Scientists have uncovered a hidden ecosystem beneath Antarctica’s frozen Lake Vostok, revealing lifeforms that have been isolated for millions of years. This groundbreaking discovery, announced on October 2, 2025, offers a glimpse into a mysterious world beneath the ice. The study highlights the resilience of life in extreme conditions and opens new avenues for scientific exploration (MSN).
The Mysterious Environment of Lake Vostok
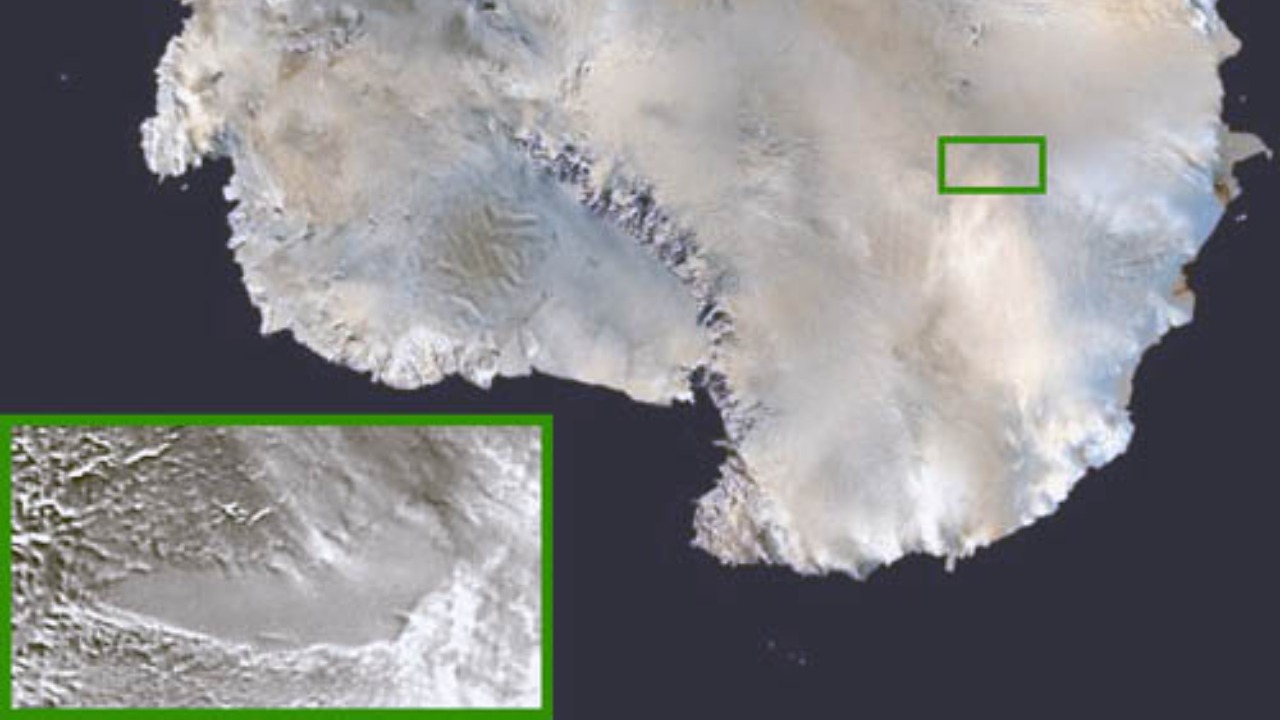

