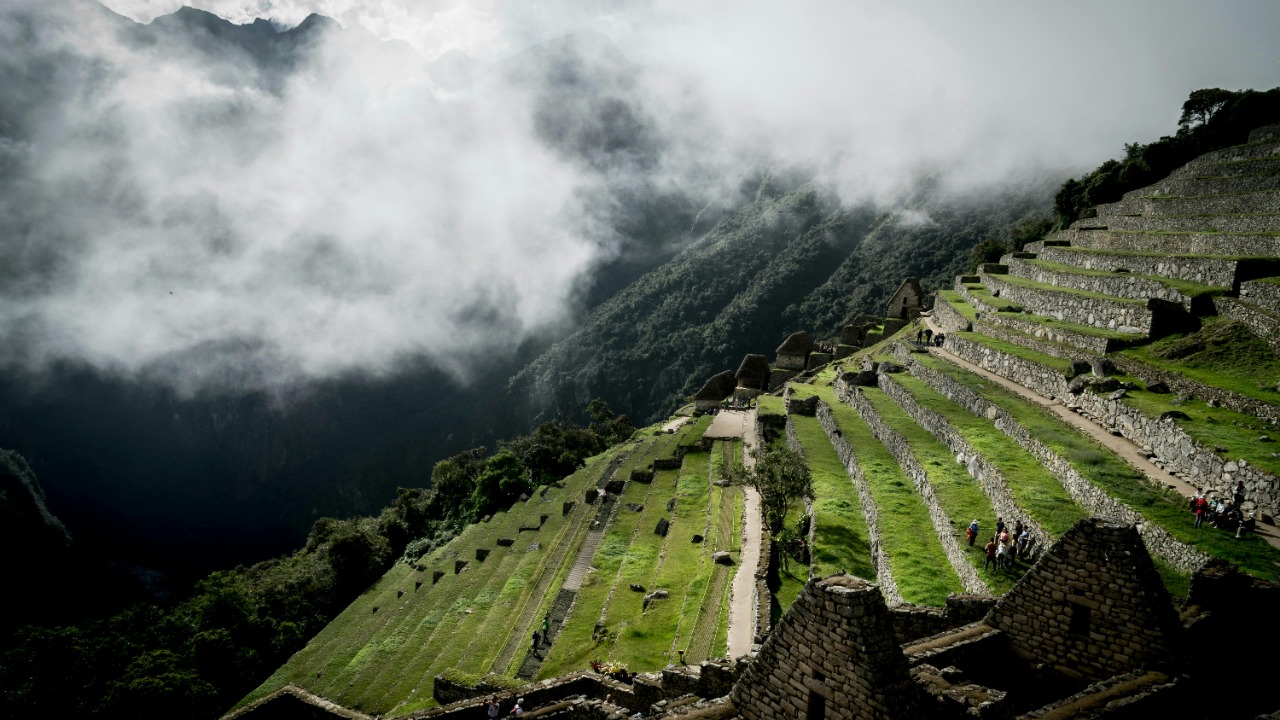

Archaeologists and researchers have uncovered a hidden world in the Andes Mountains using advanced LIDAR technology, revealing the lost civilization of the Chachapoya, often referred to as the “Cloud People.” This discovery sheds new light on the mysterious culture that thrived in the cloud forests of Peru before the conquest by the Inca Empire. The findings include over 100 ancient structures, offering a glimpse into the architectural and social intricacies of this enigmatic civilization.
The Chachapoya Civilization: An Overview

