NASA’s pursuit of nuclear propulsion technology marks a monumental advancement in the realm of space exploration. By leveraging the power of nuclear rockets, the agency is poised to redefine how we traverse the cosmos, potentially making space travel faster, safer, and more efficient. This innovation promises to transform our capabilities, expanding our understanding and exploration of the universe in unprecedented ways.
The Science Behind Nuclear Propulsion

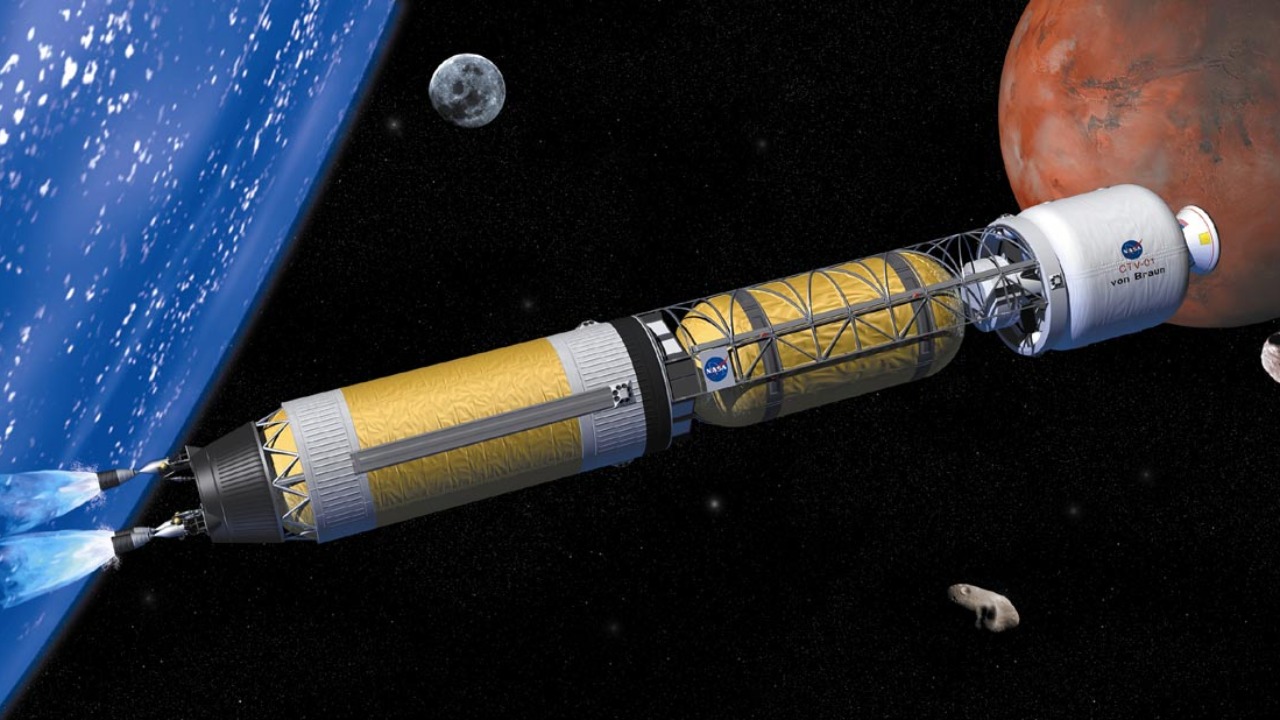
Nuclear propulsion technology is a game-changer for space travel, offering two primary methods: nuclear thermal propulsion (NTP) and nuclear electric propulsion (NEP). NTP works by heating a propellant, such as hydrogen, in a nuclear reactor and expelling it to create thrust. In contrast, NEP generates electricity from a nuclear reactor to power ion thrusters. Both methods provide a significant leap in efficiency and power compared to traditional chemical rockets, which rely on combusting fuel to produce thrust.
These nuclear systems offer distinct advantages in space travel. Primarily, they can cut travel times significantly, especially for missions to Mars and beyond. With increased speed, missions that once took months could be completed in weeks, revolutionizing human space exploration. Additionally, nuclear propulsion systems allow for longer mission durations and greater payload capacity, enabling more comprehensive scientific research and exploration in distant regions of space.
Historical Context and Development

