The James Webb Space Telescope has unveiled breathtaking images of Neptune, showcasing the planet’s elusive aurorae with unprecedented clarity. These new observations not only reveal the beauty of Neptune’s glowing skies but also provide critical insights into the planet’s atmospheric dynamics and magnetic field.
The Significance of Webb’s Discoveries

Revolutionizing our understanding of Neptune, the James Webb Space Telescope has brought to light the planet’s atmospheric phenomena with a detail never seen before. The telescope’s advanced imaging capabilities have allowed us to observe Neptune’s aurorae with remarkable precision. These glowing displays, which were once shrouded in mystery, are now being studied in ways that could reshape our comprehension of the planet’s atmospheric and magnetic properties. The clarity provided by Webb’s images offers a new perspective on how solar winds interact with Neptune’s magnetic field, generating these stunning auroral displays.
The impact of these findings extends beyond Neptune itself. They are setting new benchmarks for astronomical research, particularly in the study of outer planets. The detailed observations made possible by the James Webb Space Telescope will influence the methodologies and technologies employed in future planetary research. As scientists continue to analyze Webb’s data, they gain a deeper understanding of not only Neptune but also the broader dynamics at play within our solar system and beyond. This knowledge could lead to breakthroughs in how we study magnetic fields and atmospheric phenomena on other distant worlds.
Neptune’s Mysterious Aurorae
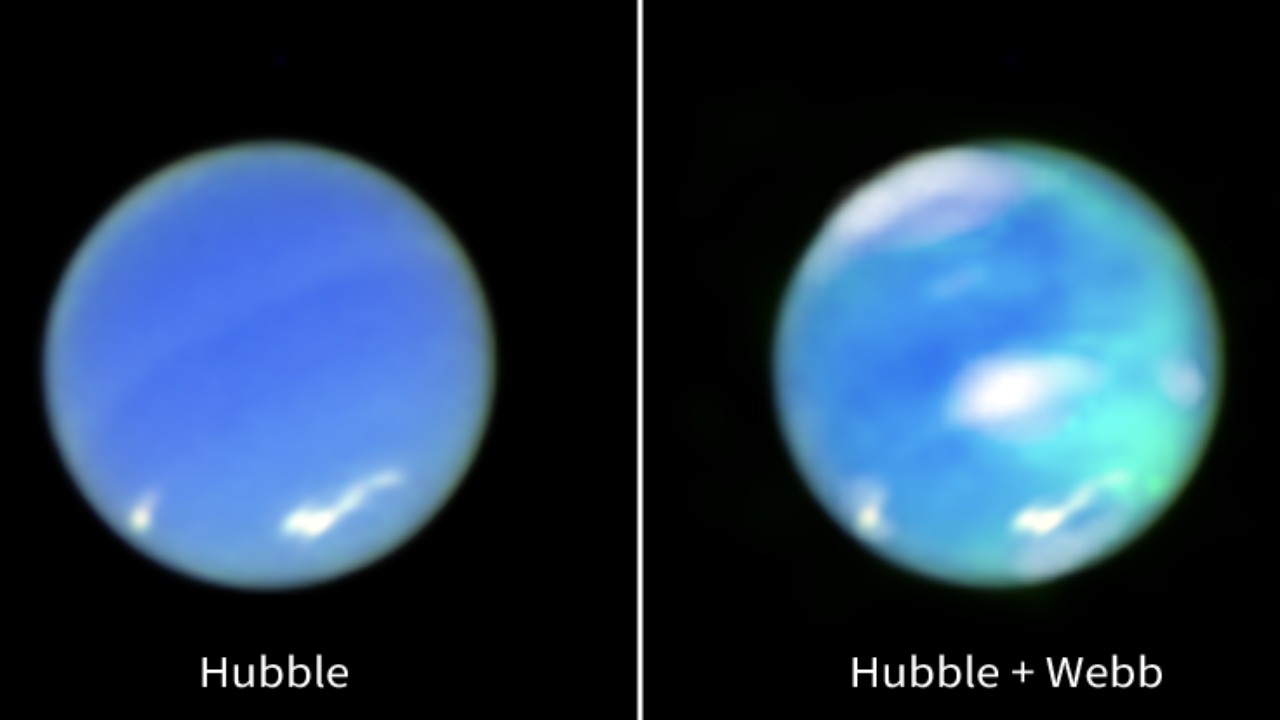
Neptune’s aurorae are particularly intriguing due to their unique characteristics compared to those on Earth and other planets. Aurorae, in general, are luminous displays caused by the interaction between charged particles from the solar wind and a planet’s magnetic field. On Neptune, these aurorae are less understood because of the planet’s vast distance from the sun and its complex magnetic field, which is tilted and offset from its rotational axis. This results in auroral patterns that are distinct from the familiar lights seen in Earth’s polar regions.
The connection between Neptune’s aurorae and its magnetic field is a focal point of current research. The new data from the James Webb Space Telescope sheds light on this relationship, helping scientists to map out the magnetic interactions that produce these ethereal displays. Understanding Neptune’s magnetic field is crucial, as it holds clues about the planet’s internal structure and its interaction with the solar wind. The insights gained from studying these aurorae are paving the way for a more comprehensive understanding of not only Neptune but also the magnetic environments of other outer planets.
Technological Marvel: The James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope is a technological marvel that has redefined our ability to observe distant celestial phenomena. Equipped with advanced imaging capabilities, Webb can capture detailed images of planets like Neptune, revealing features that were previously obscured or entirely unseen. Its instruments are designed to observe in infrared wavelengths, which is particularly useful for studying the cold and distant outer planets of our solar system. This capability allows Webb to penetrate Neptune’s thick atmosphere, providing a clear view of its aurorae and other atmospheric phenomena.
When comparing the new images and data from Webb with past observations from other telescopes, the difference in clarity and detail is striking. Previous missions, such as those by the Hubble Space Telescope, provided valuable insights but lacked the resolution and depth captured by Webb. The new images not only reveal Neptune’s aurorae in higher detail but also provide a more comprehensive understanding of its atmospheric dynamics. This leap in observational capability underscores the significant advancements in technology that continue to propel our exploration of the universe forward.
Implications for Understanding Planetary Atmospheres

