
China’s recent Mars mission, spearheaded by the Zhurong rover, has yielded groundbreaking discoveries that could reshape our understanding of the Red Planet. As the rover traverses the Martian terrain, it sends back critical data that not only enhances our knowledge of Mars’ geological and atmospheric conditions but also raises intriguing questions about potential signs of past life.
The Zhurong Rover Mission

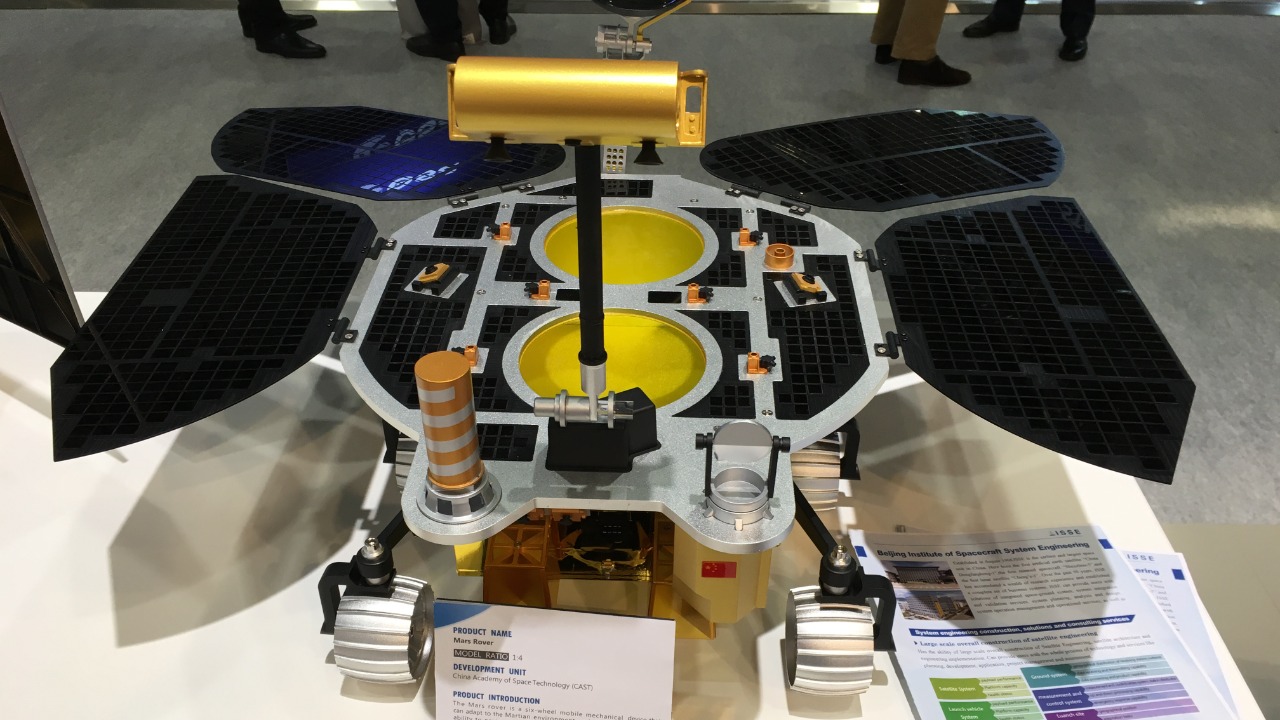
The Tianwen-1 mission represents a monumental leap in China’s space exploration efforts, featuring a comprehensive suite of components: an orbiter, a lander, and the Zhurong rover. The mission’s primary objectives include mapping the Martian surface, analyzing soil samples, and studying the planet’s atmosphere. Each component plays a crucial role in gathering data to achieve these goals, with the orbiter providing a broad overview from above, while the lander and rover offer detailed surface-level insights.
