Voyager 2, a marvel of human engineering, has been on an extraordinary journey through the outer reaches of our solar system for over 40 years. This remarkable spacecraft has recently surprised scientists by uncovering unexpected findings during its flyby of Uranus.
The insights gained about Uranus’s magnetosphere and atmospheric dynamics are challenging existing paradigms, offering new perspectives on the ice giant and solidifying the Voyager missions’ enduring legacy.
Voyager 2’s Historic Journey
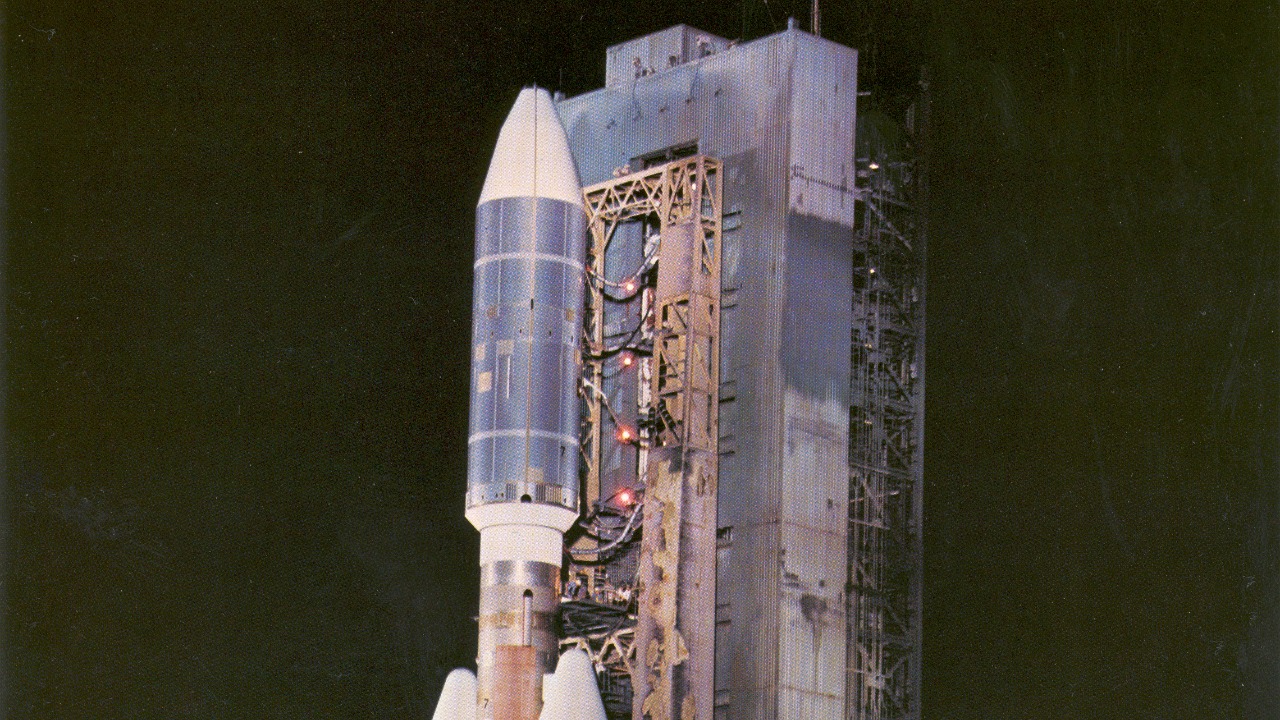
Voyager 2 was launched in 1977 with an ambitious mission: to explore the outer planets and beyond. Since its launch, it has provided invaluable data on Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, helping to expand our understanding of these distant worlds. Unlike its twin Voyager 1, which has traveled northward out of the solar system, Voyager 2’s southern trajectory allowed it to visit Uranus and Neptune, making it the only spacecraft to have done so.
The flyby of Uranus in 1986 marked a significant milestone in Voyager 2’s mission. As the first and only spacecraft to visit Uranus, it provided unprecedented insights into the planet’s atmosphere, rings, and moons. The data collected during this flyby continues to inform current research and has led to numerous scientific papers that delve into the complexities of the ice giant. For a more in-depth look at Voyager 2’s findings at Uranus, you can read this New York Times article.