The Chachapoya civilization, often shrouded in mystery, occupied the cloud forests of the Andes in what is now northern Peru. Emerging around 800 AD and flourishing until the Inca conquest in the late 15th century, the Chachapoya are renowned for their unique adaptation to the challenging mountainous environment. This period saw them develop a distinct culture characterized by impressive architectural feats and sophisticated societal structures.
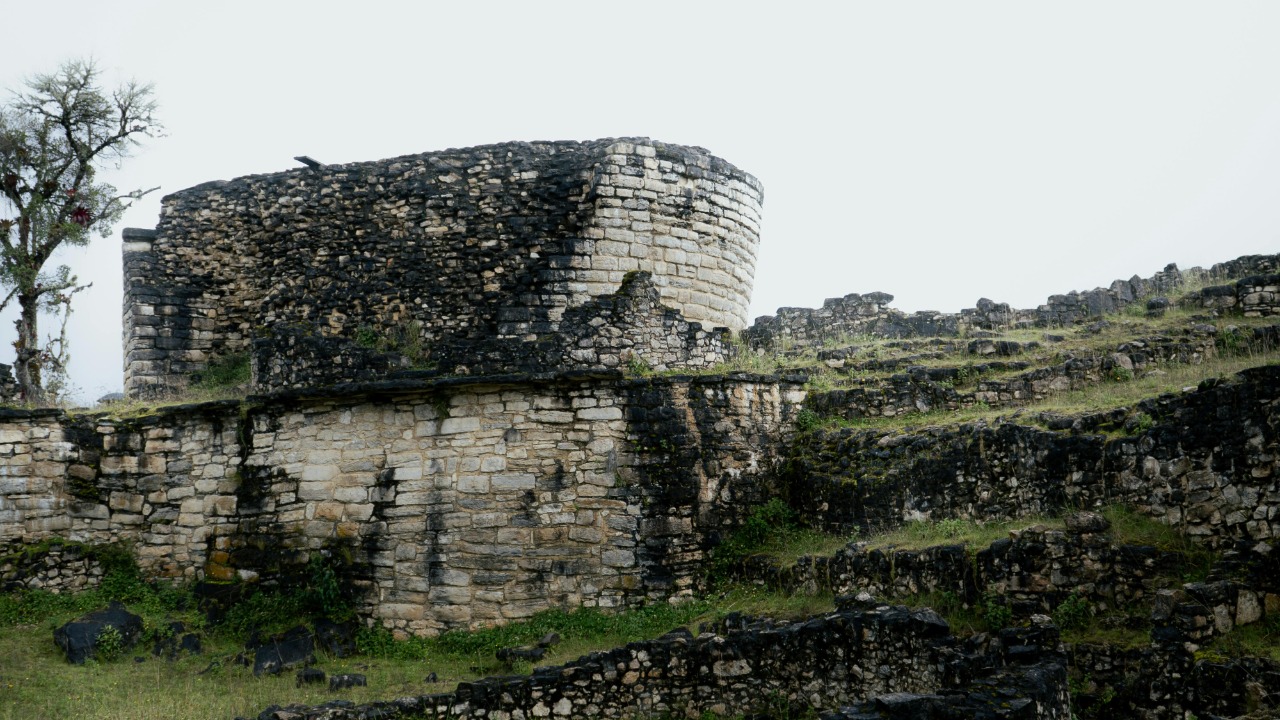
Culturally, the Chachapoya were distinct from their contemporaries. Their art and architecture reflect a deep connection to their environment, with structures harmoniously integrated into the natural landscape. Known for their striking stone constructions, the Chachapoya built intricate round houses and ceremonial centers, often adorned with geometric designs and intricate carvings. Their societal organization was equally advanced, with a complex network of communities spread across the rugged terrain, demonstrating a high degree of social cooperation and coordination.
Lidar Technology: Revolutionizing Archaeology
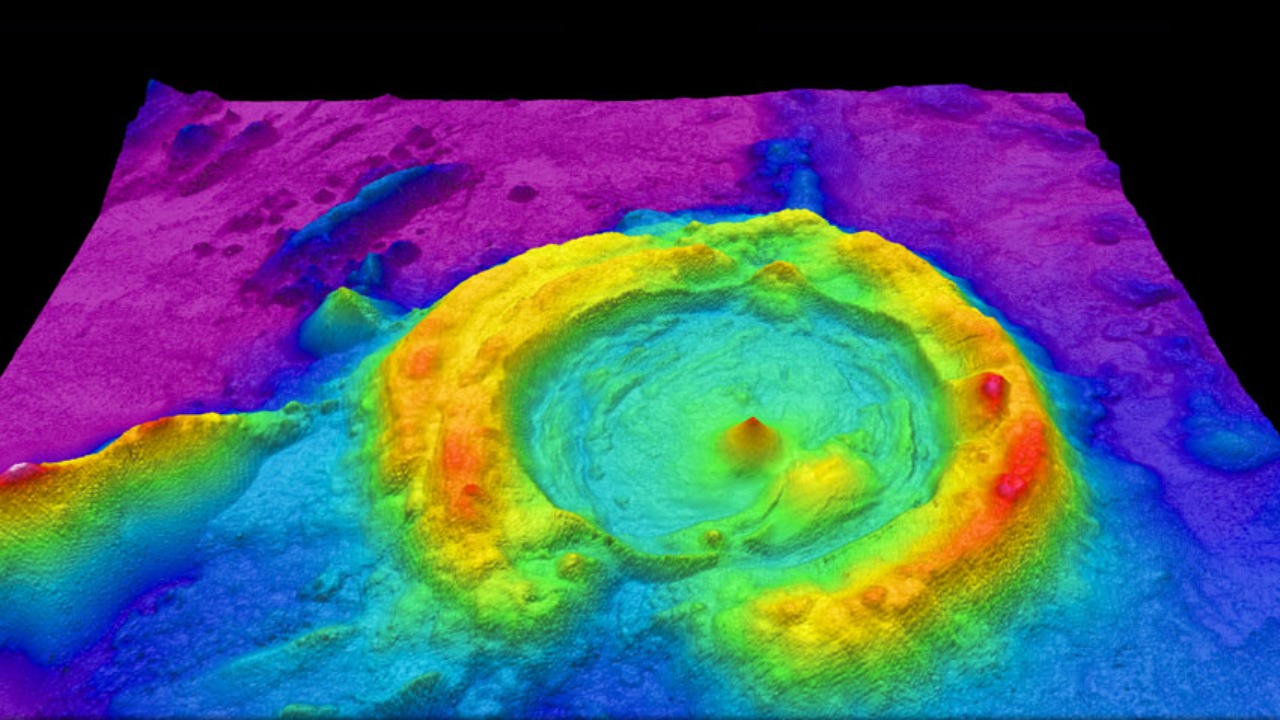
Lidar, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing technology that has transformed the field of archaeology. By emitting laser pulses from an aircraft and measuring the time it takes for these pulses to return after hitting the ground, Lidar can create detailed 3D maps of the earth’s surface. This technology is particularly effective in revealing structures hidden beneath dense vegetation, a common obstacle in areas like the cloud forests of Peru.
The impact of Lidar on archaeological discoveries cannot be overstated. It allows researchers to peer through the forest canopy, uncovering sites that were previously inaccessible or unknown. In the case of the Chachapoya, Lidar has revealed over 100 hidden structures, providing a new understanding of their societal complexity and architectural prowess. This technology is not just about discovery; it also aids in the preservation of these sites by offering detailed insights without the need for disruptive excavation.
Rediscovering the ‘Cloud People’

