclear fusion, converting hydrogen into helium in its core. Over the next few billion years, this process will cease, leading the Sun to expand into a red giant, eventually shedding its outer layers and leaving behind a dense core known as a white dwarf. During this transformation, the Sun will dramatically affect its surrounding planetary bodies, including Earth.
Many people harbor misconceptions about the Sun’s potential to explode. Unlike massive stars that end their lives in spectacular supernova explosions, our Sun lacks the mass to undergo such a cataclysmic event. Instead, it will follow a more subdued path toward becoming a white dwarf. Understanding these stages demystifies the Sun’s future and corrects common myths about its demise.
Immediate Consequences of a Solar Explosion
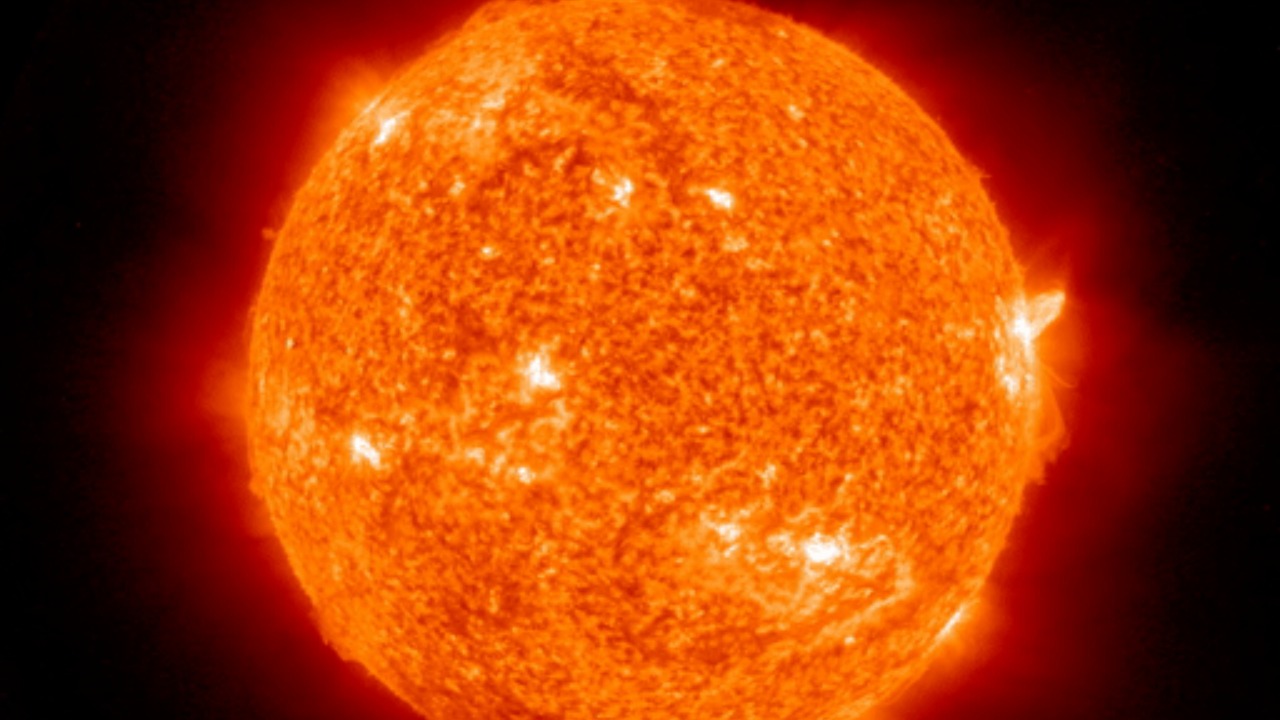

If the Sun were to explode, the immediate consequences for Earth and the inner planets would be devastating. The intense release of energy and radiation would obliterate the atmospheres of Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, causing drastic geological and atmospheric changes. The surface temperatures would skyrocket, rendering the planets uninhabitable and potentially vaporizing their surfaces.
For the outer planets, the effects would differ. The gas giants—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune—along with their moons would experience significant changes in their orbits due to the loss of the Sun’s gravitational pull. This could lead to a chaotic reconfiguration of the solar system’s structure, with celestial bodies potentially colliding or being ejected into interstellar space. The delicate balance that maintains the current solar system dynamics would be irretrievably altered.
The Science Behind Stellar Explosions

Understanding stellar explosions requires distinguishing between a supernova and what might happen if our Sun were to explode. A supernova occurs when a massive star exhausts its nuclear fuel, leading to a violent collapse and subsequent explosion that can outshine an entire galaxy. In contrast, a hypothetical solar explosion of our Sun would involve the release of accumulated energy but not at the magnitude seen in supernovae.
The energy dispersion and radiation levels following such an explosion would be immense, impacting not only the immediate solar neighborhood but potentially influencing interstellar space as well. Historical observations of supernovae, such as the famous SN 1987A, provide insights into the aftermath of stellar explosions and their impact on surrounding celestial bodies. These events contribute to the cosmic cycle of matter, seeding the universe with elements necessary for the formation of new stars and planets.
Potential for Human Survival

Technological advancements play a crucial role in evaluating our potential to survive a solar explosion. Current technologies, such as space habitats and advanced propulsion systems, offer some hope for human survival beyond Earth. However, the scale of a solar explosion’s impact would test the limits of our preparedness, highlighting the need for significant advancements in space travel and planetary colonization.
The likelihood of relocating human civilization to other planets or star systems remains a topic of speculation. While science fiction often explores these possibilities, the practical challenges are immense. Additionally, the psychological and societal impacts of such a cosmic event would be profound. The prospect of losing our home planet would force humanity to confront existential questions and redefine our place in the universe, as discussed in forums like Reddit.
Broader Implications for the Universe
A solar explosion would not only affect our solar system but could have implications for neighboring star systems. The resulting shockwaves and expelled matter could influence nearby stellar environments, contributing to the complex interplay of forces that govern the cosmos. This process highlights the interconnected nature of celestial bodies and the role of stellar explosions in cosmic recycling.
From a philosophical standpoint, contemplating the transient nature of celestial bodies encourages reflection on our place in the universe. The Sun’s eventual transformation into a white dwarf serves as a reminder of the cyclical nature of cosmic events and the ongoing process of star formation and destruction. As we ponder these broader implications, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate tapestry of the universe and our fleeting existence within it.
“`