Unexpected Discoveries at Uranus
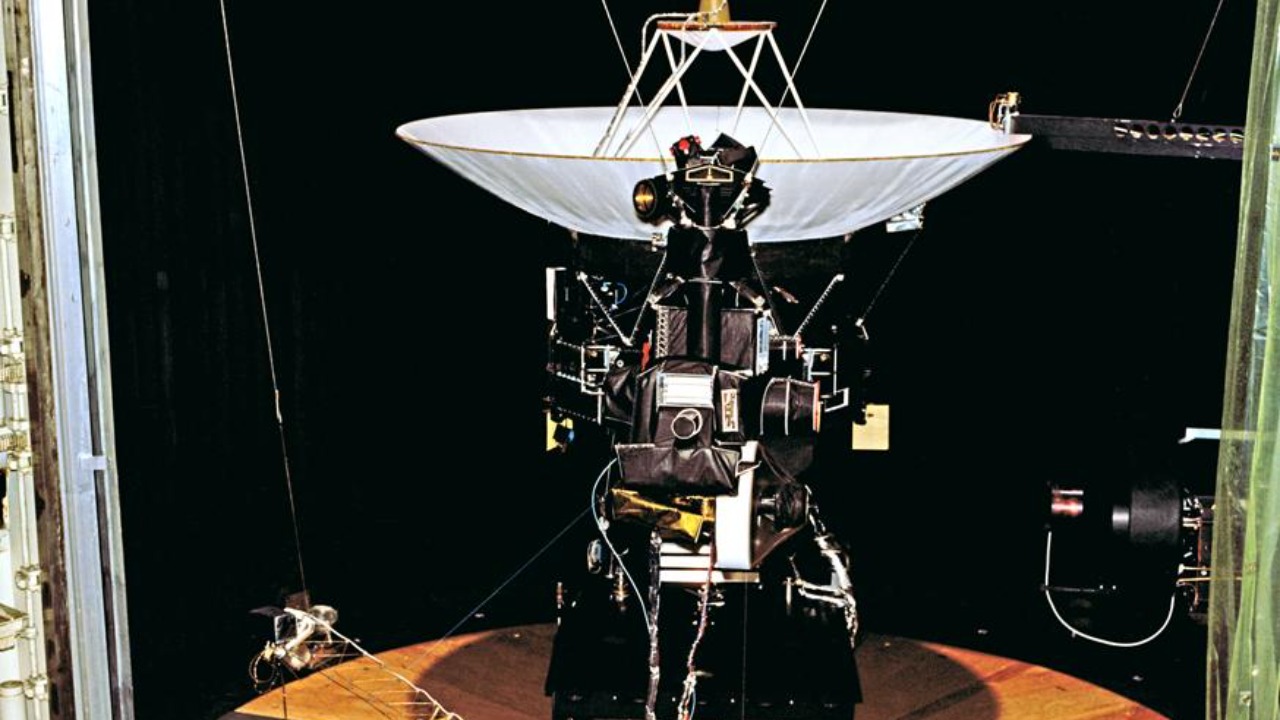
One of the most intriguing findings from Voyager 2’s flyby is the peculiar nature of Uranus’s magnetosphere. Unlike any other planet in our solar system, Uranus has a complex and unique magnetic field. According to CNN’s report, the data suggests that this magnetic field is irregularly shaped and tilted at an extreme angle relative to the planet’s rotation axis. These anomalies have led scientists to propose new theories about the planet’s interior structure and the processes that drive its magnetic field.
In addition to its magnetic field, Voyager 2’s observations of Uranus’s atmosphere revealed unexpected phenomena. The spacecraft detected unusual weather patterns that challenge our understanding of atmospheric dynamics on ice giants. Among the surprises was the discovery of a potential new layer in the atmosphere, which may play a crucial role in the planet’s heat distribution and weather systems. This revelation opens new avenues for research into the atmospheric conditions of Uranus and other similar planets.
Technological and Scientific Legacy of Voyager
The Voyager spacecraft are engineering marvels, designed to operate far longer than initially anticipated. This longevity can be attributed to innovations in spacecraft design and durability. One of the key technological advances powering Voyager is the use of radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs), which have provided a steady power supply for over four decades. The reliability of these generators has enabled Voyager to continue transmitting data from the edge of our solar system.
Voyager’s contributions to science extend far beyond its initial mission objectives. The wealth of data collected has fundamentally shaped our understanding of the outer solar system. Moreover, the mission has inspired the development of new technologies and exploration strategies, influencing future missions to distant worlds. For more on the scientific and technological impact of Voyager, NASA’s technical reports offer a comprehensive overview.