At the forefront of these discoveries is the site of Gran Pajatén, a ceremonial center nestled in the highland forests. The Lidar findings at Gran Pajatén have been particularly revealing, showcasing a series of terraces and round buildings adorned with intricate stone carvings. These structures provide critical insights into the ceremonial and social practices of the Chachapoya, suggesting a society deeply connected to its spiritual beliefs and natural surroundings.
The architectural insights gained from these discoveries are profound. The Chachapoya’s use of circular stone constructions, often with decorative friezes, indicates a sophisticated understanding of engineering and aesthetics. These stylistic elements not only highlight their architectural ingenuity but also raise questions about their cultural influences and interactions with neighboring civilizations, such as the Inca, who eventually absorbed the Chachapoya into their expanding empire.
The Significance of the Discoveries

The revelations from the Andes hold significant cultural implications. By uncovering the intricacies of the Chachapoya civilization, we gain a deeper understanding of pre-Inca societies and their interactions with each other. These findings challenge previous assumptions about the cultural landscape of ancient Peru, highlighting the Chachapoya as a vibrant and influential society that played a crucial role in the region’s history.
Preserving these newly uncovered sites is of paramount importance. The information gleaned from these structures not only enriches our understanding of the past but also informs future research directions. As researchers continue to explore the over 100 ancient structures revealed by Lidar, there is potential for further groundbreaking discoveries that could reshape our knowledge of ancient Andean civilizations.
Challenges and Opportunities in Archaeological Exploration

Despite the remarkable potential of Lidar technology, its application in archaeology is not without challenges. The interpretation of Lidar data requires significant expertise, as the raw data must be carefully analyzed to distinguish between natural and man-made features. Additionally, environmental factors such as dense vegetation and rugged terrain can affect the accuracy and resolution of Lidar scans, necessitating careful calibration and planning.
Nonetheless, the opportunities presented by Lidar far outweigh the challenges. The success of Lidar in uncovering the Chachapoya structures underscores the importance of collaborative efforts among international and interdisciplinary teams. By bringing together experts from various fields, researchers can leverage their collective knowledge to unlock the secrets of ancient civilizations and ensure the preservation of these invaluable cultural heritage sites for future generations.