The images and data provided by the James Webb Space Telescope offer crucial insights into the composition and dynamics of Neptune’s atmosphere. The detailed observations have revealed new aspects of Neptune’s atmospheric chemistry and weather patterns, providing a clearer picture of the processes occurring on this distant world. Understanding the atmospheric composition and the factors influencing Neptune’s climate helps scientists develop models that can predict atmospheric behavior on other planets as well.
These observations have broader implications for the study of exoplanets. Many exoplanets share characteristics with Neptune, such as being gas giants with thick atmospheres and complex magnetic fields. By understanding Neptune’s atmosphere and aurorae, scientists can apply this knowledge to the study of similar exoplanets, enhancing our ability to infer the atmospheric conditions and potential habitability of distant worlds. This connection between Neptune and exoplanet research highlights the importance of Webb’s discoveries in expanding our understanding of planetary sciences beyond our solar system.
The Future of Outer Solar System Exploration

Looking to the future, the discoveries made by the James Webb Space Telescope will undoubtedly shape upcoming missions and observations of Neptune and other outer planets. Several missions are already in the planning stages, with goals to further explore the outer reaches of our solar system. These missions will benefit from the foundational knowledge provided by Webb’s observations, allowing scientists to refine their objectives and improve the technology used in spacecraft and observational instruments.
The quest to explore the outer solar system continues to expand the boundaries of our knowledge, inspiring future generations of astronomers and space enthusiasts. By studying Neptune’s aurorae, we gain insights into the fundamental processes that govern planet-magnetic field interactions. This knowledge not only enriches our understanding of Neptune but also serves as a stepping stone for exploring the vast and diverse worlds that await discovery beyond our solar system.