Cultural Impact and Popularity
Beyond its scientific achievements, Voyager has captured the imagination of the public and become a cultural icon. Its influence is evident in popular culture, with references in films, television shows, and literature. One notable example is Star Trek’s Voyager, which draws inspiration from the spirit of exploration embodied by the spacecraft. This iconic status has helped inspire generations of scientists, engineers, and space enthusiasts.
Voyager’s discoveries have also fueled public engagement and outreach efforts. NASA and other organizations have leveraged these findings to bring Voyager’s story to a global audience. Through social media platforms, updates about Voyager continue to engage and educate the public, fostering a sense of connection to the ongoing journey. A recent Instagram post highlights the continued interest and excitement surrounding Voyager’s mission.
Future Prospects and Continuing Mysteries
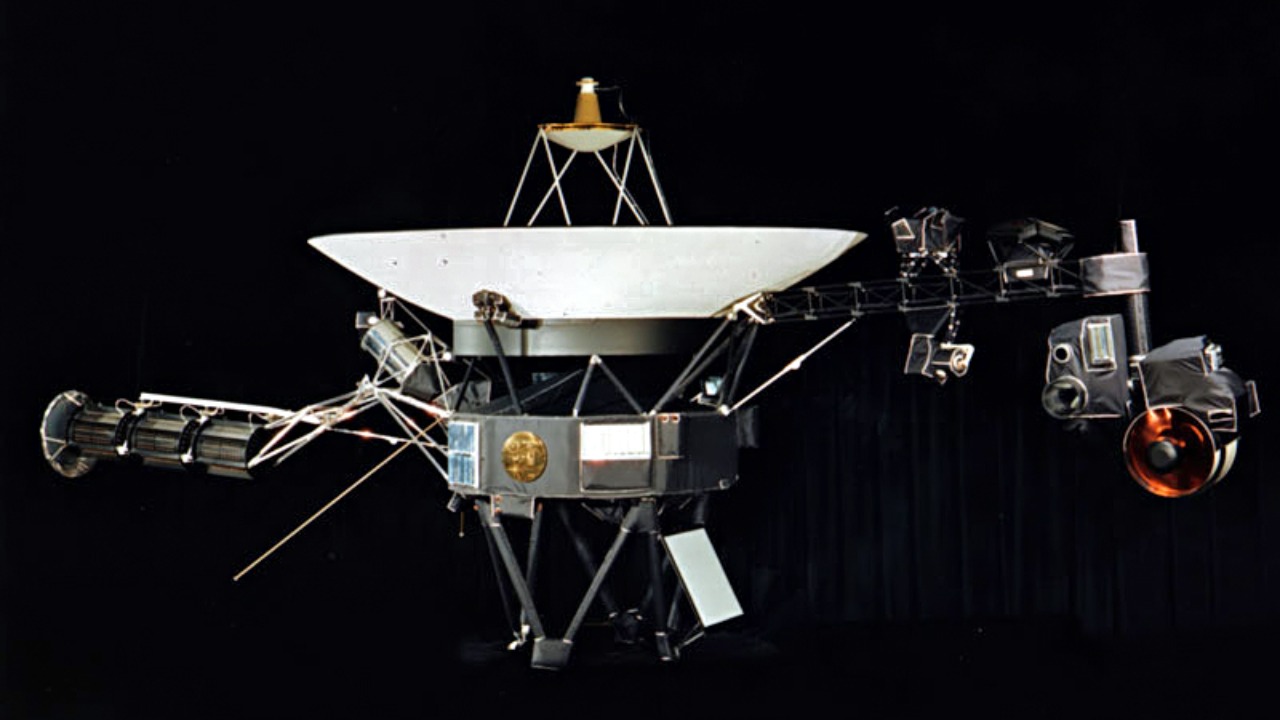

As Voyager continues its journey into interstellar space, the potential for new discoveries remains. The spacecraft is on a trajectory that will take it through the heliosphere and into the interstellar medium, offering a unique vantage point to study the boundary between our solar system and the vastness beyond. This quest for understanding the heliosphere and its interaction with interstellar space is ongoing, with Voyager playing a crucial role.
Despite its impressive achievements, many questions about the outer solar system remain unanswered. The need for new missions to Uranus and other ice giants is becoming increasingly apparent as scientists seek to build upon Voyager’s legacy. Current and upcoming missions, such as the proposed Uranus Orbiter and Probe, are poised to unravel more mysteries of these distant worlds, further advancing our knowledge of the cosmos.