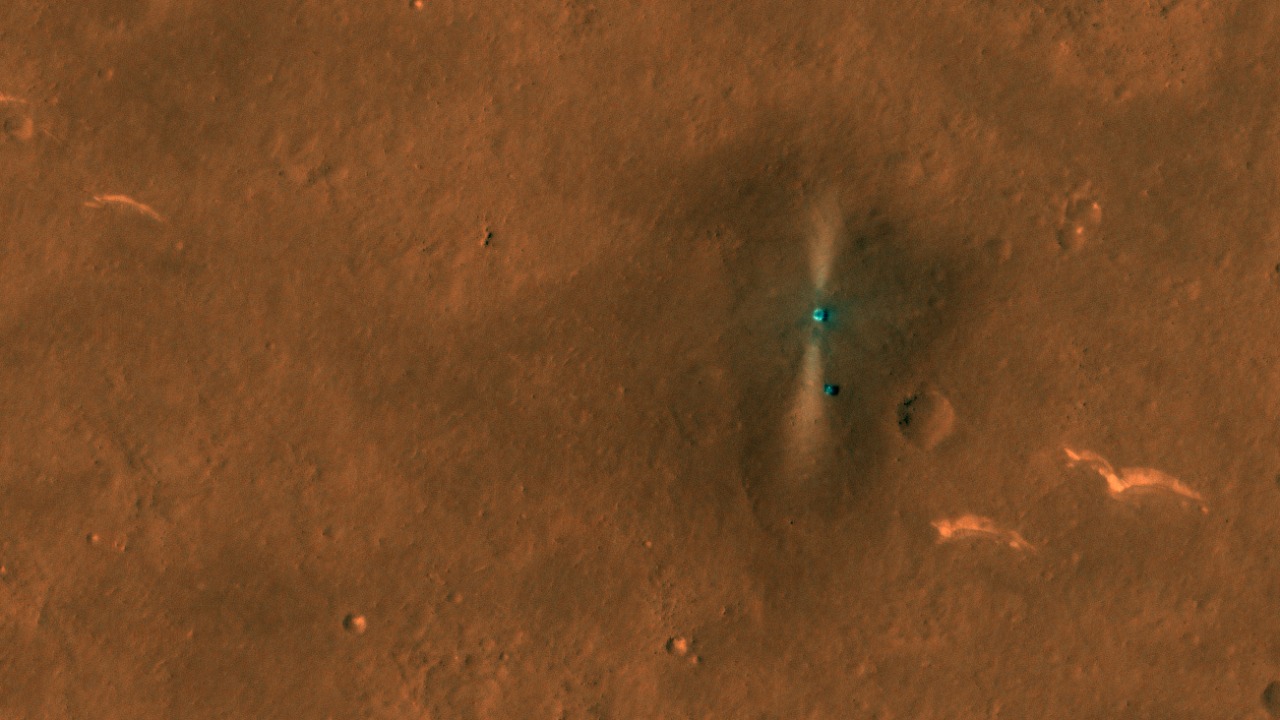
The Zhurong rover is particularly noteworthy for its technological advancements. Equipped with state-of-the-art scientific instruments, it can conduct sophisticated analyses of Martian soil and atmosphere. The rover’s design incorporates a robust mobility system, allowing it to navigate the challenging terrain of Mars, and a solar-powered system that ensures sustained operations despite the planet’s harsh conditions. Since its landing, Zhurong has achieved several milestones, including capturing high-resolution images and collecting extensive geological samples.
Geological Discoveries

The Zhurong rover’s analysis of Martian soil has unveiled fascinating insights into the planet’s mineral composition. Among the surprises are the discovery of unexpected mineral deposits, which suggest complex chemical processes that may have occurred in Mars’ past. These findings provide crucial clues about the planet’s geological evolution, indicating that Mars may have experienced more varied environmental conditions than previously thought.
In addition to soil analysis, Zhurong has documented a variety of surface features and formations. The rover has observed dunes, rocks, and formations that hint at the possibility of past water activity. Such observations are pivotal in reconstructing Mars’ geological history, offering evidence of volcanic and tectonic activities that have shaped the planet’s surface over eons. This data has profound implications for our understanding of Mars’ geological past and the potential for ancient habitable environments.
Atmospheric Insights

The thin Martian atmosphere has long been a subject of scientific inquiry, and the Zhurong rover’s findings are shedding new light on its composition and weather patterns. By analyzing atmospheric samples, the rover has provided detailed information on the presence of gases and their seasonal variations. This data is crucial for understanding how Mars’ atmosphere has evolved and its implications for the planet’s climate.
One of the most intriguing aspects of Martian weather is its dust storms, which can envelop the entire planet. Zhurong’s observations of these storms have revealed their impact on both the climate and surface conditions of Mars. Understanding these phenomena is vital, as they influence the planet’s thermal dynamics and potentially affect future missions. When compared to Earth’s atmosphere, Mars presents a stark contrast, offering insights into planetary evolution and the factors that contribute to atmospheric stability.