Lake Vostok, located beneath Antarctica’s ice, is estimated to be 15 million years old and has been isolated from the outside world for millennia. This ancient lake is considered an “ancient hidden world” due to its unique ecosystem that has evolved in complete isolation (Indian Defence Review). The lake’s environment is harsh and icy, presenting extreme conditions that challenge the survival of life, yet it hosts diverse lifeforms (Greek Reporter).
Researchers describe Lake Vostok as a place where life has adapted in extraordinary ways. The lake’s isolation has allowed its ecosystem to develop without external influences, making it a valuable site for studying life’s adaptability. The discovery of lifeforms in such an inhospitable environment underscores the potential for life in similar extreme conditions elsewhere in the universe (ExtremeTech).
Discovery of Lifeforms
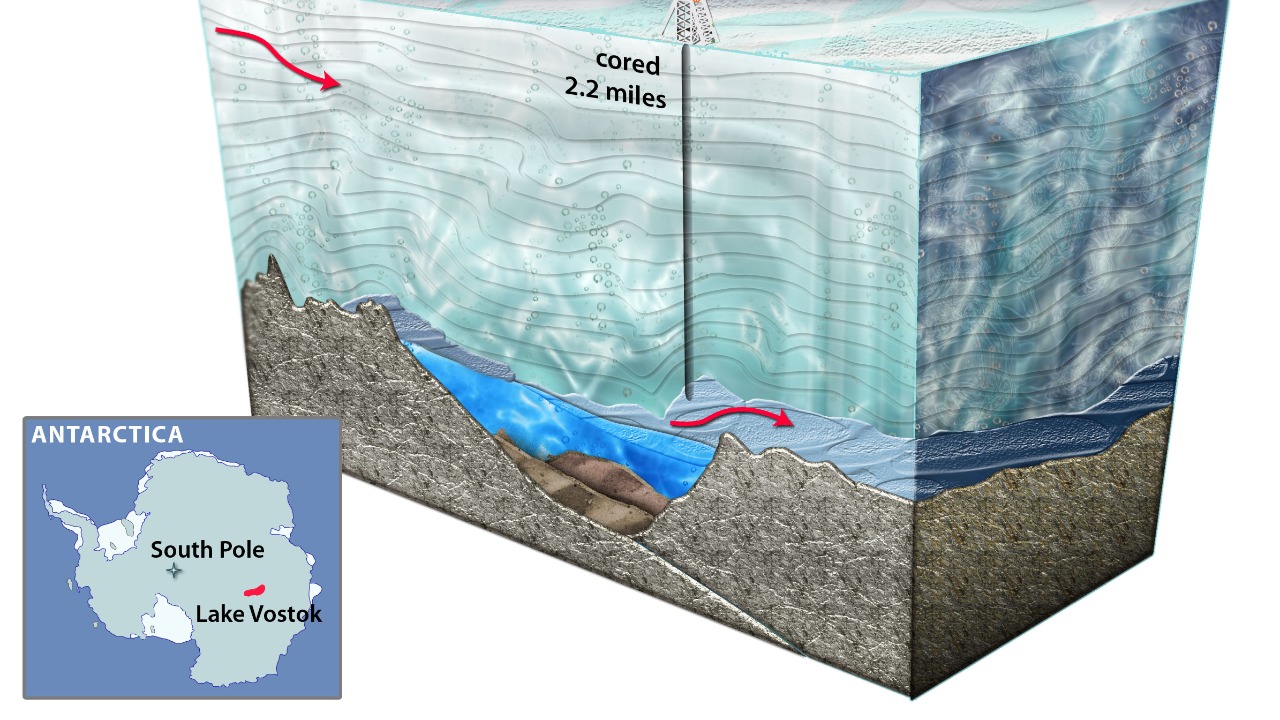
The discovery of lifeforms under Antarctica’s Lake Enigma was initially reported in December 2024, showcasing the presence of organisms in this inhospitable environment (Popular Science). Scientists have identified an “invisible ecosystem” that thrives beneath the Antarctic ice, suggesting life can adapt to extreme conditions. This finding challenges previous assumptions about the potential for life in isolated and extreme environments, providing new insights into biological resilience (MSN).
The organisms discovered in Lake Vostok are part of a complex ecosystem that has remained hidden from the world for millions of years. This discovery not only expands our understanding of life on Earth but also raises questions about the potential for similar ecosystems on other planets. The resilience of these lifeforms in such extreme conditions suggests that life might exist in environments previously thought uninhabitable (ExtremeTech).
Scientific Implications and Future Research

The findings from Lake Vostok offer significant implications for understanding the potential for life on other planets, as similar extreme conditions exist elsewhere in the solar system. Researchers are now exploring the genetic makeup of these organisms to understand how they thrive in such isolated and extreme conditions (Indian Defence Review). This research could provide valuable insights into the adaptability of life and the potential for discovering extraterrestrial life.
Future expeditions aim to delve deeper into Lake Vostok and other subglacial lakes to uncover more about these hidden ecosystems and their global significance. These efforts will not only enhance our understanding of Earth’s biodiversity but also inform the search for life beyond our planet (Greek Reporter). The study of these isolated ecosystems could lead to breakthroughs in biotechnology and other scientific fields.
Challenges of Research and Exploration

The extreme cold and remote location of Lake Vostok pose significant logistical challenges for scientists conducting research in Antarctica. Ensuring contamination-free sampling is crucial to preserving the integrity of the ecosystem and obtaining accurate scientific data (MSN). Researchers must employ advanced technologies to access and study these isolated ecosystems effectively.
Technological advancements are key to overcoming these challenges, enabling researchers to explore these hidden worlds without compromising their pristine conditions. As scientists continue to develop new methods for studying these environments, they will gain deeper insights into the resilience and adaptability of life on Earth and potentially beyond (ExtremeTech). These efforts will pave the way for future discoveries and innovations in the field of astrobiology and beyond.
In addition to the logistical and technological hurdles, researchers face the challenge of international collaboration and coordination. Antarctica is governed by the Antarctic Treaty System, which requires scientific activities to be conducted in a manner that promotes peace and cooperation among nations. This necessitates careful planning and communication among international teams to ensure that research efforts are aligned and that resources are shared efficiently. The treaty also emphasizes environmental protection, adding another layer of complexity to the planning and execution of research missions in such a sensitive and pristine environment (MSN).
Moreover, the harsh and unpredictable weather conditions in Antarctica can lead to delays and disruptions in research activities. Scientists must be prepared to adapt their plans and schedules to accommodate sudden changes in weather, which can impact the availability of transportation and the safety of field operations. These challenges require a high level of resilience and flexibility from research teams, as well as robust contingency plans to ensure that scientific objectives can still be met despite these obstacles. The ability to conduct successful research in such an extreme environment not only advances our understanding of isolated ecosystems but also enhances our capacity to explore other remote and challenging locations on Earth and beyond (ExtremeTech).