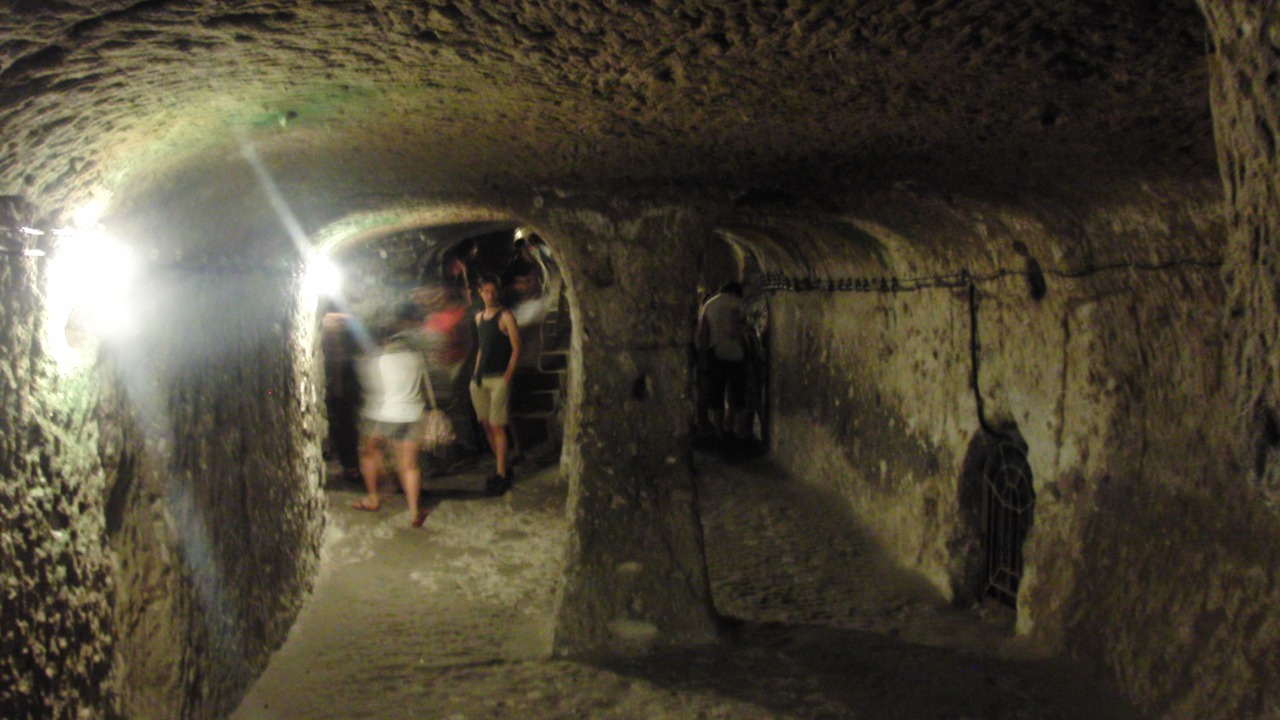

Recent scientific breakthroughs have made it possible to recreate the sounds of Turkey’s ancient underground city, a civilization that dates back 3,000 years. This innovative project uses 3D virtual soundscapes to provide a new, immersive way of experiencing the past.
The Science Behind the Soundscape
The technology used to recreate the sounds of this ancient city is a testament to the advancements in auditory reconstruction. This process involves the use of 3D virtual soundscapes, a technology that creates an immersive auditory environment, allowing listeners to experience the sounds of the past as if they were there. This technology is not without its challenges, however. The process of recreating the sounds of an ancient city requires a deep understanding of the city’s architecture, culture, and lifestyle, as well as the acoustics of the underground environment. Interesting Engineering reports that this project has highlighted the importance of sound in understanding historical contexts and environments.
As reported by Interesting Engineering, the technology used in this project is based on the principles of acoustics and sound propagation. The soundscape is created by simulating the acoustics of the underground city, taking into account factors such as the size and shape of the rooms and tunnels, the materials used in their construction, and the ambient noise levels. This involves complex mathematical modeling and computational algorithms. The sounds are then synthesized using a combination of recorded sounds and digitally created ones, resulting in a realistic and immersive auditory experience.
Unfolding the History of Turkey’s Underground City
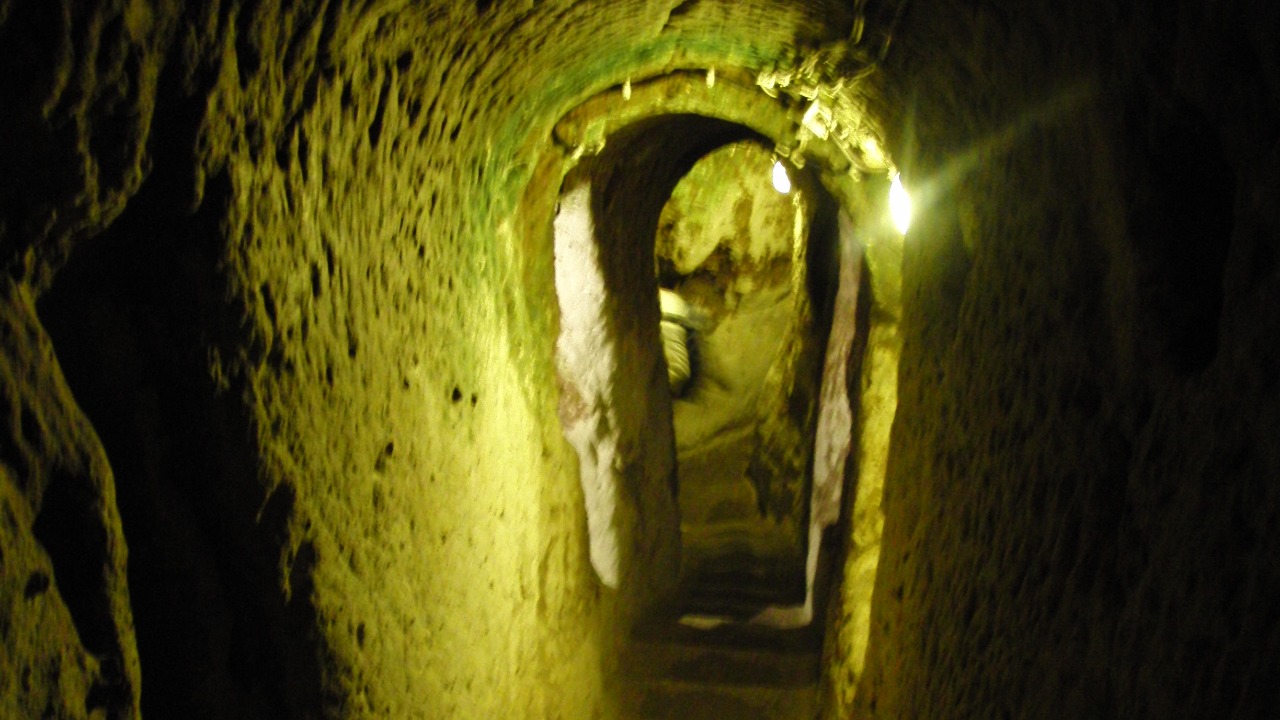

The ancient underground city in Turkey is a marvel of historical architecture. According to ZME Science, the city is approximately 3,000 years old and features a complex network of tunnels and rooms. The city’s structure and layout provide valuable insights into the lives of its ancient inhabitants. The significance of this city in historical and archaeological contexts cannot be overstated. Previous research and discoveries related to this ancient city have provided a wealth of knowledge about the civilization that once thrived there.