Search for Signs of Life
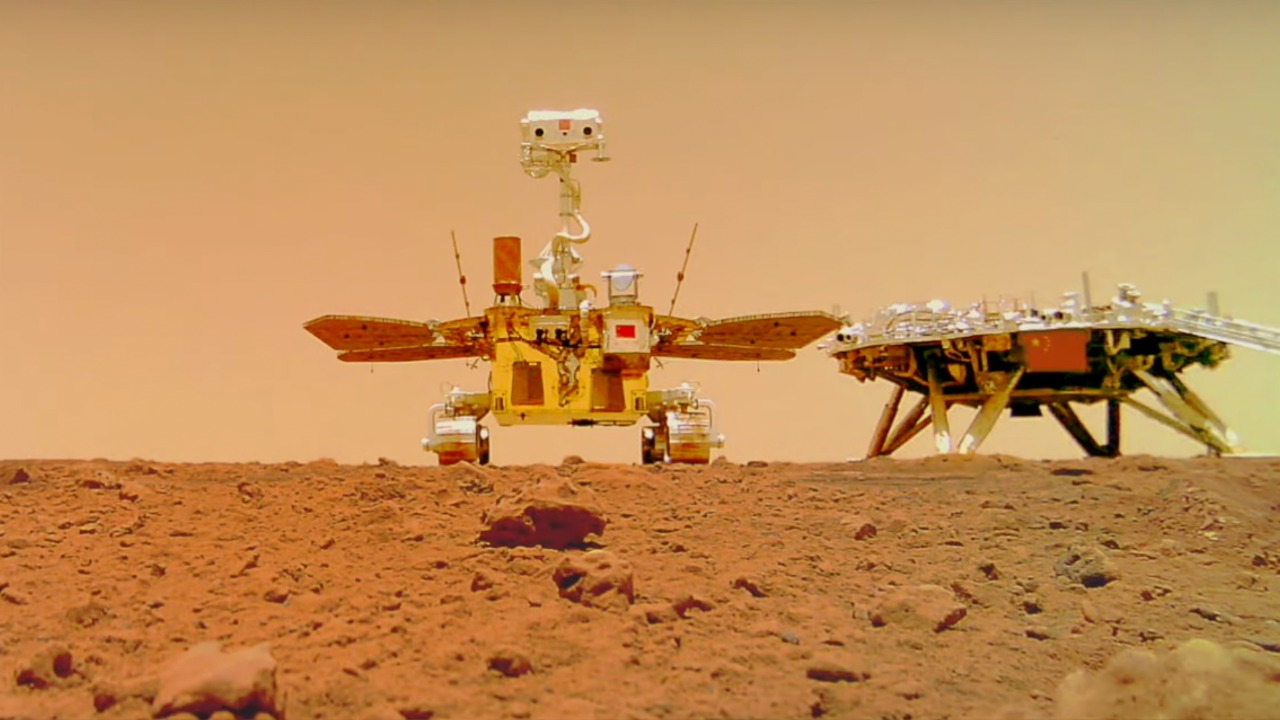
A key focus of the Zhurong rover’s mission is the search for signs of past life on Mars. The rover’s findings suggest the past presence of liquid water, a critical factor for the potential existence of life. Analyzing surface features and soil samples, Zhurong has identified areas that may have once harbored water, providing compelling evidence that Mars was more hospitable in its distant past.
The search for organic compounds and biosignatures is another crucial aspect of the mission. The rover is equipped with instruments designed to detect organic molecules and other indicators that could point to past or present life forms. These discoveries are significant not only for understanding Mars’ history but also for considering the possibility of life elsewhere in the universe. The implications of these findings extend beyond Mars, offering hope for the existence of life in other planetary systems.
Future Prospects and Challenges

Looking ahead, China has ambitious plans for continued Mars exploration. Future objectives include more in-depth analyses of Martian geology and atmosphere, as well as potential collaborations with other space agencies. Such partnerships are crucial for pooling resources and expertise, enhancing the overall success of Mars exploration. Upcoming missions may focus on returning samples to Earth, a goal that presents both technological and logistical challenges.
The challenges faced by the Tianwen-1 mission are numerous, from navigating the harsh Martian terrain to ensuring reliable communication with Earth. However, these obstacles are being overcome through innovative solutions and international cooperation. By working together, the global scientific community can advance our understanding of Mars and pave the way for future missions that may one day include human exploration.
The role of international cooperation cannot be overstated. As nations collaborate on Mars exploration, they contribute to a shared knowledge base that benefits all of humanity. This spirit of collaboration is essential for addressing the complex challenges of space exploration and unlocking the mysteries of the universe. For more in-depth information on Mars exploration, the Springer chapter on planetary exploration provides valuable insights.