The evolution of nuclear propulsion research spans decades, tracing back to early experimental concepts in the mid-20th century. During the Cold War, nuclear propulsion was explored as a strategic advantage, but practical developments were limited by technological and political challenges. More recently, there has been renewed interest and investment in nuclear space technologies, largely due to policy shifts and increased funding. The U.S. policy has evolved to support these advancements, with government initiatives and private sector partnerships playing crucial roles.
Significant milestones have marked the journey toward operational nuclear propulsion. NASA and other space agencies have conducted various tests to validate the feasibility of these technologies. Collaborations between government entities and private companies have accelerated progress, demonstrating the potential of nuclear propulsion in practical applications. These efforts lay the groundwork for future missions, providing a foundation for ongoing research and development.
Potential Impacts on Human Space Exploration
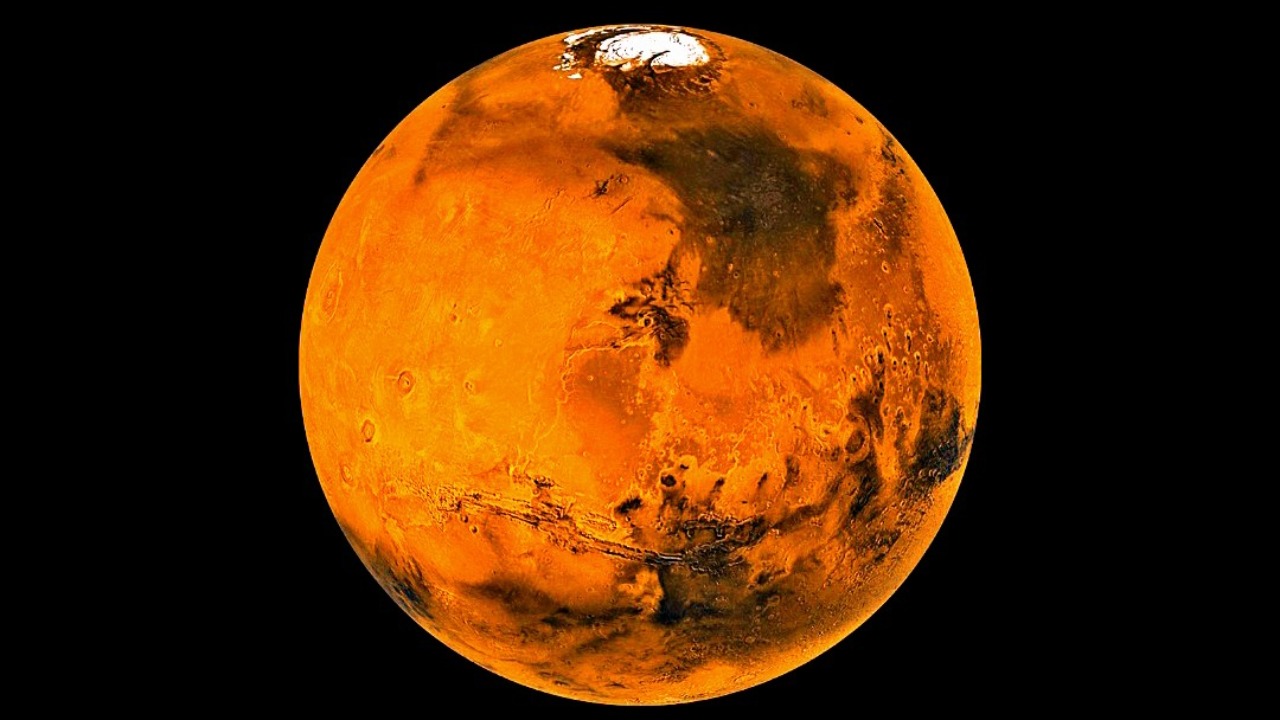

One of the most promising applications of nuclear propulsion is its potential to expedite missions to Mars. By drastically reducing travel time, nuclear rockets could make crewed missions to the Red Planet more feasible, addressing critical concerns about human survival and resource management on long-duration journeys. The reduced time spent traveling means astronauts would face fewer health risks associated with prolonged space travel, and resource requirements could be more efficiently managed.
Nuclear propulsion also opens new horizons for deep space exploration. With the capability to reach the outer planets and beyond, these advanced rockets could enable missions to explore the moons of Jupiter and Saturn, and even lay the groundwork for interstellar travel in the future. Establishing permanent bases on the Moon and Mars becomes more attainable, setting the stage for sustained human presence beyond Earth.
Challenges and Considerations

Despite its potential, nuclear propulsion technology faces several technical and engineering challenges. Key hurdles include developing reliable and safe reactor designs that can withstand the harsh conditions of space. Engineering innovations are necessary to ensure the structural integrity and operational efficiency of nuclear rockets, addressing the complexities of launching and operating nuclear systems in space.
Safety and environmental concerns are paramount when considering the deployment of nuclear technology in space. Public apprehension about the use of nuclear materials requires careful management and communication. Stringent regulatory frameworks and ethical considerations must be adhered to, ensuring that all measures are taken to mitigate risks. NASA and its partners are focused on developing robust safety protocols to address these concerns and reassure stakeholders.
Future Prospects and Vision

NASA’s roadmap for nuclear propulsion outlines a clear strategic plan for developing and testing these technologies. Key initiatives include the design and construction of test vehicles and reactors, with upcoming missions serving as potential testbeds. The agency’s ambitious timelines aim to integrate nuclear propulsion into future space missions, marking a significant shift in our approach to space travel.
In the broader context of space exploration, nuclear propulsion is integral to the vision of sustainable exploration and colonization. The technology offers a pathway to more viable and cost-effective missions, fostering international collaboration and partnerships. As global interest in space intensifies, nuclear propulsion could play a pivotal role in advancing collective efforts to explore and colonize other worlds.