The underground city in Turkey, as described by ZME Science, is believed to have been built by the Phrygians, an ancient Indo-European people, around the 8th century BC. The city was used as a refuge during times of war and invasion, providing a safe and secure living environment for its inhabitants. The city’s complex network of tunnels and rooms, which include living quarters, storage areas, and places of worship, reflect the advanced engineering skills of the Phrygians. The city’s acoustics, which have been preserved over the centuries, provide a unique opportunity to study the sound environment of an ancient civilization.
The 3D Virtual Soundscape Experience

The 3D virtual soundscape is a groundbreaking tool that brings the past to life. This technology creates an immersive auditory environment that allows users to experience the sounds of the ancient city as if they were there. According to Phys.org, the soundscape includes the sounds of daily life in the city, such as the echoes of footsteps in the tunnels, the hum of conversation, and the ambient sounds of the environment. Researchers and users who have interacted with the 3D soundscape have reported a profound sense of connection to the past. This technology has potential implications and applications in other fields of study, including archaeology, history, and education.
The 3D virtual soundscape, as explained by Phys.org, is not just a passive listening experience. Users can interact with the soundscape, moving through the virtual environment and experiencing the changes in sound as they navigate the city’s tunnels and rooms. This interactivity enhances the sense of immersion and realism, making users feel as if they are truly exploring the ancient city. The soundscape also includes sounds that reflect the daily activities of the city’s inhabitants, such as the grinding of grain, the forging of metal, and the chanting of prayers, providing a vivid and dynamic picture of life in the ancient city.
Impact on Archaeology and Historical Studies

The use of 3D virtual soundscapes in historical research, as noted by Interesting Engineering and ZME Science, is a pioneering approach that could have far-reaching implications. It offers a new way of interpreting archaeological sites, complementing traditional methods of study. By recreating the sound environment of an ancient city, researchers can gain insights into the social and cultural aspects of the civilization, such as their communication methods, religious practices, and daily activities. This could lead to new discoveries and interpretations, enriching our understanding of the past. Furthermore, the use of sound technology could also have educational applications, providing students with a more engaging and interactive way of learning about history.